Abstract
Purpose
To characterize the determinants of variability for oxaliplatin pharmacokinetics including age, renal function, and hepatic function in children and adults.
Methods
Oxaliplatin pharmacokinetic data were combined from phase I and II clinical trials: three pediatric trials (Peds1–3) and two adult NCI organ dysfunction studies (Hepatic and Renal). A population pharmacokinetic model was developed utilizing platinum ultrafiltrate concentrations to characterize changes in oxaliplatin disposition with age and organ dysfunction along with other potential sources of oxaliplatin pharmacokinetic variability.
Results
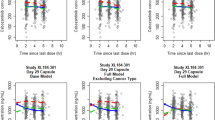
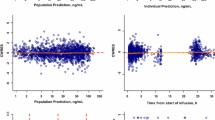
A total of 1,508 concentrations from 186 children and adults were used in the study. The data were well described by a three-compartment model. Serum creatinine (SCR) was an independent predictor of clearance (CL) while age was an independent predictor of volume of distribution. Although age was a significant covariate on CL in the univariate analysis, age effects on CL were entirely accounted for by SCR. Gender, hepatic function, and race had no effect on CL or volume of distribution. Median CL values were 0.58 (Hepatic), 0.34 (Renal), 0.78 (Peds1), 0.74 (Peds2), and 0.81 (Peds3) (L/h/kg0.75). Monte Carlo simulations of the final model with 130 mg/m2 yielded median AUC values of: 14.2 (2–6 years), 16.8 (6–12 years), 16.5 (12–18 years), and 17.3 (>18 years) (µg h/mL).
Conclusions
Renal function had the greatest effect on CL with a small age effect seen on the distribution of oxaliplatin. Young pediatric patients had higher CL values than adults as a result of better renal function.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastian G, Barrail A, Urien S (2003) Population pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in patients with metastatic cancer. Anticancer Drugs 14:817–824
Beaty O 3rd, Berg S, Blaney S, Malogolowkin M, Krailo M, Knight R, Schaiquevich P, Stewart C, Chen Z, Nelson M, Voss S, Ivy SP, Adamson PC (2010) A phase II trial and pharmacokinetic study of oxaliplatin in children with refractory solid tumors: a Children’s Oncology Group study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55:440–445
Capparelli E, Williams P (2007) Pharmacometrics in pharmacotherapy and drug development: pediatric application. In: Ette E, Williams P (eds) Pharmacometrics: the science of quantitative pharmacology. Wiley, Chichester
Ceja M, Christensen A, Yang S (2013) Dosing considerations in pediatric oncology. US Pharm 38:8–11
Delord JP, Umlil A, Guimbaud R, Gregoire N, Lafont T, Canal P, Bugat R, Chatelut E (2003) Population pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 51:127–131
Fouladi M, Blaney SM, Poussaint TY, Freeman BB 3rd, McLendon R, Fuller C, Adesina AM, Hancock ML, Danks MK, Stewart C, Boyett JM, Gajjar A (2006) Phase II study of oxaliplatin in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma, supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors, and atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors: a pediatric brain tumor consortium study. Cancer 107:2291–2297
Graham MA, Lockwood GF, Greenslade D, Brienza S, Bayssas M, Gamelin E (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin: a critical review. Clin Cancer Res 6:1205–1218
Laughon MM, Benjamin DK Jr, Capparelli EV, Kearns GL, Berezny K, Paul IM, Wade K, Barrett J, Smith PB, Cohen-Wolkowiez M (2011) Innovative clinical trial design for pediatric therapeutics. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 4:643–652
McDowell MA, Fryar CD, Hirsch R, Ogden CL (2005) Anthropometric reference data for children and adults: U.S. population, 1999–2002. Adv Data 361:1–5
Pastoor D, Lala M, Gobburu J (2013) Pharmacometrics applications to pediatric trials. In: Mulberg A, Murphy D, Dunne J, Mathis L (eds) Pediatric drug development: concepts and applications. Wiley, Chichester, pp 332–341
Raymond E, Chaney SG, Taamma A, Cvitkovic E (1998) Oxaliplatin: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Ann Oncol 9:1053–1071
Rokkam A (2012) Colorectal cancer. In: Cashen A, Van Tine BA (eds) Hematology and oncology subspecialty consult. Wolters Kluwer, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 239–245
Sanofi-Aventis (2012) Eloxatin (oxaliplatin) prescribing information: injection for intravenous use. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/021759s015lbl.pdf.
Schwartz GJ, Work DF (2009) Measurement and estimation of GFR in children and adolescents. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1832–1843
Spunt SL, Freeman BB 3rd, Billups CA, McPherson V, Khan RB, Pratt CB, Stewart CF (2007) Phase I clinical trial of oxaliplatin in children and adolescents with refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:2274–2280
Synold TW, Takimoto CH, Doroshow JH, Gandara D, Mani S, Remick SC, Mulkerin DL, Hamilton A, Sharma S, Ramanathan RK, Lenz HJ, Graham M, Longmate J, Kaufman BM, Ivy P (2007) Dose-escalating and pharmacologic study of oxaliplatin in adult cancer patients with impaired hepatic function: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group study. Clin Cancer Res 13:3660–3666
Takimoto CH, Graham MA, Lockwood G, Ng CM, Goetz A, Greenslade D, Remick SC, Sharma S, Mani S, Ramanathan RK, Synold TW, Doroshow JH, Hamilton A, Mulkerin DL, Ivy P, Egorin MJ, Grem JL (2007) Oxaliplatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in adult cancer patients with impaired renal function. Clin Cancer Res 13:4832–4839
Zisowsky J, Krause A, Dingemanse J (2010) Drug development for pedatric populations: regulatory aspects. Pharmaceutics 2:364–388
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Percy Ivy from the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Paul Juniewicz from Sanofi-Aventis for assistance with the project. We would like to thank the Children’s Oncology Group and the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium for providing the ADVL0421 and PBTC-010 data sets, respectively. This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (EVC: U54 HD071600-01, TWS: U01 CA062505, P30 CA033572), St. Jude Cancer Center Support Grant CA21765, the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC), and Kaiser Santa Clara.
Conflict of interest
Edmund Capparelli served in a consultant/advisory role at Trius Pharmaceuticals, The Medicines Company, and Cempra. Maryam Fouladi received funding from Genentech and Roche. There are no additional disclosures or potential conflicts of interest to report.
Ethical standard
The previously completed clinical trials from which data were utilized for the current analysis were approved by ethics committees at each respective institution and were performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from patients, parents, or guardians for all participants in the studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikanjam, M., Stewart, C.F., Takimoto, C.H. et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of oxaliplatin in adults and children identifies important covariates for dosing. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 495–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2667-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2667-6