Abstract
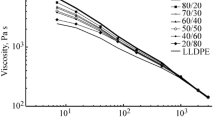
The rheological properties and the viscoelastic behaviour of blends of polyethylene with different percentages of poly(lactic acid), ranging from 0 to 100 wt%, were studied. In a first part, all blends were examined under steady conditions using a capillary rheometer (at 180, 190 and 200 °C) and dynamic conditions using a parallel plate rheometer. The results showed that all blends behaved like pseudoplastic fluids, with the power–law index values varying between those of polyethylene and polylactide (0.45–0.75 at 180 °C, 0.49–0.77 at 190 °C and 0.54–0.81 at 200 °C). It was also observed that at low shear rate, pure poly(lactic acid) and polyethylene possessed, respectively, the highest and the lowest flow activation energy (66.9 and 48.3 kJ/mol); however, at high shear rate, the greater the content of poly(lactic acid), the lower the activation energy. In addition, poly(lactic acid) exhibited lower viscosity and lower melt elasticity than either polyethylene or the blends. The dynamic rheological study demonstrated that all formulations displayed shear thinning behaviour and only virgin poly(lactic acid) exhibited a clear Newtonian plateau. Also, mainly at low frequencies, polyethylene had the higher values of storage modulus (325 Pa), loss modulus (937 Pa) and complex viscosity (9,740 Pa.s). However, blends had values lying between those of the two homopolymers without any improvement in the storage modulus, loss modulus or complex viscosity. In a second part, the viscoelastic characteristics were investigated using dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA). DMTA spectra showed an increase in the storage modulus with the increase of poly(lactic acid) content but the opposite was observed for the loss modulus. A cold crystallization of poly(lactic acid) is observed around 87–100 °C and the temperature of glass transition of poly(lactic acid) did not depend on the composition of the blend. These results indicate that LDPE and PLA are immiscible in all proportions either in the melt state or in the solid state.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gahleitner M (2001) Melt rheology of polyolefins. Prog Polym Sci 26:895–944
Dangtungee R, Desai SS, Tantayanon S et al (2006) Melt rheology and extrudate swell of low-density polyethylene/ethylene–octene copolymer blends. Polym Test 25:888–895
Baird DG (2008) First normal stress difference measurements for polymer melts at high shear rates in a slit-die using hole and exit pressure data. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 148:13–23
Ramanini D (1982) Synthesis technology, molecular structure, and rheological behaviour of polyethylene. Polym Plast Technol Eng 19:201–226
Silva ALN, Rocha MCG, Coutinho FMB (2002) Study of rheological behaviour of elastomer/polypropylene blends. Polym Test 21:289–293
Anderson KS, Lim SH, Hillmyer MA (2003) Toughening of polylactide by melt blending with linear low-density polyethylene. J Appl Polym Sci 89:3757–3768
Balakrishnan H, Hassan A, Wahit MU (2010) Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of polylactic acid/linear low density polyethylene blends. J Elastom Plast 42:223–239
Wang Y, Hillmyer MA (2001) Polyethylene-poly(l-lactide) diblock copolymers: synthesis and compatibilization of poly(l-lactide)/polyethylene blends. J Polym Sci, Part A: Polym Chem 39:2755–2766
Djellali S, Haddaoui N, Sadoun T et al (2013) Structural, morphological and mechanical characteristics of polyethylene, poly(lactic acid) and poly(ethylene-co-glycidyl methacrylate) blends. Iran Polym J 22:245–257
Yomogida Y, Tsukada H Li Y et al (2011) Reactive blending of polyethylene and poly(l-lactic acid) using a high-shear extruder. In: The 18th International conference on composite materials, Jeju Island, South Korea, 21–26 August
Jiang G, Huang HX, Chen ZK (2011) Rheological responses and morphology of polylactide/linear low density polyethylene blends produced by different mixing type. Polym Plast Technol Eng 50:1035–1039
As’habi L, Jafari SH, Khonakdar HA et al (2013) Tuning the processability, morphology and biodegradability of clay incorporated PLA/LLDPE blends via selective localization of nanoclay induced by melt mixing sequence. Express Polym Lett 7:21–39
Sadiku-Agboola O, Sadiku ER, Adegbola AT et al (2011) Rheological properties of polymers: structure and morphology of molten polymer blends. Mater Sci Appl 2:30–41
Das NC, Wang H, Mewis J et al (2005) Rheology and microstructures formation of immiscible model polymer blends under steady state and transient flows. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 43:3519–3533
Elias L, Fenouillot F, Majeste JC et al (2008) Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer 49:4378–4385
Nelson B (2003) Capillary Rheometry. In: Lobo H, Bonilla JV (eds) Handbook of plastics analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York
Macosko CW (1994) Rheology: principles, measurements, and applications. Wiley-VCH, New York
Barrera MA, Vega JF, Aguilar M et al (2006) Melt flow index on high molecular weight polyethylene: a comparative study of experiments and simulation. J Mater Process Technol 174:171–177
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F (2012) Preparation and characterization of binary and ternary blends with poly(lactic acid), polystyrene, and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 3:405–412
Sarazin P, Li G, Orts WJ et al (2008) Binary and ternary blends of polylactide, polycaprolactone and thermoplastic starch. Polymer 49:599–609
Riande E, Diaz-Calleja R, Prolongo M et al (2000) Polymer viscoelasticity: stress and strain in practice. Marcel Dekker, New York
Borah JS, Chaki TK (2012) Effect of organo-montmorillonite addition on the dynamic and capillary rheology of LLDPE/EMA blends. Appl Clay Sci 59–60:42–49
Wang X, Luo X (2004) A polymer network based on thermoplastic polyurethane and ethylene–propylene–diene elastomer via melt blending: morphology, mechanical properties and rheology. Eur Polym J 40:2391–2399
Utracki LA, Sammut P (1990) Rheology of polycarbonate/linear low density polyethylene blends. Polym Eng Sci 30:1027–1040
Xu SA, Zhu L, Xie JW et al (1999) Melt rheology of compatibilized polystyrene/low density polyethylene blends. Polym Int 48:1113–1120
Han JH, Choi-Feng C, Li DJ et al (1995) Effect of flow geometry on the rheology of dispersed two-phase blends of polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate). Polymer 36:2451–2462
Pisitsak P, Magaraphan R (2009) Rheological, morphological, thermal, and mechanical properties of blends of vectra A950 and poly(trimethylene terephthalate): a study on a high-viscosity-ratio system. Polym Test 28:116–127
Grmela M, Ait-Kadi A, Utracki LA (1998) Blends of two immiscible and rheologically different fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 77:253–259
Wang N, Yu J, Chang PR et al (2008) Influence of formamide and water on the properties of thermoplastic starch/poly(lactic acid) blends. Carbohydr Polym 71:109–118
Peacock AJ (2002) Handbook of polyethylene: Structures. Properties and Applications. Marcel Dekker, New York
Shenoy AV (1999) Rheology of filled polymer systems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Liang JZ, Yang J, Tang CY (2010) Die-swell behaviour of PP/Al(OH)3/Mg(OH)2 flame retardant composite melts. Polym Test 29:624–628
Wong ACY, Liang JZ (1997) Relationship between die swell ratio and melt flow index. Chem Eng Sci 52:3219–3221
Han CD (2007) Rheology and processing of polymeric materials: polymer rheology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Acierno D, Curto D, La Mantia FP et al (1986) Flow properties of low density/linear low density polyethylene. Polym Eng Sci 26:28–33
Liang JZ, Ness JN (1998) The melt die-swell behaviour during capillary extrusion of LDPE/PP blends. Polym Test 17:179–189
Kim J, Kim JH, Shin TK et al (2001) Miscibility and rheological characteristics of biodegradable aliphatic polyester and linear low density polyethylene blends. Eur Polym J 37:2131–2139
Joseph S, Oommen Z, Thomas S (2002) Melt elasticity and extrudate characteristics of polystyrene/polybutadiene blends. Mater Lett 53:268–276
Nair SV, Oommen Z, Thomas S (2002) Melt elasticity and flow activation energy of nylon 6/polystyrene blends. Mater Lett 57:475–480
Shan CLP, Soares JBP, Penlidis A (2003) HDPE/LLDPE reactor blends with bimodal microstructures—Part II: rheological properties. Polymer 44:177–185
Chaput S, Carrot C, Castro M et al (2004) Co-continuity interval in immiscible polymer blends by dynamic mechanical spectroscopy in the molten and solid state. Rheol Acta 43:417–426
Chuang HK, Han CD (1984) Rheological behaviour of polymer blends. J Appl Polym Sci 29:2205–2229
Yang H, Han CD, Kim JK (1994) Rheology of miscible blends of poly(methyl methacrylate) with poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) and with poly(vinylidene fluoride). Polymer 35:1503–1511
Abdel-Bary EM (2003) Handbook of plastic films. Rapra Technology, Shrewsbury
Ren Z, Dong L, Yang Y (2006) Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of plasticized poly(lactic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 101:1583–1590
Hagen R, Salmen L, Lavebratt H et al (1994) Comparison of dynamic mechanical measurements and Tg determinations with two different instruments. Polym Test 13:113–128
Rieger J (2001) The glass transition temperature Tg of polymers—Comparison of the values from differential thermal analysis (DTA, DSC) and dynamic mechanical measurements (torsion pendulum). Polym Test 20:199–204
Pluta M (2004) Morphology and properties of polylactide modified by thermal treatment, filling with layered silicates and plasticization. Polymer 45:8239–8251
Pluta M, Murariu M, Alexandre M et al (2008) Polylactide compositions: the influence of ageing on the structure, thermal and viscoelastic properties of PLA/calcium sulfate composites. Polym Degrad Stabil 93:925–931
Menard KP (2003) Thermomechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Analysis. In: Lobo H, Bonilla JW (eds) Handbook of plastic analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djellali, S., Sadoun, T., Haddaoui, N. et al. Viscosity and viscoelasticity measurements of low density polyethylene/poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym. Bull. 72, 1177–1195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1331-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1331-6