Abstract
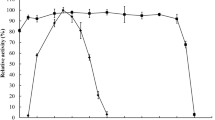
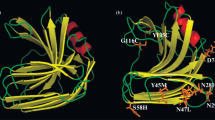
Xylanase is one of the most important hemicellulases in industry. However, its low thermostability limits its applications. In this study, one thermostable xylanase-producing strain 400264 was obtained from screening 11 Aspergillus niger strains (producing thermotolerant xylanase), and the optimum temperature of crude xylanase extracted from it was 55°C. Original activity of the crude xylanase is 64% at 60°C and 55% at 85°C with an incubation time of 30 min, respectively. After the expression of recombinant xylanase gene (xynA/xynB), the XYNB (xylanase B) showed higher thermostability than XYNA (xylanase A). Recombinant enzyme XYNB retained 94% of its activity for 10 min at 85°C, while XYNA with no activity left. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed to replace Ala33 of XYNB by Ser33 resulting 19% decrease in enzyme activity after incubating at 85°C for 30 min. It suggested that the Ala33 residue may have a certain effect on the thermophilic adaptation of xylanase.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polizeli ML, Rizzatti AC, Monti R, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Amorim DS (2005) Xylanases from fungi properties and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(5):577–591
Li Y, Zhang B, Chen X, Chen Y, Cao Y (2009) Improvement of Aspergillus sulphureus Endo-beta-1,4-xylanase expression in Pichia pastoris by codon optimization and analysis of the enzymic characterization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8621-0
Shanklin J (2008) Enzyme engineering. Adv Plant Biochem Mol Biol 1:29–47
Wang J, Zhang WW, Liu JN, Cao YL, Bai XT, Gong YS, Cen PL, Yang MM (2009) An alkali-tolerant xylanase produced by the newly isolated alkaliphilic Bacillus pumilus from paper mill effluent. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9915-6
Yi X, Sun L, Liu X, Tao HH, Abudukerim M, Rahman E (2007) Xylanase production and properties by newly isolated from thermostable alkaliphilic Chinese Bacillus strains. Biotechnology 17(5):31–35
Annamalai N, Thavasi R, Jayalakshmi S, Balasubramanian T (2009) Thermostable and alkaline tolerant xylanase production by Bacillus subtilis isolated form marine environment. Indian J Biotechnol 8(3):291–297
Roberge M, Shareck F, Morosoli R, Kluepfel D, Dupont C (1998) Site-directed mutagenesis study of a conserved residue in family 10 glycanase:histidine 86 of xylanase A from Streptomyces licidans. Protein Eng 11(5):399–404
Turunen O, Vuorio M, Fenel F, Leisola M (2002) Engineering of multiple arginines into the Ser/Thr surface of Trichoderma reesei endo-1,4-beta-xylanase II increase the thermotolerance and shifts the pH optimum towards alkaline pH. Protein Eng 15(2):141–145
You C, Huang Q, Xue HP, Xu Y, Lu H (2009) Potential hydrophobic interaction between two cysteines in interior hydrophobic region improves thermostability of a family 11 xylanase from N. patriciarum. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.22623
Vries DE, Visser J (2001) Aspergillus enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65(4):497–522
Weng XY, Sun JY (2005) Construction, expression, and characterization of a thermostable xylanase. Curr Microbiol 51(3):188–192
Krisana A, Rutchadaporn S, Jarupan G, Lily E, Sutipa T, Kanyawim K (2005) Endo-1, 4-xylanase B from Aspergillus cf. niger BCC14405 isolated in Thailand: purification, characterization and gene isolation. J Biochem Mol Biol 38(1):17–23
Kavya V, Padmavathi T (2009) Optimization of growth conditions for xylanase production by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation. Pol J Microbiol 58(2):125–130
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270
LaemmLi UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assemble of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Bai YG, Wang JS, Zhang ZF, Yang PL, Shi PJ, Luo HY, Meng K, Huang HQ, Yao B (2010) A new xylanase from thermoacidophilic Alicyclobacillus sp. A4 with broad-range pH activity and pH stability. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37(2):187–194
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL Workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Krengel U, Dijkstra BW (1996) Three-dimensional structure of endo-1, 4-β-xylanase I from Aspergillus niger: molecular basis for its low pH optimum. J Mol Biol 263:70–78
Luttig M, Pretorius IS, Van Zyl WH (1997) Cloning of two β-xylanase-encoding genes from Aspergillus niger and their expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 19(5):411–415
Luo HY, Wang YR, Li J, Wang H, Yang J, Yang YH, Huang HQ, Fan YL, Yao B (2009) Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel acidic xylanase, XYL11B1, from the acidophilic fungus Bispora sp. MEY-1. Enzyme Microb Technol 45(2):126–133
Cao YH, Chen XL, He PL, Lu WQ (2006) Cloning, expression and enzyme characterization analysis of A. sulphureus xylanase gene xynA. Lett Biotechnol 17(6):878–881
Van Ooyen AJJ, De Graaff LH, Van Den Broeck HC, Visser J (1994) Cloning and expression of xylanase B. International Patent Application WO94/14965 Gist-Brocades Delft
Sriprang R, Asano K, Gobsuk J, Tanapongpipat S, Champreda V, Eurwilaichitr L (2006) Improvement of thermostability of fungal xylanase by using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biotechnol 126(4):454–462
Moreau A, Shareck F, Kluepfel D, Morosoli R (1994) Increase in catalytic activity and thermostability of the xylanase A of Streptomyces lividans 1326 by site specific mutagenesis. Enzyme Microb Technol 16(5):420–424
Al Balaa B, Brijs K, Gebruers K, Vandenhaute J, Wouters J, Housen I (2009) Xylanase XYL1p from Scytalidium acidophilium: site-directed mutagenesis and acidophilic adaption. Bioresour Technol 100(24):6465–6571
Liu LW, Wang B, Chen HG, Wang SY, Wang MD, Zhang SM, Song AD, Shen JW, Wu K, Jia XC (2009) Rational pH-engineering of the thermostable xylanase based on computational model. Process Biochem 44:912–915
Payan F, Flatman R, Porciero S, Williamson G, Juge N, Roussel A (2003) Structural analysis of xylanase inhibitor protein I (XIP-I), a proteinaceous xylanase inhibitor from wheat (Triticum aestivum, var. Soisson). Biochemical J 372:399–405
Natesh R, Manikandan K, Bhanumoorthy P, Viswamitra MA, Ramakumar S (2003) Thermostable xylanase from Thermoascus aurantiacus at ultrahigh resolution (0.89 A) at 100 K and atomic resolution (1.11 A) at 293 K refined anisotropically to small molecule accuracy. Acta Crystallogr Sect D 59:105–117
Davoodi J, Wakarchuk WW, Carey PR, Surewicz WK (2007) Mechanism of stabilization of Bacillus circulans xylanase upon the introduction of disulfide bonds. Biophys Chem 125:453–461
Malik A, Ahmad S (2007) Sequence and structural features of carbohydrate binding in proteins and assessment of predictability using a neural network. BMC Struct Biol 7(1):1–14
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Special Basic Research Projects of China (Grant No. SB2007FY400-4), by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (Grant No. 2009CB125910).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, J., Song, L., Li, X. et al. Site-Directed Mutagenesis and Thermostability of Xylanase XYNB from Aspergillus niger 400264. Curr Microbiol 62, 242–248 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9697-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9697-z