Abstract
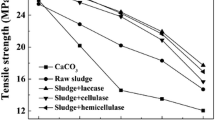
This study presents the characterization and thermal kinetic analysis of LDPE/carbonation sludge composites with different weight fractions (10%, 20%, 30%, 40% and 50%). Tensile, Young's modulus, hardness, morphological, thermal stability, flame retardant and dynamic mechanical properties of the produced LDPE/carbonation sludge composites were evaluated and compared. Analysis results revealed that the incorporation of calcium carbonate-based industrial waste into the LDPE matrix decreased tensile strength by 27.6%, while Young's modulus and hardness enhanced by 101.67% and 23.8%, respectively. A remarkable enhancement in both storage (Eı) and loss (Eıı) modulus were observed for LDPE/carbonation sludge composites compared to LDPE polymer. Furthermore, a significant improvement was noticed in the properties of composites containing 50% carbonation sludge due to the efficient dispersion and interface interaction between LDPE and carbonation sludge. Although the LOI value increases from 16 to 21% with the addition of waste, it is not sufficient in terms of flame retardant. For the thermal kinetic analysis, Coast-Redfern integral method was applied to three thermal decomposition zones of the composites. Accordingly, Ea and A values in zone II are higher than in zone I and III for all reaction models of composites. Overall, LDPE/carbonation sludge composites exhibited better thermal stability and dynamic properties than LDPE polymer.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data and materials are available.
References
Ku H, Wang H, Pattarachaiyakoop N, Trada M (2011) A review on the tensile properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos Part B Eng 42:856–873
Kılınc AC, Atagur M, Ozdemir O et al (2016) Manufacturing and characterization of vine stem reinforced high density polyethylene composites. Compos Part B Eng 91:267–274
Kumar S, Hatha AAM, Christi KS (2007) Diversity and effectiveness of tropical mangrove soil microflora on the degradation of polythene carry bags. Rev Biol Trop 55:777–786
Eze IO, Madufor IC, Obidiegwu MU (2013) The effects of bamboo powder on some mechanical properties of recycled low density polyethylene (RLDPE) composites. Acad Res Int 4:409
Contat-Rodrigo L, Ribes Greus A (2002) Biodegradation studies of LDPE filled with biodegradable additives: morphological changes. I J Appl Polym Sci 83:1683–1691
Stock T, Seliger G (2016) Opportunities of sustainable manufacturing in industry 4.0. Procedia Cirp 40:536–541
Uygunoğlu T, Topçu İB, Çelik AG (2014) Use of waste marble and recycled aggregates in self-compacting concrete for environmental sustainability. J Clean Prod 84:691–700
Awad AH, El-gamasy R, El-Wahab AAA, Abdellatif MH (2019) Mechanical behavior of PP reinforced with marble dust. Constr Build Mater 228:116766
Awad AH, Abdellatif MH (2019) Assessment of mechanical and physical properties of LDPE reinforced with marble dust. Compos Part B Eng 173:106948
Kaya N, Atagur M, Akyuz O et al (2018) Fabrication and characterization of olive pomace filled PP composites. Compos Part B Eng 150:277–283
Bledzki AK, Mamun AA, Volk J (2010) Barley husk and coconut shell reinforced polypropylene composites: the effect of fibre physical, chemical and surface properties. Compos Sci Technol 70:840–846
Habibi Y, El-Zawawy WK, Ibrahim MM, Dufresne A (2008) Processing and characterization of reinforced polyethylene composites made with lignocellulosic fibers from Egyptian agro-industrial residues. Compos Sci Technol 68:1877–1885
Saleh HM, Salman AA, Faheim AA, El-Sayed AM (2020) Sustainable composite of improved lightweight concrete from cement kiln dust with grated poly (styrene). J Clean Prod 277:123491
Eskander SB, Bayoumi TA, Saleh HM (2012) Performance of aged cement–polymer composite immobilizing borate waste simulates during flooding scenarios. J Nucl Mater 420:175–181
Saleh HM, Tawfik ME, Bayoumi TA (2011) Chemical stability of seven years aged cement–PET composite waste form containing radioactive borate waste simulates. J Nucl Mater 411:185–192
Saleh HM, Eskander SB (2019) Impact of water flooding on hard cement-recycled polystyrene composite immobilizing radioactive sulfate waste simulate. Constr Build Mater 222:522–530
Çınar ME, Kar F (2018) Characterization of composite produced from waste PET and marble dust. Constr Build Mater 163:734–741
Nourbakhsh A, Ashori A (2010) Wood plastic composites from agro-waste materials: analysis of mechanical properties. Bioresour Technol 101:2525–2528
Vaccari G, Tamburini E, Sgualdino G et al (2005) Overview of the environmental problems in beet sugar processing: possible solutions. J Clean Prod 13:499–507
Šárka E, Bubník Z, Kadlec P, Veselá-Trilčová A (2008) The particle size of carbonation mud, and possibilities for influencing it. J Food Eng 87:45–50
Shoira M (2006) Application of defecation lime from sugar industry in Uzbekistan
Yaras A, Sutcu M, Gencel O, Erdogmus E (2019) Use of carbonation sludge in clay based building materials processing for eco-friendly, lightweight and thermal insulation. Constr Build Mater 224:57–65
Wunderlich B (2005) Thermal analysis of polymeric materials. Springer Science & Business Media
Vyazovkin S, Wight CA (1998) Isothermal and non-isothermal kinetics of thermally stimulated reactions of solids. Int Rev Phys Chem 17:407–433
Jayaraman K, Kok MV, Gokalp I (2017) Thermogravimetric and mass spectrometric (TG-MS) analysis and kinetics of coal-biomass blends. Renew Energy 101:293–300
Hu J, Danish M, Lou Z et al (2018) Effectiveness of wind turbine blades waste combined with the sewage sludge for enriched carbon preparation through the co-pyrolysis processes. J Clean Prod 174:780–787
Bockhorn H, Hornung A, Hornung U, Schawaller D (1999) Kinetic study on the thermal degradation of polypropylene and polyethylene. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 48:93–109
Cho Y-S, Shim M-J, Kim S-W (1998) Thermal degradation kinetics of PE by the Kissinger equation. Mater Chem Phys 52:94–97
Vasile C, Costea E, Odochian L (1991) The thermoxidative decomposition of low density polyethylene in non-isothermal conditions. Thermochim Acta 184:305–311
Ptiček Siročić A, Kratofil Krehula L, Katančić Z, Hrnjak-Murgić Z (2014) Kinetic analysis of thermal and thermo-oxidative degradation of polyethylene (nano) composites. Compos Interfaces 21:179–189
Coats AW, Redfern JP (1964) Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 201:68–69
Horgnies M, Willieme P, Gabet O (2011) Influence of the surface properties of concrete on the adhesion of coating: characterization of the interface by peel test and FT-IR spectroscopy. Prog Org Coat 72:360–379
Mehta D, Mondal P, George S (2016) Utilization of marble waste powder as a novel adsorbent for removal of fluoride ions from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 4:932–942
Magalhães WLE, Pianaro SA, Granado CJF, Satyanarayana KG (2013) Preparation and characterization of polypropylene/heart-of-peach palm sheath composite. J Appl Polym Sci 127:1285–1294
Esnaashari C, Khorasani SN, Entezam M, Khalili S (2013) Mechanical and water absorption properties of sawdust: low density polyethylene nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 127:1295–1300
Shumigin D, Tarasova E, Krumme A, Meier P (2011) Rheological and mechanical properties of poly (lactic) acid/cellulose and LDPE/cellulose composites. Mater Sci 17:32–37
Reyes JEP (2015) Effect of surface treatment and particle loading on the mechanical properties of CFB fly ash reinforced thermoset composite. Int J Chem Eng Appl 6:6
Prachayawarakorn J, Khunsumled S, Thongpin C et al (2008) Effects of silane and MAPE coupling agents on the properties and interfacial adhesion of wood-filled PVC/LDPE blend. J Appl Polym Sci 108:3523–3530
Mahfoudh A, Cloutier A, Rodrigue D (2013) Characterization of UHMWPE/wood composites produced via dry-blending and compression molding. Polym Compos 34:510–516
Hassanien MS, Seedahmed AI (2015) Mechanical and rheological properties of polypropylene (PP)/linear low density polyethylene (LDPE) blend filled with talc and calcium carbonate compositions. Int J Eng Sci Res Technol 2277:383–387
Huang R, Xu X, Lee S et al (2013) High density polyethylene composites reinforced with hybrid inorganic fillers: morphology, mechanical and thermal expansion performance. Materials (Basel) 6:4122–4138
Greene JP, Wilkes JO (1995) Steady-State and dynamic properties of concentrated fiber-filled thermoplastics. Polym Eng Sci 35:1670–1681
Wang C, Ying S (2013) Thermal, tensile and dynamic mechanical properties of short carbon fibre reinforced polypropylene composites. Polym Polym Compos 21:65–72
Luyt AS, Dramićanin MD, Antić Ž, Djoković V (2009) Morphology, mechanical and thermal properties of composites of polypropylene and nanostructured wollastonite filler. Polym Test 28:348–356
Cheewawuttipong W, Fuoka D, Tanoue S et al (2013) Thermal and mechanical properties of polypropylene/boron nitride composites. Energy Procedia 34:808–817
Zarandi MB, Bioki HA (2013) Thermal and mechanical properties of blends of LDPE and EVA crosslinked by electron beam radiation. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 63:21101
Balasundram V, Ibrahim N, Kasmani RM et al (2017) Thermogravimetric catalytic pyrolysis and kinetic studies of coconut copra and rice husk for possible maximum production of pyrolysis oil. J Clean Prod 167:218–228
DIN I (2006) Plastics–Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index–Part 2: Ambient-temperature test (ISO 4589–2: 1996+ Amd. 1: 2005)(includes Amendment A1: 2006) English version of DIN EN ISO 4589–2: 2006–06
Gulmine JV, Janissek PR, Heise HM, Akcelrud L (2002) Polyethylene characterization by FTIR. Polym Test 21:557–563
Funding
There is no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AY: Conceptualization, methodology, software, writing—reviewing and editing, original draft preparation. BD: Original draft preparation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, software. FA: Original draft preparation, conceptualization, software, validation. HA: Original draft preparation, visualization, investigation, Writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors declare that this manuscript is consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaras, A., Demirel, B., Akkurt, F. et al. Carbonation sludge reinforced LDPE composites: flame-retardant, dynamic mechanical properties, thermal degradation behaviors. Polym. Bull. 79, 6475–6496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03800-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03800-z