Abstract
Purpose
Combination of two differentiation agents such as phenylbutyrate (PB) and 13-cis-retinoic acid (CRA) has been shown to have an additive inhibitory effect on tumor growth in preclinical studies. In this report we explored the hypotheses that these “cytostatic” agents may have a greater antitumor activity in combination with “cytotoxic” compounds and their biological effect may be sequence-dependent.
Methods
The antitumor activity of combination of PB and CRA with paclitaxel (TX ) and doxorubicin (DOXO) on human prostate and colon carcinoma cell lines was assessed both in vitro and in vivo. The effect on cell cycle, apoptotic rate, cycline expression and induction of p21 expression was also determined.
Results
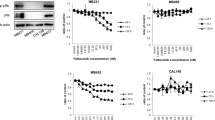
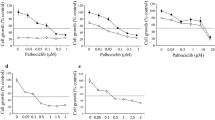
Following treatment of tumor cells with PB + CRA + TX or DOXO, inhibition of tumor cell growth was greatly enhanced as compared to PB + CRA, TX or DOXO alone, with >90% growth inhibition. However, when the cells were pretreated with PB + CRA followed by TX or DOXO, the enhanced inhibition was abolished suggesting a protective effect to this sequence. Interestingly treatment with PB + CRA restored sensitivity to DOXO in PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line. PB + CRA induced p21 expression and cell-cycle arrest in G1 phase, while TX and DOXO induced G2/M arrest. p21 and p53-deficient colon carcinoma cell lines were more sensitive to the effect of PB + CRA and TX as single agents and in combination, as compared to the wild type cells. When p21-deficient cells were pretreated with PB + CRA followed by TX the protective effect was still observed. Treatment of tumor cells with combination of these drugs induced cell cycle delay at multiple mitotic checkpoints before undergoing apoptosis. Tumor growth was significantly inhibited and delayed in animals treated with either TX or concomitantly with TX and PB + CRA as compared to control. Animals treated with all three agents demonstrated further growth inhibition or delay than the TX alone or PB + CRA arm.
Conclusions
These results suggest a rational therapeutic approach for combination of differentiation-inducing agents with cytotoxic drugs given concomitantly, but not sequentially.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altucci L, Gronemeyer H (2001) The promise of retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:181–193
Bacoyiannis C, Dimopoulos MA, Kalofonos HP, Nicolaides C, Aravantinos G, Bafaloukos D, Samelis G, Onyenadum A, Kiamouris C, Skarlos D et al (2002) Vinblastine and interferon-gamma combination with and without 13-cis retinoic acid for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Results of two phase II clinical trials. Oncology 63:130–138
Bible KC, Kaufmann SH (1997) Cytotoxic synergy between flavopiridol (NSC 649890, L86–8275) and various antineoplastic agents: the importance of sequence of administration. Cancer Res 57:3375–3380
Bug G, Ritter M, Wassmann B, Schoch C, Heinzel T, Schwarz K, Romanski A, Kramer OH, Kampfmann M, Hoelzer D et al (2005) Clinical trial of valproic acid and all-trans retinoic acid in patients with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 104:2717–2725
Carducci MA, Nelson JB, Chan-Tack KM, Ayyagari SR, Sweatt WH, Campbell PA, Nelson WG, Simons JW (1996) Phenylbutyrate induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer and is more potent than phenylacetate. Clin Cancer Res 2:379–387
Carducci MA, Gilbert J, Bowling MK, Noe D, Eisenberger MA, Sinibaldi V, Zabelina Y, Chen TL, Grochow LB, Donehower RC (2001) A Phase I clinical and pharmacological evaluation of sodium phenylbutyrate on an 120-h infusion schedule. Clin Cancer Res 7:3047–3055
Jung CP, Motwani MV, Schwartz GK (2001) Flavopiridol increases sensitization to gemcitabine in human gastrointestinal cancer cell lines and correlates with down-regulation of ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit. Clin Cancer Res 7:2527–2536
Kalemkerian GP, Ou X (1999) Activity of fenretinide plus chemotherapeutic agents in small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43:145–150
Li CJ, Li YZ, Pinto AV, Pardee AB (1999) Potent inhibition of tumor survival in vivo by beta-lapachone plus taxol: combining drugs imposes different artificial checkpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(23):13369–13374
Marchion DC, Bicaku E, Daud AI, Richon V, Sullivan DM, Munster PN (2004) Sequence-specific potentiation of topoisomerase II inhibitors by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. J Cell Biochem 92:223–237
Moffatt KA, Johannes WU, Hedlund TE, Miller GJ (2001) Growth inhibitory effects of 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) are mediated by increased levels of p21 in the prostatic carcinoma cell line ALVA-31. Cancer Res 61:7122–7129
Mork CN, Faller DV, Spanjaard RA (2005) A mechanistic approach to anticancer therapy: targeting the cell cycle with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 11:1091–1104
Motwani M, Jung C, Sirotnak FM, She Y, Shah MA, Gonen M, Schwartz GK (2001) Augmentation of apoptosis and tumor regression by flavopiridol in the presence of CPT-11 in Hct116 colon cancer monolayers and xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 7:4209–4219
Motwani M, Rizzo C, Sirotnak F, She Y, Schwartz GK (2003) Flavopiridol enhances the effect of docetaxel in vitro and in vivo in human gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2:549–555
Pettersson F, Colston KW, Dalgleish AG (2001) Retinoic acid enhances the cytotoxic effects of gemcitabine and cisplatin in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Pancreas 23:273–279
Phuphanich S, Baker SD, Grossman SA, Carson KA, Gilbert MR, Fisher JD, Carducci MA (2005) Oral sodium phenylbutyrate in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas: a dose escalation and pharmacologic study. Neuro-oncol 7:177–182
Pili R, Kruszewski MP, Hager BW, Lantz J, Carducci MA (2001) Combination of phenylbutyrate and 13-cis retinoic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 61:1477–1485
Pinedo HM, Giaccone G (1997) Chemotherapy. Lancet 349(Suppl 2):SII7–SII9
Qian DZ, Wang X, Kachhap SK, Kato Y, Wei Y, Zhang L, Atadja P, Pili R (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 inhibits angiogenesis and has a greater antitumor effect in combination with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res 64:6626–6634
Raffoux E, Chaibi P, Dombret H, Degos L (2005) Valproic acid and all-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 90:986–988
Rudek MA, Zhao M, He P, Hartke C, Gilbert J, Gore SD, Carducci MA, Baker SD (2005) Pharmacokinetics of 5-azacitidine administered with phenylbutyrate in patients with refractory solid tumors or hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 23:3906–3911
Schwartz GK, Shah MA (2005) Targeting the cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 23:9408–9421
Solit DB, She Y, Lobo J, Kris MG, Scher HI, Rosen N, Sirotnak FM (2005) Pulsatile administration of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib is significantly more effective than continuous dosing for sensitizing tumors to paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 11:1983–1989
Soriano AF, Helfrich B, Chan DC, Heasley LE, Bunn PA Jr, Chou TC (1999) Synergistic effects of new chemopreventive agents and conventional cytotoxic agents against human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 59:6178–6184
Tabe Y, Konopleva M, Contractor R, Munsell M, Schober WD, Jin L, Tsutsumi-Ishii Y, Nagaoka I, Igari J, Andreeff M (2006) Up-regulation of MDR1 and induction of doxorubicin resistance by histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide (FK228) and ATRA in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood 107:1546–1554
Thalasila A, Poplin E, Shih J, Dvorzhinski D, Capanna T, Doyle-Lindrud S, Beers S, Goodin S, Rubin E, DiPaola RS (2003) A phase I trial of weekly paclitaxel, 13- cis-retinoic acid, and interferon alpha in patients with prostate cancer and other advanced malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52:119–124
Vaishampayan U, Flaherty L, Du W, Hussain M (2001) Phase II evaluation of paclitaxel, alpha-interferon, and cis-retinoic acid in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 92:519–523
van Vugt MA, Bras A, Medema RH (2005) Restarting the cell cycle when the checkpoint comes to a halt. Cancer Res 65:7037–7040
Wang XF, Qian DZ, Ren M, Kato Y, Wei Y, Zhang L, Fansler Z, Clark D, Nakanishi O, Pili R (2005) Epigenetic modulation of retinoic acid receptor beta2 by the histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 in human renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:3535–3542
Wieder R, Pavlick AC, Bryan M, Hameed M, Baredes S, Pliner L, Saunders T, Korah R (2002) Phase I/II trial of accutane as a potentiator of carboplatin and paclitaxel in squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Clin Oncol 25:447–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported in part by NIH Grants K08-CA69164, R01-CA75525, CaPCURE. Grant (M.A.C.) and DOD-DAMD17-02-1-0077 (R.P.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verheul, H.M.W., Qian, D.Z., Carducci, M.A. et al. Sequence-dependent antitumor effects of differentiation agents in combination with cell cycle-dependent cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 60, 329–339 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-006-0379-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-006-0379-2