Abstract
Purpose
The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) has displayed significant efficiency against pancreatic cancer cells. However, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we tested if ceramide production was involved in the bortezomib’s effect.
Methods
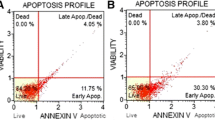
Two transformed pancreatic cancer cell lines (PANC-1 and Mia) and the primary pancreatic cancer cells were used. Cell death was analyzed by MTT viability assay and trypan blue staining. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by Histone DNA-ELISA assay and Annexin V FACS. Western blots were used to test signal protein changes. The cellular ceramide level after bortezomib treatment was also determined.
Results
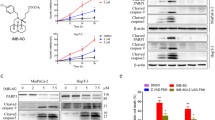
In cultured pancreatic cancer cells, bortezomib increased cellular ceramide production to promote cell apoptosis. The ceramide de novo synthase inhibitor fumonisin B1 (F-B1) suppressed bortezomib-induced ceramide production and apoptosis, while exogenously added C6-ceramide facilitated bortezomib-induced pancreatic cancer cell death. Meanwhile, 1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol (PDMP), the inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthetase as well as the sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitors (SKI-II and SKI-IV), facilitated bortezomib-induced ceramide production and subsequent cell apoptosis. Further, bortezomib-induced pro-apoptotic c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation was also associated with ceramide production. JNK activation by bortezomib was suppressed by F-B1, but was enhanced by SKI-II and PDMP in pancreatic cancer cells. Finally, C6-ceramide, SKI-II, and PDMP dramatically enhanced bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultured pancreatic cancer cells.
Conclusions
We found that bortezomib-induced apoptosis was associated with ceramide production in primary and transformed pancreatic cancer cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- SphK1:
-
Sphingosine kinase 1
- F-B1:
-
Fumonisin B1
- PDMP:
-
1-Phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol
References
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M (2011) Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 378(9791):607–620. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0
Hidalgo M (2010) Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 362(17):1605–1617. doi:362/17/1605
Colucci G, Labianca R, Di Costanzo F, Gebbia V, Carteni G, Massidda B, Dapretto E, Manzione L, Piazza E, Sannicolo M, Ciaparrone M, Cavanna L, Giuliani F, Maiello E, Testa A, Pederzoli P, Falconi M, Gallo C, Di Maio M, Perrone F (2010) Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin compared with single-agent gemcitabine as first-line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: the GIP-1 study. J Clin Oncol 28(10):1645–1651. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4433
Jenks S (2011) AACR highlights: promise for treating pancreatic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(10):786–787. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr183
Costello E, Neoptolemos JP (2011) Pancreatic cancer in 2010: new insights for early intervention and detection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(2):71–73
Wong HH, Lemoine NR (2009) Pancreatic cancer: molecular pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(7):412–422. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2009.89
Boccadoro M, Morgan G, Cavenagh J (2005) Preclinical evaluation of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell Int 5(1):18. doi:1475-2867-5-18
Montagut C, Rovira A, Mellado B, Gascon P, Ross JS, Albanell J (2005) Preclinical and clinical development of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cancer treatment. Drugs Today (Barc) 41(5):299–315. doi:893706
Richardson PG, Mitsiades C, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2006) Bortezomib: proteasome inhibition as an effective anticancer therapy. Annu Rev Med 57:33–47. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.57.042905.122625
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Dunner K Jr, Boise LH, Chiao PJ, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL, McConkey DJ (2005) Bortezomib inhibits PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase and induces apoptosis via ER stress in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 65(24):11510–11519. doi:65/24/11510
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Pino MS, Highshaw RA, Dunner K Jr, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL, McConkey DJ (2005) Bortezomib sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res 65(24):11658–11666. doi:65/24/11658
Schroder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res 569(1–2):29–63. doi:S0027-5107(04)00371-9
Podar K, Gouill SL, Zhang J, Opferman JT, Zorn E, Tai YT, Hideshima T, Amiot M, Chauhan D, Harousseau JL, Anderson KC (2008) A pivotal role for Mcl-1 in Bortezomib-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 27(6):721–731. doi:1210679
Chen KF, Yeh PY, Yeh KH, Lu YS, Huang SY, Cheng AL (2008) Down-regulation of phospho-Akt is a major molecular determinant of bortezomib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 68(16):6698–6707. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0257
Lauricella M, Emanuele S, D’Anneo A, Calvaruso G, Vassallo B, Carlisi D, Portanova P, Vento R, Tesoriere G (2006) JNK and AP-1 mediate apoptosis induced by bortezomib in HepG2 cells via FasL/caspase-8 and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Apoptosis 11(4):607–625. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-4689-y
Dimanche-Boitrel MT, Rebillard A, Gulbins E (2011) Ceramide in chemotherapy of tumors. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 6(3):284–293. doi:10.2174/157489211796957838
Wu C-H, Cao C, Kim JH, Hsu C-H, Wanebo HJ, Bowen WD, Xu J, Marshall J (2012) Trojan-horse nanotube on-command intracellular drug delivery. Nano Lett 12(11):5475–5480. doi:10.1021/nl301865c
Yao C, Wu S, Li D, Ding H, Wang Z, Yang Y, Yan S, Gu Z (2012) Co-administration phenoxodiol with doxorubicin synergistically inhibit the activity of sphingosine kinase-1 (SphK1), a potential oncogene of osteosarcoma, to suppress osteosarcoma cell growth both in vivo and in vitro. Mol Oncol 6(4):392–404. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2012.04.002
Merrill AH Jr, van Echten G, Wang E, Sandhoff K (1993) Fumonisin B1 inhibits sphingosine (sphinganine) N-acyltransferase and de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in cultured neurons in situ. J Biol Chem 268(36):27299–27306
Yao C, Wei JJ, Wang ZY, Ding HM, Li D, Yan SC, Yang YJ, Gu ZP (2012) Perifosine induces cell apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells: new implication for osteosarcoma therapy? Cell Biochem Biophys. doi:10.1007/s12013-012-9423-5
Shida D, Takabe K, Kapitonov D, Milstien S, Spiegel S (2008) Targeting SphK1 as a new strategy against cancer. Curr Drug Targets 9(8):662–673
Yu C, Rahmani M, Dent P, Grant S (2004) The hierarchical relationship between MAPK signaling and ROS generation in human leukemia cells undergoing apoptosis in response to the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib. Exp Cell Res 295(2):555–566. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.02.001
Kurinna SM, Tsao CC, Nica AF, Jiffar T, Ruvolo PP (2004) Ceramide promotes apoptosis in lung cancer-derived A549 cells by a mechanism involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Cancer Res 64(21):7852–7856. doi:64/21/7852
Verheij M, Bose R, Lin XH, Yao B, Jarvis WD, Grant S, Birrer MJ, Szabo E, Zon LI, Kyriakis JM, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z, Kolesnick RN (1996) Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature 380(6569):75–79. doi:10.1038/380075a0
Adams J (2002) Preclinical and clinical evaluation of proteasome inhibitor PS-341 for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6(4):493–500. doi:S1367593102003435
Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Singhal S, Jagannath S, Irwin D, Rajkumar SV, Srkalovic G, Alsina M, Alexanian R, Siegel D, Orlowski RZ, Kuter D, Limentani SA, Lee S, Hideshima T, Esseltine DL, Kauffman M, Adams J, Schenkein DP, Anderson KC (2003) A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed, refractory myeloma. N Engl J Med 348(26):2609–2617. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030288
Bold RJ, Virudachalam S, McConkey DJ (2001) Chemosensitization of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of the 26S proteasome. J Surg Res 100(1):11–17. doi:10.1006/jsre 2001.6194
Shah SA, Potter MW, McDade TP, Ricciardi R, Perugini RA, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Callery MP (2001) 26S proteasome inhibition induces apoptosis and limits growth of human pancreatic cancer. J Cell Biochem 82(1):110–122. doi:10.1002/jcb.1150
Nawrocki ST, Sweeney-Gotsch B, Takamori R, McConkey DJ (2004) The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib enhances the activity of docetaxel in orthotopic human pancreatic tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3(1):59–70
Mullen TD, Obeid LM (2012) Ceramide and apoptosis: exploring the enigmatic connections between sphingolipid metabolism and programmed cell death. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 12(4):340–363
Tafesse FG, Ternes P, Holthuis JC (2006) The multigenic sphingomyelin synthase family. J Biol Chem 281(40):29421–29425. doi:R600021200
Andrieu-Abadie N, Gouaze V, Salvayre R, Levade T (2001) Ceramide in apoptosis signaling: relationship with oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 31(6):717–728. doi:S0891584901006554
Hannun YA, Obeid LM (2002) The ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J Biol Chem 277(29):25847–25850. doi:10.1074/jbc.R200008200
Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K, Ichijo H (1998) ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell 2(3):389–395
Tobiume K, Matsuzawa A, Takahashi T, Nishitoh H, Morita K, Takeda K, Minowa O, Miyazono K, Noda T, Ichijo H (2001) ASK1 is required for sustained activations of JNK/p38 MAP kinases and apoptosis. EMBO Rep 2(3):222–228
Morad SA, Cabot MC (2013) Ceramide-orchestrated signalling in cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer 13(1):51–65. doi:10.1038/nrc3398
Chen MB, Zhang Y, Wei MX, Shen W, Wu XY, Yao C, Lu PH (2013) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) mediates plumbagin-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition in cultured human colon cancer cells. Cell Signal. doi:S0898-6568(13)00157-5
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lei Gong, Bo Yang and Ming Xu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, L., Yang, B., Xu, M. et al. Bortezomib-induced apoptosis in cultured pancreatic cancer cells is associated with ceramide production. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 69–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2318-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2318-3