Abstract
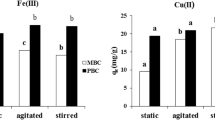
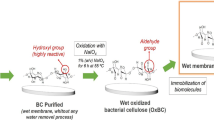
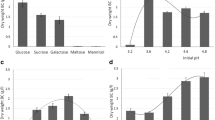
Bacterial cellulose (BC) was homogenously modified with succinic anhydride in N,N-dimethylacetamide/LiCl in the presence of triethylamine and heterogeneously in pyridine in the presence of 4-dimethylaminopyridine. FTIR, XRD, 13C CP MAS NMR, SEM were used to characterize BC and succinylated bacterial cellulose (SBC). For homogeneous modification, the degree of substitution (DS) of SBC differs from 0.21 to 1.45 with the variation of the adding amount of succinic anhydrate, temperature, reaction time, and the amount of triethylamine. DS and XRD profiles reveal that heterogenous reaction mainly happens on the surface of BC membrane. The adsorption capacity and mechanism of Cu2+ onto BC and SBC were investigated. The result shows the adsorption is affected by the morphology and the DS of adsorbents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backdahl H, Helenius G, Bodin A, Nannmark U, Johansson BR, Risberg B, Gatenholm P (2006) Mechanical properties of bacterial cellulose and interactions with smooth muscle cells. Biomaterials 27:2141–2149
Geyer U, Heinze T, Stein A, Marsch S, Klemm D, Schumann D, Schmauder HP (1994) Formation, derivatization and applications of bacterial cellulose. Int J Biol Macromol 16:343–347
Schlufter K, Schmauder H, Dorn S, Heinze T (2006) Efficient homogeneous chemical modification of bacterial cellulose in the ionic liquid 1-N-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Macromol Rapid Commun 27:1670–1676
Heinze T (1998) New ionic polymers by cellulose functionalization. Macromol Chem Phys 199:2341–2364
Oshima T, Kondo K, Ohto K, Inoue K, Baba Y (2008) Preparation of phosphorylated bacterial cellulose as an adsorbent for metal ions. React Funct Polym 68:376–383
Wang Y, Luo Q, Peng B, Pei Ch (2008) A novel thermotropic liquid crystalline-benzoylated bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 74:875–879
Ifuku Sh, Nogi M, Abe K, Handa K, Nakatsubo F, Yano H (2007) Surface modification of bacterial cellulose nanofibers for property enhancement of optically transparent composites: dependence on acetyl-group DS. Biomacromolecules 8:1973–1978
Heinze T, Koshcella A (2005) Carboxymethyl esters of cellulose and starch—a review. Macromol Symp 223:13–39
Koschella A, Fenn D, Heinze T (2006) Water soluble 3-mono-O-ethyl cellulose: synthesis and characterization. Polym Bull 57:33–41
Li WY, Jin AX, Liu CF, Sun RC, Zhang AP, Kennedy JF (2009) Homogeneous modification of cellulose with succinic anhydride in ionic liquid using 4-dimethyl amino pyridine as a catalyst. Carbohydr Polym 78:389–395
Wong S, Kasapis S, Tan MY (2009) Bacterial and plant cellulose modification using ultrasound irradiation. Carbohydr Polym 77:280–287
Liu CF, Zhang AP, Li WY, Yue FX, Sun RC (2009) Homogeneous modification of cellulose in ionic liquid with succinic anhydride using N-bromosuccinimide as a catalyst. J Agric Food Chem 57:1814–1820
Yoshimura T, Matsuo K, Fujioka R (2006) Novel biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogels derived from cotton cellulose and succinic anhydride: synthesis and characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 99:3251–3256
Heinze T, Liebert T, Koschella A (2006) Esterification of polysaccharides. Springer, Berlin
Liu CF, Sun RC, Zhang AP, Ren JL, Wang XA, Qin MH, Chao ZN, Luo W (2007) Homogeneous modification of sugarcane bagasse cellulose with succinic anhydride using a ionic liquid as reaction medium. Carbohydr Res 342:919–926
Masud K, Adachi M, Hirai A, Yamamoto H, Kaji H, Horii F (2003) Solid-state 13C and 1H spin diffusion NMR analyses of the microfibril structure for bacterial cellulose. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 23:198–212
Tokoh C, Takabe K, Fujita M, Saiki H (1998) Cellulose synthesized by acetobacter xylinum in the presence of acetyl glucomannan. Cellulose 5:26–249
Shen W, Chen S, Shi S, Li X, Zhang X, Hu W, Wang H (2009) Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) on to diethylenetriamine bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 75:110–114
Zou Y, Chen S, Wang J, Shi S, Yan Zh, Wang H (2008) Adsorption of Cu2+ by bacterial cellulose. J Mater Sci Eng 26:426–429
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from National Nature Science foundation of China (Project No. 50863002, 50763002), and Nature Science foundation of Hainan Province (Project No. 2080302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Yu, C., Zhang, X. et al. Comparison of succinylation methods for bacterial cellulose and adsorption capacities of bacterial cellulose derivatives for Cu2+ ion. Polym. Bull. 67, 401–412 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-010-0388-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-010-0388-5