Abstract
Purpose
Paris Saponin II (PSII) is an active component of Rhizoma Paridis—an essential ingredient in traditional Chinese herbal medicines. PSII can induce cytotoxic effects in cancer cells and inhibit ovarian cancer growth. Since pathological angiogenesis (henceforth, angiogenesis) is often associated with gynecological cancers, here, we investigated whether PSII renders effects on angiogenesis and examined possible molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of PSII.
Methods
The effects of PSII on the biofunctions of endothelial cells (EC), the crucial components of blood vessels, were examined by standardized angiogenesis in vitro and ex vivo assays, Western blot analysis, ELISA, and kinase assay. Angiogenesis in a xenograft mouse model of ovarian cancer was evaluated by color Doppler ultrasound and immunohistochemistry.
Results
PSII exerted marked inhibitory effect on the growth of VEGF-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a dose–time-dependent manner, inhibited cell’s motility, and interfered with tubulogenesis. PSII also blocked microvessel outgrowth in a rat aortic ring assay and compromised angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma using either SKOV3 or HOC-7 cell lines. VEGF levels in PSII-treated EC and tumor cells were reduced. In EC, PSII blocked the activation of VEGFR2 in dose-dependent manner leading to the reduction of VEGF-induced phosphorylation on several intracellular pro-angiogenic kinase, including the extracellular signal-related kinase, Src family kinase, focal adhesion kinase, and AKT kinase.
Conclusions
The results provided the first insight into the anti-angiogenesis properties of Saponin family in solid tumors and suggested a promising therapeutic potential of PSII in the ovarian cancer treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (2006) Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med 57:1–18
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–286
Gomez-Raposo C, Mendiola M, Barriuso J, Casado E, Hardisson D, Redondo A (2009) Angiogenesis and ovarian cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 11:564–571
Yap TA, Carden CP, Kaye SB (2009) Beyond chemotherapy: targeted therapies in ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:167–181
Schmitt J, Matei D (2012) Targeting angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 38:272–283
Albini A, Indraccolo S, Noonan DM, Pfeffer U (2010) Functional genomics of endothelial cells treated with anti-angiogenic or angiopreventive drugs. Clin Exp Metastasis 27:419–439
Nor JE, Christensen J, Mooney DJ, Polverini PJ (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis is associated with enhanced endothelial cell survival and induction of Bcl-2 expression. Am J Pathol 154:375–384
Kaneko T, Zhang Z, Mantellini MG, Karl E, Zeitlin B, Verhaegen M, Soengas MS, Lingen M, Strieter RM, Nunez G, Nor JE (2007) Bcl-2 orchestrates a cross-talk between endothelial and tumor cells that promotes tumor growth. Cancer Res 67:9685–9693
Nor JE, Christensen J, Liu J, Peters M, Mooney DJ, Strieter RM, Polverini PJ (2001) Up-Regulation of Bcl-2 in microvascular endothelial cells enhances intratumoral angiogenesis and accelerates tumor growth. Cancer Res 61:2183–2188
Karl E, Warner K, Zeitlin B, Kaneko T, Wurtzel L, Jin T, Chang J, Wang S, Wang CY, Strieter RM, Nunez G, Polverini PJ, Nor JE (2005) Bcl-2 acts in a proangiogenic signaling pathway through nuclear factor-kappaB and CXC chemokines. Cancer Res 65:5063–5069
Cosgrove D (2003) Angiogenesis imaging–ultrasound. Br J Radiol 76(1):S43–S49
Howard-Claudio C (2005) MRI methods for the detection of angiogenesis. Appl Radiol 34:9–24
Man S, Gao W, Zhang Y, Jin X, Ma C, Huang X, Li Q (2009) Characterization of steroidal saponins in saponin extract from Paris polyphylla by liquid chromatography tandem multi-stage mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:495–505
Liang Y, Liu Z, Gao W, Man S (2012) Determination of nine steroidal saponins in Paris polyphylla from different areas of Guizhou province by HPLC. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37:2309–2312
Man S, Gao W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhao W, Huang L, Liu C (2010) Qualitative and quantitative determination of major saponins in Paris and trillium by HPLC-ELSD and HPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 878:2943–2948
Xiao X, Bai P, Bui NTM, Xiao J, Liu S, Yang G, Hu L, Chen X, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang H (2009) The antitumoral effect of Paris Saponin I associated with the induction of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 8:1179–1188
Siu FM, Ma DL, Cheung YW, Lok CN, Yan K, Yang Z, Yang M, Xu S, Ko BC, He QY, Che CM (2008) Proteomic and transcriptomic study on the action of a cytotoxic saponin (Polyphyllin D): induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathways. Proteomics 8:3105–3117
Yang YH, Dai LJ, He KH, Wei JR, Zhao TZ, Su B, Wang MH (2012) Relation between soil nutrient of artificially cultivated area and rhizome quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Zhong Yao Cai 35:1557–1561
Chiang HC, Wang JJ, Wu RT (1992) Immunomodulating effects of the hydrolysis products of formosanin C and beta-ecdysone from Paris formosana Hayata. Anticancer Res 12:1475–1478
Xiao X, Zou J, Bui-Nguyen TM, Bai P, Gao L, Liu J, Liu S, Xiao J, Chen X, Zhang X, Wang H (2012) Paris saponin II of Rhizoma Paridis: a novel inducer of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Biosci Trends 6:201–211
Finley SD, Popel AS (2013) Effect of tumor microenvironment on tumor VEGF during anti-VEGF treatment: systems biology predictions. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:802–811
Sun ZG, Zhang L, Li LJ, Tian JK (2007) Studies on the extraction process of total saponins from Paris polyphylla Smith. Zhong Yao Cai 30:726–729
Nguyen TM, Subramanian IV, Kelekar A, Ramakrishnan S (2007) Kringle 5 of human plasminogen, an angiogenesis inhibitor, induces both autophagy and apoptotic death in endothelial cells. Blood 109:4793–4802
Nicosia RF, Ottinetti A (1990) Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest 63:115–122
Watanabe M, Fujioka-Kaneko Y, Kobayashi H, Kiniwa M, Kuwano M, Basaki Y (2005) Involvement of integrin-linked kinase in capillary/tube-like network formation of human vascular endothelial cells. Biol Proced Online 7:41–47
Bentink S, Haibe-Kains B, Risch T, Fan JB, Hirsch MS, Holton K, Rubio R, April C, Chen J, Wickham-Garcia E, Liu J, Culhane A, Drapkin R, Quackenbush J, Matulonis UA (2012) Angiogenic mRNA and microRNA gene expression signature predicts a novel subtype of serous ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e30269
Coultas L, Chawengsaksophak K, Rossant J (2005) Endothelial cells and VEGF in vascular development. Nature 438:937–945
Dias S, Hattori K, Heissig B, Zhu Z, Wu Y, Witte L, Hicklin DJ, Tateno M, Bohlen P, Moore MA, Rafii S (2001) Inhibition of both paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathways is essential to induce long-term remission of xenotransplanted human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10857–10862
Sakai Y, Goodison S, Cao W, Urquidi V, Namiki K, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C, Rosser CJ (2009) VEGF induces expression of Bcl-2 and multiple signaling factors in microvascular endothelial cells in a prostate cancer model. World J Urol 27:659–666
Markowska A, Lubin J, Madry R, Markowska J (2013) Development of antiangiogenic therapies for ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 34:303–306
Sia D, Alsinet C, Newell P, Villanueva A (2013) VEGF signaling in cancer treatment. Curr Pharm Des [Epub ahead of print]
Wei J (1998) Determination of steroidal saponins in Rhizoma Paridis by RP-HPLC. Yao Xue Xue Bao 33:465–468
Huang Y, Cui LJ, Liu WN, Wang Q (2006) Quantitative analysis of steroidal saponins in Chinese material medica Rhizoma Paridis by HPLC-ELSD. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 31:1230–1233
Li ZH, Wan JY, Wang GQ, Zhao FG, Wen JH (2013) Identification of compounds from Paris polyphylla (ChongLou) active against Dactylogyrus intermedius. Parasitology 140:952–958
Wen F, Yin H, Chen C, Liu X, Xue D, Chen T, He J, Zhang H (2012) Chemical characteristics of saponins from Paris fargesii var. brevipetala and cytotoxic activity of its main ingredient, paris saponin H. Fitoterapia 83:627–635
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Wyllie AH (1980) Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 284:555–556
Namiki A, Brogi E, Kearney M, Kim EA, Wu T, Couffinhal T, Varticovski L, Isner JM (1995) Hypoxia induces vascular endothelial growth factor in cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 270:31189–31195
Bertin S, Mohsen-Kanson T, Baque P, Gavelli A, Momier D, Anjuere F, Carle GF, Pierrefite-Carle V (2010) Tumor microenvironment modifications induced by soluble VEGF receptor expression in a rat liver metastasis model. Cancer Lett 298:264–272
Shuli M, Wenyuan G, Yanjun Z, Chaoyi M, Liu Y, Yiwen L (2011) Paridis saponins inhibiting carcinoma growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Arch Pharm Res 34:43–50
Xiao X, Yang M, Bai P, Chen XL, Liu SL, Zou J, Wang H (2012) Observation on anticancer function of PS II isolated from Rhizoma Paridis. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 43:651–656
Cosgrove D, Lassau N (2009) Assessment of tumour angiogenesis using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. J Radiol 90:156–164
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fund of National Nature Science Foundations Grant No. 81001159/81202387/81101991, Sichuan Province Science and Technology plan Project No. 2013JY0013. We would like to thank Dr. Meifang Xiao and Dr. Hong Zou for providing us with PSI and PSII compounds. We thank Diane Hackett and Maude E. Veech for technical support. We also thank Dr. Tri Bui-Nguyen for his review and insightful comments on this project.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xue Xiao and Mei Yang have contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
280_2014_2408_MOESM1_ESM.tif
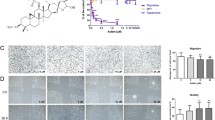
Supplementary Fig.S1 PSII treatment induced apoptosis in both high-grade serous OC SKOV3 cells and low-grade serous OC HOC-7 cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner (P<0.05). TUNEL data presented as the percentage of apoptotic cells (green fluorescence) per the total number of treated cells (blue fluorescence). Ten random fields were selected per slide. Representative figures of PSII-treated cells labeled for TUNEL and counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) are provided. Columns, mean; bars, SE. (TIFF 13762 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Yang, M., Xiao, J. et al. Paris Saponin II suppresses the growth of human ovarian cancer xenografts via modulating VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and tumor cell migration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 807–818 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2408-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2408-x