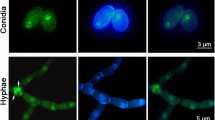
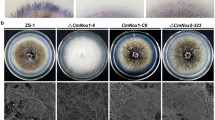
Abstract
Conidia play important roles in primary and secondary infections of airborne fungal pathogens. In this study, an insertional mutant with reduced capacity for conidiation was isolated from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. The mutant has a T-DNA insertion that disrupts a gene named MoCPS1. The deduced MoCps1 protein contains three AMP-binding domains. Gene complementation and gene knockout assays confirmed that MoCPS1 is important for conidiation. Conidia produced by the MoCPS1 deletion mutants are much more slender and longer than those produced by the wild-type strain. The Mocps1 mutants are less efficient in both appressorial penetration and invasive growth of infection hyphae, resulting in attenuated virulence toward host plants. MoCPS1 is highly expressed in a mature appressorium. Interestingly, the expression levels of several genes related to conidiation and pathogenicity have been significantly altered in the MoCPS1 deletion mutants. Taken together, our results indicated that MoCPS1 is important for conidiogenesis, conidial morphogenesis, and pathogenesis in the rice blast fungus.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhadauria V, Wang LX, Peng YL (2010) Proteomic changes associated with deletion of the Magnaporthe oryzae conidial morphology-regulating gene COM1. Biol Direct 5:61
Braga Gilberto UL, Rangel Drauzio EN, Fernandes Éverton KK, Flint SD, Roberts DW (2015) Molecular and physiological effects of environmental UV radiation on fungal conidia. Curr Genet 61:405–425
Burkard TR, Planyavsky M, Kaupe I, Breitwieser FP, Burckstummer T, Bennett KL, Superti-Furga G, Colinge J (2011) Initial characterization of the human central proteome. BMC Syst Biol 5:17
Chen J, Zheng W, Zheng S, Zhang D, Sang W, Chen X, Li G, Lu G, Wang Z (2008) Rac1 is required for pathogenecity and Chm1-dependent conidiogenesis in rice fungal pathogen Magnaporthe grisea. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000202
Chen XL, Yang J, Peng YL (2011) Large scale insertional mutagenesis by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Methods Mol Biol 722:213–224
Conti E, Franks NP, Brick P (1996) Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure 4:287–298
Dean RA, Talbot NJ, Ebbole DJ, Farman ML, Mitchell TK, Orbach MJ, Thon M, Kulkarni R, Xu JR, Pan HQ, Read ND, Lee YH, Carbone I, Brown D, Oh YY, Donofrio N, Jeong JS, Soanes DM, Djonovic S, Kolomiets E, Rehmeyer C, Li WX, Hardling M, Kim S, Lebrun MH, Bohnert H, Coughlan S, Butler J, Calvo S, Ma LJ, Nicol R, Purcell S, Nusbaum C, Galagan JE, Birren BW (2005) The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Nature 434:980–986
Dean R, Van Kan JA, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack KE, Di Pietro A, Spanu PD, Rudd JJ, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster GD (2012) The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:414–430
Dou X, Wang Q, Qi Z, Song W, Wang W, Guo M, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Wang P, Zheng X (2011) MoVam7, a conserved SNARE involved in vacuole assembly, is required for growth, endocytosis, ROS accumulation, and pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS One 6:e16439
Du Y, Shi Y, Yang J, Chen X, Xue M, Zhou W, Peng YL (2013) A serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP2A catalytic subunit is essential for asexual development and plant infection in Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr Genet 59:33–41
Goh J, Kim KS, Park J, Jeon J, Park SY, Lee YH (2011) The cell cycle gene MoCDC15 regulates hyphal growth, asexual development and plant infection in the rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 48:784–792
Guo M, Chen Y, Du Y, Dong Y, Guo W, Zhai S, Zhang H, Dong S, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wang P, Zheng X (2011) The bZIP transcription factor MoAP1 mediates the oxidative stress response and is critical for pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001302
Jeon J, Park SY, Chi MH, Choi J, Park J, Rho HS, Kim S, Goh J, Yoo S, Choi J, Park JY, Yi M, Yang S, Kwon MJ, Han SS, Kim BR, Khang CH, Park B, Lim SE, Jung K, Kong S, Karunakaran M, Oh HS, Kim H, Kim S, Park J, Kang S, Choi WB, Kang S, Lee YH (2007) Genome-wide functional analysis of pathogenicity genes in the rice blast fungus. Nat Genet 39:561–565
Kang Z, Zingen-Sell I, Buchenauer H (2005) Infection of wheat spikes by Fusarium avenaceum and alterations of cell wall components in the infected tissue. Eur J Plant Pathol 111:19–28
Kankanala P, Czymmek K, Valent B (2007) Roles for rice membrane dynamics and plasmodesmata during biotrophic invasion by the blast fungus. Plant Cell 19:706–724
Kim KS, Lee YH (2012) Gene expression profiling during conidiation in the rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS One 7:e43202
Kim S, Park SY, Kim KS, Rho HS, Chi MH, Choi J, Park J, Kong S, Park J, Goh J, Lee YH (2009) Homeobox transcription factors are required for conidiation and appressorium development in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS Genet 5:e1000757
Kong LA, Yang J, Li GT, Qi LL, Zhang Y, Wang CF, Zhao WS, Xu JR, Peng YL (2012) Different chitin synthase genes are required for various developmental and plant infection processes in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS Pathog 8:1002526
Lau GW, Hamer JE (1998) Acropetal: a genetic locus required for conidiophore architecture and pathogenicity in the rice blast fungus. Fungal Genet Biol 24:228–239
Li L, Xue CY, Bruno K, Nishimura M, Xu JR (2004) Two PKA kinase genes, CHM1 and MST20, have distinct functions in Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:547–556
Li X, Han X, Liu Z, He C (2013) The function and properties of the transcriptional regulator COS1 in Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Biol 117:239–249
Li C, Yang J, Zhou W, Chen XL, Huang JG, Cheng ZH, Zhao WS, Zhang Y, Peng YL (2014) A spindle pole antigen gene MoSPA2 is important for polar cell growth of vegetative hyphae and conidia, but is dispensable for pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr Genet 60:255–263
Li Y, Que YW, Liu YT, Yue XF, Meng XL, Zhang ZG, Wang ZY (2015) The putative Gγ subunit gene MGG1 is required for conidiation, appressorium formation, mating and pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr Genet 61:641–651
Liu YG, Mitsukawa N, Oosumi T, Whittier RF (1995) Efficient isolation and mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insert junctions by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant J 8:457–463
Liu W, Xie S, Zhao X, Chen X, Zheng W, Lu G, Xu JR, Wang Z (2010) A homeobox gene is essential for conidiogenesis of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:366–375
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu SW, Kroken S, Lee BN, Robbertse B, Churchill ACL, Yoder OC, Turgeon BG (2003) A novel class of gene controlling virulence in plant pathogenic ascomycete fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5980–5985
Lu JP, Feng XX, Liu XH, Lu Q, Wang HK, Lin FC (2007) Mnh6, a histone protein, is required for fungal development and pathogenecity of Magnaporthe grisea. Fungal Genet Biol 44:819–829
Nagase T, Kikuno R, Ishikawa K, Hirosawa M, Ohara O (2000) Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro. DNA Res 7:143–150
Nishimura M, Hayashi N, Jwa NS, Lau GW, Hamer JE, Hasebe A (2000) Insertion of the LINE retrotransposon MGL causes a conidiophore pattern mutation in Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:892–894
Odenbach D, Breth B, Thines E, Weber RW, Anke H, Foster AJ (2007) The transcription factor Con7p is a central regulator of infection-related morphogenesis in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Microbiol 64:293–307
Ouchi N, Asaumi Y, Ohashi K, Higuchi A, Sono-Romanelli S, Oshima Y, Walsh K (2010) DIP2A functions as a FSTL1 receptor. J Biol Chem 285:7127–7134
Peng YL, Shishiyama J (1988) Temporal sequence of cytological events in rice leaves infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Can J Bot 66:730–735
Qi Z, Wang Q, Dou X, Wang W, Zhao Q, Lv R, Zhang H, Zheng X, Wang P, Zhang Z (2012) MoSwi6, an APSES family transcription factor, interacts with MoMps1 and is required for hyphal and conidial morphogenesis, appressorial function and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Pathol 13:677–689
Ren J, Wen L, Gao X, Jin C, Xue Y, Yao X (2009) DOG 1.0: illustrator of protein domain structures. Cell Res 19:271–273
Rountree MR, Bachman KE, Baylin SB (2000) DNMT1 binds HDAC2 and a new co-repressor, DMAP1, to form a complex at replication foci. Nat Genet 25:269–277
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schmelz S, Naismith JH (2009) Adenylate-forming enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:666–671
Shi Z, Leung H (1995) Genetic analysis of sporulation in Magnaporthe grisea by chemical and insertional mutagenesis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:949–959
Shi Z, Christian D, Leung H (1998) Interactions between spore morphogenetic mutations affect cell types, sporulation, and pathogenesis in Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:199–207
Skamnioti P, Gurr SJ (2007) Magnaporthe grisea cutinase2 mediates appressorium differentiation and host penetration and is required for full virulence. Plant Cell 19:2674–2689
Talbot NJ (2003) On the trail of a cereal killer: exploring the biology of Magnaporthe grisea. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:177–202
Talbot NJ, Kershaw MJ, Wakley GE, de Vries O, Wessels J, Hamer JE (1996) MPG1 encodes a fungal hydrophobin involved in surface interactions during infection-related development of Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 8:985–999
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanaka M, Murakami K, Ozaki S, Imura Y, Tong XP, Watanabe T, Sawaki T, Kawanami T, Kawabata D, Fujii T, Usui T, Masaki Y, Fukushima T, Jin ZX, Umehara H, Mimori T (2010) DIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A (Drosophila) is a candidate receptor for follistatin-related protein/follistatin-like 1-analysis of their binding with TGF-β superfamily proteins. FEBS J 277:4278–4289
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tsuji G, Fujii S, Fujihara N, Hirose C, Tsuge S, Shiraishi T, Kubo Y (2003) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation for random insertional mutagenesis in Colletotrichum lagenarium. J Plant Pathol 69:230–239
Xu JR, Hamer JE (1996) MAP kinase and cAMP signaling regulate infection structure formation and pathogenic growth in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Genes Dev 10:2696–2706
Xu JR, Xue C (2002) Time for a blast: genomics of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Pathol 3:173–176
Yang J, Zhao X, Sun J, Kang Z, Ding S, Xu JR, Peng YL (2010) A novel protein Com1 is required for normal conidium morphology and full virulence in Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:112–123
Yang J, Kong LA, Chen XL, Wang DW, Qi LL, Zhao WS, Zhang Y, Liu XZ, Peng YL (2012) A carnitine-acylcarnitine carrier protein, MoCrc1, is essential for pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae. Curr Genet 58:139–148
Yi M, Park JH, Ahn JH, Lee YH (2008) MoSNF1 regulates sporulation and pathogenicity in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1172–1181
Zheng W, Chen J, Liu W, Zheng S, Zhou J, Lu G, Wang Z (2007) A Rho3 homolog is essential for appressorium development and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea. Eukaryot Cell 6:2240–2250
Zheng W, Zhao Z, Chen J, Liu W, Ke H, Zhou J, Lu G, Darvill AG, Albersheim P, Wu S, Wang Z (2009) A Cdc42 ortholog is required for penetration and virulence of Magnaporthe grisea. Fungal Genet Biol 46:450–460
Zhou Z, Li G, Lin C, He C (2009) Conidiophore stalk-less1 encodes a putative zinc-finger protein involved in the early stage of conidiation and mycelial infection in Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:402–410
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31371885), the 973 program (Grant No. 2012CB114000), and the China Agricultural University Education Foundation (Grant No. 1011-2413002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Y. Wang and D. He contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., He, D., Chu, Y. et al. MoCps1 is important for conidiation, conidial morphology and virulence in Magnaporthe oryzae . Curr Genet 62, 861–871 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-016-0593-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-016-0593-3