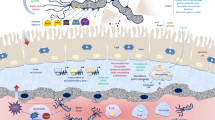
Abstract
Epithelial cells contribute to innate immunity by releasing antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) onto mucosal surfaces. In the small bowel, Paneth cells at the base of the crypts of Lieberkühn secrete α-defensins and additional AMPs at high levels in response to cholinergic stimulation and when exposed to bacterial antigens. The release of Paneth cell products into the crypt lumen is inferred to protect mitotically active crypt cells that renew the epithelial cell monolayer from colonization by potentially pathogenic microbes and to confer protection from enteric infection. The most compelling evidence for a Paneth cell role in enteric resistance to infection is evident from studies of mice transgenic for a human Paneth cell α-defensin, HD-5, which are completely immune to infection and systemic disease from orally administered Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Cystic fibrosis mice are subject to small bowel bacterial overgrowth that is associated with impaired dissolution of released Paneth cell granules in the crypt lumen. Mutations that cause defects in the activation, secretion, dissolution, and bactericidal effects of Paneth cell AMPs may alter crypt innate immunity and contribute to immunopathology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldhous MC, Nimmo ER, Satsangi J (2003) NOD2/CARD15 and the Paneth cell: another piece in the genetic jigsaw of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 52:1533–1535
Aley SB, Zimmerman M, Hetsko M, Selsted ME, Gillin FD (1994) Killing of giardia lamblia by cryptdins and cationic neutrophil peptides. Infect Immun 62:5397–5403
Alnadjim Z, Cohn SM, Ayabe T, Biafora S, Ouellette AJ, Barrett TA (2001) T cell activation instructs epithelial lineage development by inducing Paneth cell expansion and cryptdin production in intestinal crypts. Gastroenterology 120:A21 (Abstract)
Ayabe T, Satchell DP, Wilson CL, Parks WC, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2000) Secretion of microbicidal alpha-defensins by intestinal Paneth cells in response to bacteria. Nat Immunol 1:113–118
Ayabe T, Satchell DP, Pesendorfer P, Tanabe H, Wilson CL, Hagen SJ, Ouellette AJ (2002) Activation of Paneth cell alpha-defensins in mouse small intestine. J Biol Chem 277:5219–5228
Ayabe T, Wulff H, Darmoul D, Cahalan MD, Chandy KG, Ouellette AJ (2002) Modulation of mouse Paneth cell alpha-defensin secretion by mIKCa1, a Ca2+-activated, intermediate conductance potassium channel. J Biol Chem 277:3793–3800
Bajaj-Elliott M, Fedeli P, Smith GV, Domizio P, Maher L, Ali RS, Quinn AG, Farthing MJ (2002) Modulation of host antimicrobial peptide (beta-defensins 1 and 2) expression during gastritis. Gut 51:356–361
Bals R, Wang X, Meegalla RL, Wattler S, Weiner DJ, Nehls MC, Wilson JM (1999) Mouse beta-defensin 3 is an inducible antimicrobial peptide expressed in the epithelia of multiple organs. Infect Immun 67:3542–3547
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Georgel P, Tabeta K, Du X (2004) Genetic analysis of innate immunity: TIR adapter proteins in innate and adaptive immune responses. Microbes Infect 6:1374–1381
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Shamel L (2004) Forward genetic dissection of afferent immunity: the role of TIR adapter proteins in innate and adaptive immune responses. C R Biol 327:571–580
Bjerknes M, Cheng H (1981) The stem-cell zone of the small intestinal epithelium. I. Evidence from Paneth cells in the adult mouse. Am J Anat 160:51–63
Bry L, Falk P, Huttner K, Ouellette A, Midtvedt T, Gordon JI (1994) Paneth cell differentiation in the developing intestine of normal and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:10335–10339
Cheng H (1974) Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. IV. Paneth cells. Am J Anat 141:521–535
Clarke LL, Gawenis LR, Bradford EM, Judd LM, Boyle KT, Simpson JE, Shull GE, Tanabe H, Ouellette AJ, Franklin CL, Walker NM (2004) Abnormal Paneth cell granule dissolution and compromised resistance to bacterial colonization in the intestine of CF mice. Am J Physiol Gasterointest Liver Physiol 286:G1050–G1058
Cummings JE, Satchell DP, Shirafuji Y, Ouellette AJ, Vanderlick TK (2003) Electrostatically controlled interactions of mouse Paneth cell alpha-defensins with phospholipid membranes. Austr J Chem 56:1031–1034
Cuthbert AP, Fisher SA, Mirza MM, King K, Hampe J, Croucher PJ, Mascheretti S, Sanderson J, Forbes A, Mansfield J, Schreiber S, Lewis CM, Mathew CG (2002) The contribution of NOD2 gene mutations to the risk and site of disease in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 122:867–874
Dale BA, Kimball JR, Krisanaprakornkit S, Roberts F, Robinovitch M, O’Neal R, Valore EV, Ganz T, Anderson GM, Weinberg A (2001) Localized antimicrobial peptide expression in human gingiva. J Periodontal Res 36:285–294
Darmoul D, Brown D, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (1997) Cryptdin gene expression in developing mouse small intestine. Am J Physiol 272:G197–G206
Eisenhauer PB, Harwig SS, Lehrer RI (1992) Cryptdins: antimicrobial defensins of the murine small intestine. Infect Immun 60:3556–3565
Fellermann K, Wehkamp J, Herrlinger KR, Stange EF (2003) Crohn’s disease: a defensin deficiency syndrome? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:627–634
Ganz T, Selsted ME, Szklarek D, Harwig SS, Daher K, Bainton DF, Lehrer RI (1985) Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest 76:1427–1435
Ganz T, Liu L, Valore EV, Oren A (1993) Posttranslational processing and targeting of transgenic human defensin in murine granulocyte, macrophage, fibroblast, and pituitary adenoma cell lines. Blood 82:641–650
Ganz T, Lehrer RI (1998) Antimicrobial peptides of vertebrates. Curr Opin Immunol 10:41–44
Ganz T (2003) Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 3:710–720
Ganz T (2004) Antimicrobial polypeptides. J Leukoc Biol 75:34–38
Ganz T (2004) Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of vertebrates. C R Biol 327:539–549
Garabedian EM, Roberts LJ, McNevin MS, Gordon JI (1997) Examining the role of Paneth cells in the small intestine by lineage ablation in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 272:23729–23740
Ghosh D, Porter E, Shen B, Lee SK, Wilk D, Drazba J, Yadav SP, Crabb JW, Ganz T, Bevins CL (2002) Paneth cell trypsin is the processing enzyme for human defensin-5. Nat Immunol 3:583–590
Gordon JI, Hermiston ML (1994) Differentiation and self-renewal in the mouse gastrointestinal epithelium. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:795–803
Gordon JI, Hooper LV, McNevin MS, Wong M, Bry L (1997) Epithelial cell growth and differentiation. III. Promoting diversity in the intestine: conversations between the microflora, epithelium, and diffuse GALT. Am J Physiol 273:G565–G570
Grimm MC, Pavli P (2004) NOD2 mutations and Crohn’s disease: are Paneth cells and their antimicrobial peptides the link? Gut 53:1558–1560
Hampe J, Frenzel H, Mirza MM, Croucher PJ, Cuthbert A, Mascheretti S, Huse K, Platzer M, Bridger S, Meyer B, Nurnberg P, Stokkers P, Krawczak M, Mathew CG, Curran M, Schreiber S (2002) Evidence for a NOD2-independent susceptibility locus for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:321–326
Hill CP, Yee J, Selsted ME, Eisenberg D (1991) Crystal structure of defensin HNP-3, an amphiphilic dimer: mechanisms of membrane permeabilization. Science 251:1481–1485
Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2001) Commensal host–bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 292:1115–1118
Hristova K, Selsted ME, White SH (1996) Interactions of monomeric rabbit neutrophil defensins with bilayers: comparison with dimeric human defensin HNP-2. Biochemistry 35:11888–11894
Hristova K, Selsted ME, White SH (1997) Critical role of lipid composition in membrane permeabilization by rabbit neutrophil defensins. J Biol Chem 272:24224–24233
Huang HW (1999) Peptide–lipid interactions and mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides. Novartis Found Symp 225:188–200; discussion 200–186
Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, Lesage S, Cezard JP, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O’Morain CA, Gassull M, Binder V, Finkel Y, Cortot A, Modigliani R, Laurent-Puig P, Gower-Rousseau C, Macry J, Colombel JF, Sahbatou M, Thomas G (2001) Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 411:599–603
Jia HP, Wowk SA, Schutte BC, Lee SK, Vivado A, Tack BF, Bevins CL, McCray PB Jr (2000) A novel murine beta-defensin expressed in tongue, esophagus, and trachea. J Biol Chem 275:33314–33320
Jones DE, Bevins CL (1992) Paneth cells of the human small intestine express an antimicrobial peptide gene. J Biol Chem 267:23216–23225
Jones DE, Bevins CL (1993) Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel. FEBS Lett 315:187–192
Judge T, Lichtenstein GR (2002) The NOD2 gene and Crohn’s disease: another triumph for molecular genetics. Gastroenterology 122:826–828
Kamal M, Wakelin D, Ouellette AJ, Smith A, Podolsky DK, Mahida YR (2001) Mucosal T cells regulate Paneth and intermediate cell numbers in the small intestine of T. spiralis-infected mice. Clin Exp Immunol 126:117–125
Krisanaprakornkit S, Weinberg A, Perez CN, Dale BA (1998) Expression of the peptide antibiotic human beta-defensin 1 in cultured gingival epithelial cells and gingival tissue. Infect Immun 66:4222–4228
Krisanaprakornkit S, Kimball JR, Weinberg A, Darveau RP, Bainbridge BW, Dale BA (2000) Inducible expression of human beta-defensin 2 by Fusobacterium nucleatum in oral epithelial cells: multiple signaling pathways and role of commensal bacteria in innate immunity and the epithelial barrier. Infect Immun 68:2907–2915
Lala S, Ogura Y, Osborne C, Hor SY, Bromfield A, Davies S, Ogunbiyi O, Nunez G, Keshav S (2003) Crohn’s disease and the NOD2 gene: a role for Paneth cells. Gastroenterology 125:47–57
Lehrer RI, Barton A, Daher KA, Harwig SS, Ganz T, Selsted ME (1989) Interaction of human defensins with Escherichia coli. Mechanism of bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest 84:553–561
Lehrer RI, Ganz T (2002) Defensins of vertebrate animals. Curr Opin Immunol 14:96–102
Lehrer RI, Ganz T (2002) Cathelicidins: a family of endogenous antimicrobial peptides. Curr Opin Hematol 9:18–22
Leonova L, Kokryakov VN, Aleshina G, Hong T, Nguyen T, Zhao C, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI (2001) Circular minidefensins and posttranslational generation of molecular diversity. J Leukoc Biol 70:461–464
Lesage S, Zouali H, Cezard JP, Colombel JF, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O’Morain C, Gassull M, Binder V, Finkel Y, Modigliani R, Gower-Rousseau C, Macry J, Merlin F, Chamaillard M, Jannot AS, Thomas G, Hugot JP (2002) CARD15/NOD2 Mutational analysis and genotype–phenotype correlation in 612 patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Hum Genet 70:845–857
Maemoto A, Qu X, Rosengren KJ, Tanabe H, Henschen-Edman A, Craik DJ, Ouellette AJ (2004) Functional analysis of the α-defensin disulfide array in mouse cryptdin-4. J Biol Chem 279:44188–44196
Mallow EB, Harris A, Salzman N, Russell JP, DeBerardinis RJ, Ruchelli E, Bevins CL (1996) Human enteric defensins. Gene structure and developmental expression. J Biol Chem 271:4038–4045
Mardini H, de Villiers WJ (2004) To (I)B(D) or NOD2 (I)B(D)–are Paneth cells the answer? Inflamm Bowel Dis 10:696–697
Matsuzaki K, Mitani Y, Akada KY, Murase O, Yoneyama S, Zasloff M, Miyajima K (1998) Mechanism of synergism between antimicrobial peptides magainin 2 and PGLa. Biochemistry 37:15144–15153
Michaelson D, Rayner J, Couto M, Ganz T (1992) Cationic defensins arise from charge-neutralized propeptides: a mechanism for avoiding leukocyte autocytotoxicity? J Leukoc Biol 51:634–639
Murakami M, Ohtake T, Dorschner RA, Gallo RL (2002) Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides are expressed in salivary glands and saliva. J Dent Res 81:845–850
Norkina O, Burnett TG, De Lisle RC (2004) Bacterial overgrowth in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator null mouse small intestine. Infect Immun 72:6040–6049
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R, Britton H, Moran T, Karaliuskas R, Duerr RH, Achkar JP, Brant SR, Bayless TM, Kirschner BS, Hanauer SB, Nunez G, Cho JH (2001) A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 411:603–606
Ogura Y, Lala S, Xin W, Smith E, Dowds TA, Chen FF, Zimmermann E, Tretiakova M, Cho JH, Hart J, Greenson JK, Keshav S, Nunez G (2003) Expression of NOD2 in Paneth cells: a possible link to Crohn’s ileitis. Gut 52:1591–1597
O’Neil DA, Porter EM, Elewaut D, Anderson GM, Eckmann L, Ganz T, Kagnoff MF (1999) Expression and regulation of the human beta-defensins hBD-1 and hBD-2 in intestinal epithelium. J Immunol 163:6718–6724
O’Neil DA, Cole SP, Martin-Porter E, Housley MP, Liu L, Ganz T, Kagnoff MF (2000) Regulation of human beta-defensins by gastric epithelial cells in response to infection with Helicobacter pylori or stimulation with interleukin-1. Infect Immun 68:5412–5415
Ouellette AJ, Hsieh MM, Nosek MT, Cano-Gauci DF, Huttner KM, Buick RN, Selsted ME (1994) Mouse Paneth cell defensins: primary structures and antibacterial activities of numerous cryptdin isoforms. Infect Immun 62:5040–5047
Ouellette AJ, Selsted ME (1996) Paneth cell defensins: endogenous peptide components of intestinal host defense. FASEB J 10:1280–1289
Ouellette AJ, Darmoul D, Tran D, Huttner KM, Yuan J, Selsted ME (1999) Peptide localization and gene structure of cryptdin 4, a differentially expressed mouse Paneth cell alpha-defensin. Infect Immun 67:6643–6651
Ouellette AJ, Bevins CL (2001) Paneth cell defensins and innate immunity of the small bowel. Inflamm Bowel Dis 7:43–50
Pardi A, Zhang XL, Selsted ME, Skalicky JJ, Yip PF (1992) NMR studies of defensin antimicrobial peptides. 2. Three-dimensional structures of rabbit NP-2 and human HNP-1. Biochemistry 31:11357–11364
Patil A, Hughes AL, Zhang G (2004) Rapid evolution and diversification of mammalian α-defensins as revealed by comparative analysis of rodent and primate genes. Physiol Genomics
Peeters T, Vantrappen G (1975) The Paneth cell: a source of intestinal lysozyme. Gut 16:553–558
Porter EM, Liu L, Oren A, Anton PA, Ganz T (1997) Localization of human intestinal defensin 5 in Paneth cell granules. Infect Immun 65:2389–2395
Porter EM, Bevins CL, Ghosh D, Ganz T (2002) The multifaceted Paneth cell. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:156–170
Rubin DC, Swietlicki E, Roth KA, Gordon JI (1992) Use of fetal intestinal isografts from normal and transgenic mice to study the programming of positional information along the duodenal-to-colonic axis. J Biol Chem 267:15122–15133
Salzman NH, Polin RA, Harris MC, Ruchelli E, Hebra A, Zirin-Butler S, Jawad A, Martin Porter E, Bevins CL (1998) Enteric defensin expression in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 44:20–26
Salzman NH, Ghosh D, Huttner KM, Paterson Y, Bevins CL (2003) Protection against enteric salmonellosis in transgenic mice expressing a human intestinal defensin. Nature 422:522–526
Satchell DP, Sheynis T, Kolusheva S, Cummings JE, Vanderlick TK, Jelinek R, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2003) Quantitative interactions between cryptdin-4 amino terminal variants and membranes. Peptides 24:1793–1803
Satchell DP, Sheynis T, Shirafuji Y, Kolusheva S, Ouellette AJ, Jelinek R (2003) Interactions of mouse Paneth cell alpha-defensins and alpha-defensin precursors with membranes: prosegment inhibition of peptide association with biomimetic membranes. J Biol Chem 278:13838–13846
Satoh Y, Habara Y, Ono K, Kanno T (1995) Carbamylcholine- and catecholamine-induced intracellular calcium dynamics of epithelial cells in mouse ileal crypts. Gastroenterology 108:1345–1356
Savidge TC, Morey AL, Ferguson DJ, Fleming KA, Shmakov AN, Phillips AD (1995) Human intestinal development in a severe-combined immunodeficient xenograft model. Differentiation 58:361–371
Schenkels LC, Veerman EC, Nieuw Amerongen AV (1995) Biochemical composition of human saliva in relation to other mucosal fluids. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 6:161–175
Schonwetter BS, Stolzenberg ED, Zasloff MA (1995) Epithelial antibiotics induced at sites of inflammation. Science 267:1645–1648
Selsted ME, Miller SI, Henschen AH, Ouellette AJ (1992) Enteric defensins: antibiotic peptide components of intestinal host defense. J Cell Biol 118:929–936
Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (1995) Defensins in granules of phagocytic and non-phagocytic cells. Trends Cell Biol 5:114–119
Shai Y (1999) Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by alpha-helical antimicrobial and cell non-selective membrane-lytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1462:55–70
Shirafuji Y, Tanabe H, Satchell DP, Henschen-Edman A, Wilson CL, Ouellette AJ (2003) Structural determinants of procryptdin recognition and cleavage by matrix metalloproteinase-7. J Biol Chem 278:7910–7919
Simon TC, Gordon JI (1995) Intestinal epithelial cell differentiation: new insights from mice, flies and nematodes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:577–586
Stappenbeck TS, Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2002) Developmental regulation of intestinal angiogenesis by indigenous microbes via Paneth cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15451–15455
Stappenbeck TS, Hooper LV, Manchester JK, Wong MH, Gordon JI (2002) Laser capture microdissection of mouse intestine: characterizing mRNA and protein expression, and profiling intermediary metabolism in specified cell populations. Methods Enzymol 356:167–196
Stappenbeck TS, Mills JC, Gordon JI (2003) Molecular features of adult mouse small intestinal epithelial progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:1004–1009
Tanabe H, Qu X, Weeks CS, Cummings JE, Kolusheva S, Walsh KB, Jelinek R, Vanderlick TK, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2004) Structure–activity determinants in Paneth cell alpha-defensins: loss-of-function in mouse cryptdin-4 by charge-reversal at arginine residue positions. J Biol Chem 279:11976–11983
Tanabe H, Yuan J, Zaragoza MM, Dandekar S, Henschen-Edman A, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2004) Paneth cell alpha-defensins from rhesus macaque small intestine. Infect Immun 72:1470–1478
Tang YQ, Yuan J, Osapay G, Osapay K, Tran D, Miller CJ, Ouellette AJ, Selsted ME (1999) A cyclic antimicrobial peptide produced in primate leukocytes by the ligation of two truncated alpha-defensins. Science 286:498–502
Tannock GW (2000) The intestinal microflora: potentially fertile ground for microbial physiologists. Adv Microb Physiol 42:25–46
Tannock GW (2001) Molecular assessment of intestinal microflora. Am J Clin Nutr 73:410S–414S
Tarver AP, Clark DP, Diamond G, Russell JP, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Cohen KS, Jones DE, Sweeney RW, Wines M, Hwang S, Bevins CL (1998) Enteric beta-defensin: molecular cloning and characterization of a gene with inducible intestinal epithelial cell expression associated with Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Infect Immun 66:1045–1056
Tran D, Tran PA, Tang YQ, Yuan J, Cole T, Selsted ME (2002) Homodimeric theta-defensins from rhesus macaque leukocytes: isolation, synthesis, antimicrobial activities, and bacterial binding properties of the cyclic peptides. J Biol Chem 277:3079–3084
Valore EV, Ganz T (1992) Posttranslational processing of defensins in immature human myeloid cells. Blood 79:1538–1544
Valore EV, Martin E, Harwig SS, Ganz T (1996) Intramolecular inhibition of human defensin HNP-1 by its propiece. J Clin Invest 97:1624–1629
Watanabe T, Kitani A, Murray PJ, Strober W (2004) NOD2 is a negative regulator of toll-like receptor 2-mediated T helper type 1 responses. Nat Immunol 5:800–808
Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weichenthal M, Schwab M, Schaffeler E, Schlee M, Herrlinger KR, Stallmach A, Noack F, Fritz P, Schroder JM, Bevins CL, Fellermann K, Stange EF (2004) NOD2 (CARD15) mutations in Crohn’s disease are associated with diminished mucosal alpha-defensin expression. Gut 53:1658–1664
Weinberg A, Krisanaprakornkit S, Dale BA (1998) Epithelial antimicrobial peptides: review and significance for oral applications. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 9:399–414
White SH, Wimley WC, Selsted ME (1995) Structure, function, and membrane integration of defensins. Curr Opin Struck Biol 5:521–527
Wilson CL, Ouellette AJ, Satchell DP, Ayabe T, Lopez-Boado YS, Stratman JL, Hultgren SJ, Matrisian LM, Parks WC (1999) Regulation of intestinal alpha-defensin activation by the metalloproteinase matrilysin in innate host defense. Science 286:113–117
Wimley WC, Selsted ME, White SH (1994) Interactions between human defensins and lipid bilayers: evidence for formation of multimeric pores. Protein Sci 3:1362–1373
Zanetti M, Gennaro R, Romeo D (1997) The cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptide precursors: a component of the oxygen-independent defense mechanisms of neutrophils. Ann N Y Acad Sci 832:147–162
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395
Jing W, Hunter HN, Tanabe H, Ouellette AJ, Vogel HJ (2004) Solution structure of cryptdin-4, a mouse Paneth cell α-defensin. Biochemistry 43:15759–15766
Tanabe H, Ayabe T, Bainbridge B, Guina T, Ernst RK, Darveau RP, Miller SI, Ouellette AJ (2005) Mouse Paneth cell secretory responses to cell surface glycolipids of virulent and attenuated pathogenic bacteria. Infect Immun 73:2312–2320
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH Grant DK044632, Human Frontiers Science Program, DANONE Vitapole and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouellette, A.J. Paneth cell α-defensins: peptide mediators of innate immunity in the small intestine. Springer Semin Immun 27, 133–146 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-005-0202-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-005-0202-x