Abstract.
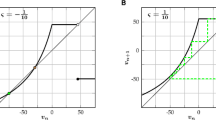
In this paper we make a rigorous mathematical analysis of one-dimensional spiking neuron models in a unified framework. We find that, under conditions satisfied in particular by the periodically and aperiodically driven leaky integrator as well as some of its variants, the spike map is increasing on its range, which leaves no room for chaotic behavior. A rigorous expression of the Lyapunov exponent is derived. Finally, we analyse the periodically driven perfect integrator and show that the restriction of the phase map to its range is always conjugated to a rotation, and we provide an explicit expression of the invariant measure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alstrom, P., Christiansen, B., Levinsen, M.T.: Nonchaotic transition from quasiperiodicity to complete phase locking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 1679–1682 (1988)
Artun, O., Shouval, H., Cooper, L.: The effect of dynamic synapses on spatiotemporal receptive fields in visual cortex. PNAS 95, 11999–12003 (1998)
Ascoli, C., Barbi, M., Chillemi, S., Petracchi, D.: Phase-locked responses in the Limulus lateral eye. Theoretical and experimental investigation. Biophys. J. 19, 219–40 (1977)
Brette, R.: Rotation numbers of discontinuous orientation-preserving circle maps. Set-Valued Anal. 2003, in press
Brette, R., Guigon, E.: Reliability of spike timing is a general property of spiking model neurons. Neural Comput. 15, 279–308 (2003)
Coombes, S.: Liapunov exponents and mode-locked solutions for integrate-and-fire dynamical systems. Phys. Lett. A, (1999)
Cornfeld, I., Fomin, S., Sinai, Y.: Ergodic theory, no. 245 in Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften, Springer-Verlag, 1981
de~Melo, W., van Strien, S.: One-dimensional dynamics. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1993
Denjoy, A.: Sur les courbes définies par les équations différentielles à la surface du tore. J. Math. Pures Appl. 9, 333–375 (1932)
Ermentrout, B.: Type i membranes, phase resetting curves, and synchrony. Neural Comput. 8, 979–1001 (1996)
Ermentrout, B., Kopell, N.: Parabolic bursting in an excitable system coupled with a slow oscillation. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 46, 233–253 (1986)
Glass, L., Bélair, J.: Continuation of Arnold tongues in mathematical models of periodically forced biological oscillators. In: Nonlinear oscillations in Biology and Chemistry, H. Othmer, (ed.), no. 66 in Lecture Notes in Biomathematics. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1986, pp. 232–243
Glass, L., Perez, R.: Fine structure of phase locking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1772–1775 (1982)
Guttman, R., Feldman, L., Jakobsson, E.: Frequency entrainment of squid axon membrane. J. Membrane Biol. 56, 9–18 (1980)
Herman, M.: Mesure de Lebesgue et nombre de rotation. Lecture Notes in Math, Vol. 597, Berlin: Springer, 1977, pp. 271–293
Hodgkin, A., Huxley, A.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 500–544 (1952)
Jensen, M., Bak, P., Bohr, T.: Complete devil’s staircase, fractal dimension and universality of mode-locking structure in the circle map. Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 1637–1639 (1983)
Keener, J., Hoppensteadt, F., Rinzel, J.: Integrate-and-fire models of nerve membrane response to oscillatory input. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 41, 503–517 (1981)
Keener, J.P.: Chaotic behavior in piecewise continuous difference equations. Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 261, 589–604 (1980)
Knight, B.W.: Dynamics of encoding in a population of neurons. J. Gen. Physiol. 59, 734–66 (1972)
Koppl, C.: Phase locking to high frequencies in the auditory nerve and cochlear nucleus magnocellularis of the barn owl. Tyto alba. J. Neurosci. 17, 3312–21 (1997)
Kwapisz, J.: Poincare rotation number for maps of the real line with almost periodic displacement. Nonlinearity 13, 1841–1854 (2000)
Lapicque, L.: Recherches quantitatives sur l’excitation électrique des nerfs traitée comme une polarisation. J. Physiol. Pathol. Gen. 9, 620–635 (1907)
Latham, P., Richmond, B., Nelson, P., Nirenberg, S.: Intrinsic dynamics in neuronal networks. i. theory. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 808–27 (2000)
Poincaré, H.: Sur les courbes définies par les équations différentielles. J. Math. Pures. App. I, 167, (1885)
Rescigno, A., Stein, R., Purple, R., Poppele, R.: A neuronal model for the discharge patterns produced by cyclic inputs. Bull Math. Biophys. 32, 337–353 (1970)
Rhodes, F., Thompson, C.: Rotation numbers for monotone functions on the circle. J. London Math. Soc. 2, 360–368 (1986)
Rhodes, F., Thompson, C.: Topologies and rotation numbers for families of monotone functions on the circle. J. London Math. Soc. 2, 156–170 (1991)
Somers, D., Nelson, S., Mriganka, S.: An emergent model of orientation selectivity in cat visual cortical simple cells. J. Neurosci. 15, 5448–5465 (1995)
Song, S., Abbot, L.: Cortical development and remapping through spike timing-dependent plasticity. Neuron. 32, 339–350 (2001)
Song, S., Miller, K., Abbott, L.: Competitive Hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nature neurosci. 3, 919–926 (2000)
Swiatek, G.: Rational rotation numbers for maps of the circle. Commun. Math. Phys. 119, 109–128 (1988)
Tass, P., Rosenblum, M., Weule, J., Kurths, J., Pikovsky, A., Volkmann, J., Schnitzler, A., Freund, H.: Detection of n:m phase locking from noisy data: application to magnetoencephalography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3291–3294 (1998)
Tiesinga, P.: Precision and reliability of periodically and quasiperiodically driven integrate-and-fire neurons. Phys. Rev. E, 65, (2002)
Troyer, T., Miller, K.: Physiological gain leads to high ISI variability in a simple model of a cortical regular spiking cell. Neural Comput. 9, 971–83 (1997)
Veerman, J.J.P.: Irrational rotation numbers. Nonlinearity 2, 419–428 (1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brette, R. Dynamics of one-dimensional spiking neuron models. J. Math. Biol. 48, 38–56 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-003-0223-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-003-0223-9