Abstract
Purpose
Eg5, a mitotic motor kinesin protein, plays an essential role in bipolar spindle formation in the M phase of the cell cycle. LY2523355 (litronesib) is an allosteric inhibitor of Eg5. This phase 1 and dose-finding study aimed to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), recommended dose for further studies, and preliminary efficacy in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors.
Methods
LY2523355 was given on days 1, 2, and 3 every 3 weeks at one of three dose levels: 2, 4, and 5 mg/m2/day. Toxicity was assessed according to NCI-CTCAE version 4.0, and tumor response according to RECIST version 1.1. granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) was used only for grade 4 neutropenia or grade 3 febrile neutropenia.
Results
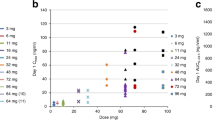
Twelve patients were treated at doses of 2 (n = 3), 4 (n = 3), and 5 (n = 6) mg/m2/day. Most frequent treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia and leukopenia (100 %). Grade 4 neutropenia was observed in 83 %, but all recovered to above 500 neutrophils/μl within 7 days. All patients at 4 and 5 mg/m2/day required G-CSF support. No dose-limiting toxicities were reported up to 5 mg/m2/day. In PK analysis, LY2523355 exposure increased in a dose-dependent manner. The PK parameters for LY2523355 were similar to those observed in Western populations. No objective tumor responses were observed.
Conclusions
The recommended dose of LY2523355 with therapeutic G-CSF use for further studies was determined to be 5 mg/m2/day in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blangy A, Lane HA, d’Hérin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA (2005) Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell 83:1159–1169
Sakowicz R, Finer JT, Beraud C, Crompton A, Lewis E, Fritsch A, Lee Y, Mak J, Moody R, Turincio R, Chabala JC, Gonzales P, Roth S, Weitman S, Wood KW (2004) Antitumor activity of a kinesin inhibitor. Cancer Res 64:3276–3280
Marcus AI, Peters U, Thomas SL, Garrett S, Zelnak A, Kapoor TM, Giannakakou P (2005) Mitotic kinesin inhibitors induce mitotic arrest and cell death in Taxol-resistant and -sensitive cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280:11569–11577
Wiltshire C, Singh BL, Stockley J, Fleming J, Doyle B, Barnetson R, Robson CN, Kozielski F, Leung HY (2010) Docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells remain sensitive to S-trityl-l-cysteine–Mediated Eg5 inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther 9:1730–1739
Hedge P, Cogswell J, Carrick K, Jackson JR, Wood KW, Eng WK, Brawner M, Huang PS, Bergsma D (2003) Differential gene expression analysis of kinesin spindle protein in human solid tumors. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:abst 535
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Shi Y, Schober WD, Wang RY, Konopleva M, Koller E, Dean NM, Andreeff M (2006) Regulation and targeting of Eg5, a mitotic motor protein in blast crisis CML: overcoming imatinib resistance. Cell Cycle 5:2223–2229
Saijo T, Ishii G, Ochiai A, Yoh K, Goto K, Nagai K, Kato H, Nishiwaki Y, Saijo N (2006) Eg5 expression is closely correlated with the response of advanced non-small cell lung cancer to antimitotic agents combined with platinum chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 54:217–225
Ye XS, Fan L, Van Horn R, Yin T, Nakai R, Ohta Y, Credille K, Donoho G, Akinaga S, Murakata C, Perkins E, Ocheltree S, Yamashita Y, Blanchard K, Westin E (2009) A novel Eg5 inhibitor that causes mitotic arrest leading to rapid cancer cell death shows broad-spectrum antitumor activity in preclinical xenograft tumor models. In: Proceedings of the 2009 AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics; 2009 Nov 15–19; Boston, MA: AACR; Mol Cancer Ther 8(12 Suppl 1): Abstract nr A62
Verschraegen C, Cohen RB, Olszanski AJ, Shaheen M, Nishida Y, Bauman J, Li L, Brandt JT, Nasir A, Hynes SM, Leohr JK, McGlothlin A, Westin EH (2011) A phase 1 study of LY2523355, an Eg5 inhibitor, administered on Days 1, 2, and 3 with or without pegfilgrastim in patients with advanced malignancy (NCT01214642). In: Proceedings of the 2011 AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics; 2011 Nov 12–16; San Francisco, California. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Mol Cancer Ther 10(11 Suppl): Abstract nr A86
Shih KC, Infante JR, Papadopoulos KP, Bendell JC, Tolcher AW, Burris HA, Beeram M, Jackson L, Arcos R, Westin EH, Farrington D, McGlothlin A, Hynes S, Leohr J, Brandt JT, Nasir A, Patnaik A (2011) A phase I dose-escalation study of LY2523355, an Eg5 inhibitor, administered either on days 1, 5, and 9; days 1 and 8; or days 1 and 5 with pegfilgrastim (peg) every 21 days (NCT01214642). J Clin Oncol 29:(suppl; abstr 2600)
Infante JR, Kurzrock R, Spratlin J, Burris HA, Eckhardt SG, Li J, Wu K, Skolnik JM, Hylander-Gans L, Osmukhina A, Huszar D, Herbst RS (2012) A Phase I study to assess the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of AZD4877, an intravenous Eg5 inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:165–172
Kantarjian HM, Padmanabhan S, Stock W, Tallman MS, Curt GA, Li J, Osmukhina A, Wu K, Huszar D, Borthukar G, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Kadia T, Sankhala K, Odenike O, Altman JK, Minden M (2012) Phase I/II multicenter study to assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AZD4877 in patients with refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Invest New Drugs 30:1107–1115
Shah JJ, Zonder J, Cohen A, Orlowski RZ, Alexanian R, Thomas SK, Weber D, Kaufman JL, Harvey RD, Walker D, Litwiler K, Karan S, Hilder B, Ptaszynski AM, Lonial S (2011) ARRY-520 shows Durable responses in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in a phase 1 dose-escalation study. Blood 118:2011 (ASH Annual Meeting; abstract 1860)
Khoury HJ, Garcia-Manero G, Borthakur G, Kadia T, Foudray MC, Arellano M, Langston A, Bethelmie-Bryan B, Rush S, Litwiler K, Karan S, Simmons H, Marcus AI, Ptaszynski M, Kantarjian H (2012) A phase 1 dose-escalation study of ARRY-520, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, in patients with advanced myeloid leukemias. Cancer 118:3556–3564
4SC (2012) Press release: 4SC reports positive data from clinical Phase I trial with 4SC-205 in cancer patients and initiates study amendment. http://www.4sc.de/news-media/corporate-news/2012. Accessed 12 Feb 2014
Burris HA 3rd, Jones SF, Williams DD, Kathman SJ, Hodge JP, Pandite L, Ho PT, Boerner SA, Lorusso P (2011) A phase I study of ispinesib, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, administered weekly for three consecutive weeks of a 28-day cycle in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 29:467–472
Gomez HL, Philco M, Pimentel P, Kiyan M, Monsalvo ML, Conlan MG, Saikali KG, Chen MM, Seroogy JJ, Wolff AA, Escandon RD (2012) Phase I dose-escalation and pharmacokinetic study of ispinesib, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, administered on days 1 and 15 of a 28-day schedule in patients with no prior treatment for advanced breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 23:335–341
Souid AK, Dubowy RL, Ingle AM, Conlan MG, Sun J, Blaney SM, Adamson PC (2010) A pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of ispinesib: a Children’s Oncology Group phase I consortium study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55:1323–1328
Blagden SP, Molife LR, Seebaran A, Payne M, Reid AH, Protheroe AS, Vasist LS, Williams DD, Bowen C, Kathman SJ, Hodge JP, Dar MM, de Bono JS, Middleton MR (2008) A phase I trial of ispinesib, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, with docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 98:894–899
Calvo E, Chu Q, Til E, Rowinsky E, Patnaik A, Takimoto C, Kathman S, Williams D, Bowen C, Hodge J, Dar M, Tolcher A (2005) Phase I Study Of Ispinesib In Combination With Capecitabine in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. AACR-NCI-EORTC, November 2005
Esaki T, Seto T, Ariyama H, Arita S, Fujimoto C, Tsukasa K, Kometani T, Nosaki K, Hirai F, Yagawa K (2011) Phase I study to assess the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of AZD4877 in Japanese patients with solid tumors. Arch Drug Inf 4:23–31
Gerecitano JF, Stephenson JJ, Lewis NL, Osmukhina A, Li J, Wu K, You Z, Huszar D, Skolnik JM, Schwartz GK (2013) A Phase I trial of the kinesin spindle protein (Eg5) inhibitor AZD4877 in patients with solid and lymphoid malignancies. Invest New Drugs 31:355–362
Shah JJ, Feng L, Thomas SK, Weber DM, Wang M, Hilder B, Alexanian R, Orlowski RZ (2013) Phase 1 study of the novel kinesin spindle protein inhibitor ARRY-520 (Filanesib) + Carfilzomib (Car) in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Annual Meeting of ASH: abstract 1982
Chari A, Htut M, Zonder J, Fay JW, Jakubowiak AJ, Harrison B, Lau K, Hilder B, Ptaszynski A, Rush SA, Kaufman JL, Burt SM (2013) A phase 1 study of ARRY-520 (Filanesib) with bortezomib (BTZ) and dexamethasone (dex) in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Annual Meeting of ASH: abstract 1938
Holen KD, Belani CP, Wilding G, Ramalingam S, Volkman JL, Ramanathan RK, Vasist LS, Bowen CJ, Hodge JP, Dar MM, Ho PT (2011) A first in human study of SB-743921, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, to determine pharmacokinetics, biologic effects and establish a recommended phase II dose. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:447–454
Tabernero J, Shapiro GI, Lorusso PM, Cervantes A, Schwartz GK, Weiss GJ, Paz-Ares L, Cho DC, Infante JR, Alsina M, Gounder MM, Falzone R, Harrop J, White AC, Toudjarska I, Bumcrot D, Meyers RE, Hinkle G, Svrzikapa N, Hutabarat RM, Clausen VA, Cehelsky J, Nochur SV, Gamba-Vitalo C, Vaishnaw AK, Sah DW, Gollob JA, Burris HA 3rd (2013) First-in-humans trial of an RNA interference therapeutic targeting VEGF and KSP in cancer patients with liver involvement. Cancer Discov 3:406–417
Holen K, DiPaola R, Liu G, Tan AR, Wilding G, Hsu K, Agrawal N, Chen C, Xue L, Rosenberg E, Stein M (2012) A phase I trial of MK-0731, a kinesin spindle protein (KSP) inhibitor, in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 30:1088–1095
Rosen L, Chen L, Iyengar T, Goldman J, Lahr S, Savage R, Wang Y, Kazakin J, Chan TCK, Schwartz B, Abbadessa G, Von Hoff D (2011) First in human study with ARQ 621, a novel inhibitor of Eg5: final results. Annual Meeting of ASCO: abstract 3076
Hollebecque A, Deutsch E, Massard C, Gomez-Roca C, Bahleda R, Ribrag V, Bourgier C, Lazar V, Lacroix L, Gazzah A, Varga A, de Baere T, Beier F, Kroesser S, Trang K, Zenke FT, Klevesath M, Soria JC (2013) A phase I, dose-escalation study of the Eg5-inhibitor EMD 534085 in patients with advanced solid tumors or lymphoma. Invest New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-013-0026-9
Huang HC, Shi J, Orth JD, Mitchison TJ (2009) Evidence that mitotic exit is a better cancer therapeutic target than spindle assembly. Cancer Cell 16:347–358
Komlodi-Pasztor E, Sackett D, Wilkerson J, Fojo T (2011) Mitosis is not a key target of microtubule agents in patient tumors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:244–250
Komlodi-Pasztor E, Sackett DL, Fojo AT (2012) Inhibitors targeting mitosis: tales of how great drugs against a promising target were brought down by a flawed rationale. Clin Cancer Res 18:51–63
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients, their families and caregivers, and all personnel who contributed to patient care and data collection. This study was sponsored by Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakui, H., Yamamoto, N., Kitazono, S. et al. A phase 1 and dose-finding study of LY2523355 (litronesib), an Eg5 inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74, 15–23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2467-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2467-z