Abstract
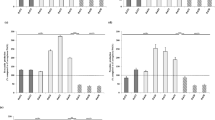
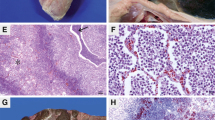
Investigation of a serious pig disease with high mortality and typical lung lesions yielded a bacterial isolate identified as Providencia alcalifaciens based on the 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. The pathogenicity of this bacterial isolate was confirmed in piglets and mice. The bacterial strain caused the typical illness in piglets, which suffered serious dyspnea and hemorrhagic pneumonia. The drug resistance spectrum of the bacterium was also determined. The results indicated that the isolate is resistant to 12 antibiotics and intermediately resistant to 10 antibiotics out of the 34 antibiotics tested. The current study is the first to report a serious lung disease in piglets caused by a multidrug resistant P. alcalifaciens isolate, which should be given more attention during surveillance and diagnostics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert M, Alam K, Ansaruzzaman M, Islam M, Rahman A, Haider K, Bhuiyan N, Nahar S, Ryan N, Montanaro J (1992) Pathogenesis of Providencia alcalifaciens-induced diarrhea. Infect Immun 60:5017–5024
Camus A, Hawke J (2002) Providencia rettgeri-associated septicemia and meningoencephalitis in juvenile farmed American alligators Alligator mississippiensis. J Aquat Anim Health 14:149–153
Chen S, Wang Y, Chen F, Yang H, Gan M, Zheng SJ (2007) A highly pathogenic strain of Staphylococcus sciuri caused fatal exudative epidermitis in piglets. PLoS One 2:e147
Cheng HR, Jiang N (2006) Extremely rapid extraction of DNA from bacteria and yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 28:55–59
Costas M, Holmes B, Wood A, On S (1989) Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of Providencia rettgeri strains from human faeces, urine and other specimens. J Appl Bacteriol 67:441–452
Dajani AS, Clyde WA, Denny FW (1965) Experimental infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Eaton’s agent). J Exp Med 121:1071
Davies J, Davies D (2010) Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:417–433
Guth B, Irino K, Trabulsi L (1999) Clonal structure of Providencia alcalifaciens strains isolated from diarrhoeal stools in Sāo Paulo, Brazil. J Med Microbiol 48:205–209
Guth BEC, Perrella E (1996) Prevalence of invasive ability and other virulence-associated characteristics in Providencia alcalifaciens strains isolated in Sao Paulo, Brazil. J Med Microbiol 45:459–462
Hawkey P (1984) Providencia stuartii: a review of a multiply antibiotic-resistant bacterium. J Antimicrob Chemother 13:209–226
Haynes J, Hawkey PM (1989) Providencia alcalifaciens and travellers’ diarrhoea. BMJ 299:94
Highland MA, Byrne BA, DebRoy C, Samitz EM, Peterson TS, Oslund KL (2009) Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli-induced pneumonia in three kittens and fecal prevalence in a clinically healthy cohort population. J Vet Diagn Invest 21:609
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2006) The enterobacteria, 92nd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 137–150
Janda JM, Abbott SL, Woodward D, Khashe S (1998) Invasion of HEp-2 and other eukaryotic cell lines by Providenciae: further evidence supporting the role of Providencia alcalifaciens in bacterial gastroenteritis. Curr Microbiol 37:159–165
Johnson JR, O’Bryan TT, Low DA, Ling G, Delavari P, Fasching C, Russo TA, Carlino U, Stell AL (2000) Evidence of commonality between canine and human extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains that express papG allele III. Infect Immun 68:3327–3336
Juneja P, Lazzaro BP (2009) Providencia sneebia sp. nov. and Providencia burhodogranariea sp. nov., isolated from wild Drosophila melanogaster. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1108–1111
Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HLT (2004) Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:123–140
Krake PR, Tandon N (2004) Infective endocarditis due to Providencia stuartii. SMJ 97:1022
Ladds P, Bradley J, Hirst R (1996) Providencia rettgeri meningitis in hatchling saltwater crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus). Aust Vet J 74:397–398
Luzzaro F, Mezzatesta M, Mugnaioli C, Pirelli M, Stefan S, Amicosante G, Rossellini G, Toniolo A (2006) Trends in production of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases among enterobacteria of medical Interest. Report of the Second Italian Nationwide Survey. J Clin Microbiol 44:1659–1664
Müller H, O’hara C, Fanning G, Hickman-Brenner F, Swenson J, Brenner DJ (1986) Providencia heimbachae, a new species of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from animals. Int J Syst Bacteriol 36:252–256
Murata T, Iida T, Shiomi Y, Tagomori K, Akeda Y, Yanagihara I, Mushiake S, Ishiguro F, Honda T (2001) A large outbreak of foodborne infection attributed to Providencia alcalifaciens. J Infect Dis 184:1050
O’Hara CM, Brenner FW, Miller JM (2000) Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:534–546
O’Hara CM, Steigerwalt AG, Green D, McDowell M, Hill BC, Brenner DJ, Miller JM (1999) Isolation of Providencia heimbachae from human feces. J Clin Microbiol 37:3048–3050
Papadogiannakis E, Perimeni D, Velonakis E, Kontos V, Vatopoulos A (2007) Providencia stuartii infection in a dog with severe skin ulceration and cellulitis. J Small Anim Pract 48:343–345
Russo TA, Johnson JR (2000) Proposal for a new inclusive designation for extraintestinal pathogenic isolates of Escherichia coli: ExPEC. J Infect Dis 181:1753–1754
Simon C, Dieli M, Brucato A, Pedrotti P, Brambilla P, Curri SF, Senni M, Pericotti S, Suter F, Ferrazzi P (2010) Bacterial Pericarditis due to Providencia stuartii. Circulation 122:e401–e403
Sipahi OR, Bardak-Ozcem S, Ozgiray E, Aydemir S, Yurtseven T, Yamazhan T, Tasbakan M, Ulusoy S (2010) Meningitis due to Providencia stuartii. J Clin Microbiol 48:4667
Sobreira M, Leal NC, Magalhães M, Guth BE, Almeida AM (2001) Molecular analysis of clinical isolates of Providencia alcalifaciens. J Med Microbiol 50:29–34
Somvanshi VS, Lang E, Sträubler B, Spröer C, Schumann P, Ganguly S, Saxena AK, Stackebrandt E (2006) Providencia vermicola sp. nov., isolated from infective juveniles of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema thermophilum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:629–633
Stock I, Wiedemann B (1998) Natural antibiotic susceptibility of Providencia stuartii, P. rettgeri, P. alcalifaciens and P. rustigianii strains. J Med Microbiol 47:629–642
Sura R, Van Kruiningen H, DebRoy C, Hinckley L, Greenberg K, Gordon Z, French R (2007) Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli-induced acute necrotizing pneumonia in cats. Zoonoses Public Health 54:307–313
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tribe GW, Rood MJ (2002) Providencia alcalifaciens in diarrhoeic dogs and cats. Vet Rec 150:386
Tumbarello M, Citton R, Spanu T, Sanguinetti M, Romano L, Fadda G, Cauda R (2004) ESBL-producing multidrug-resistant Providencia stuartii infections in a university hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother 53:277–282
Vieira ABR, Koh IHJ, Guth BEC (2003) Providencia alcalifaciens strains translocate from the gastrointestinal tract and are resistant to lytic activity of serum complement. J Med Microbiol 52:633–636
Yokoyama K, Doi Y, Yamane K, Kurokawa H, Shibata N, Shibayama K, Yagi T, Kato H, Arakawa Y (2003) Acquisition of 16S rRNA methylase gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet 362:1888–1893
Zapantis A, Lacy MK, Horvat RT, Grauer D, Barnes BJ, O’Neal B, Couldry R (2005) Nationwide antibiogram analysis using NCCLS M39-A guidelines. J Clin Microbiol 43:2629–2634
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the basic research universities special fund operations (QN2011106) and Northwest A&F University PhD Research Start-up funds (2010BSJJ014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xinglong Wang and Jinqiu Wang equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, J., Hao, H. et al. Pathogenic Providencia alcalifaciens Strain that Causes Fatal Hemorrhagic Pneumonia in Piglets. Curr Microbiol 68, 278–284 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0470-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0470-y