Abstract
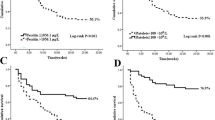
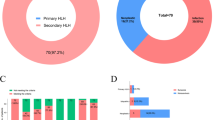
Recently, more and more attention has been paid on adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), a disease with complicated symptoms and high mortality. In order to analyze the clinical characteristics and prediction risk factors of mortality, we designed a retrospective study with 1-year follow-up and included 155 patients admitted to Tongji Hospital diagnosed as HLH. One hundred seven patients formed the training cohort for nomogram development, and 48 patients formed the validation cohort to confirm the model’s performance. All patients’ clinical characteristics, laboratory results, medical records, and prognosis were analyzed. Among all the 107 patients in the training cohort, 46 were male and 61 were female, with the median age of 49.0 (IQR 31.0–63.0). The 1-year mortality rate was 43.9% (47/107) and 45.8% (22/48) in the training and validation cohort, respectively. And further multivariate logistic regression analysis in the training cohort showed that male (odds ratio 5.534, 95% CI 1.507–20.318, p = 0.010), altered mental status (11.876, 1.882–74.947, p = 0.008), serum ferritin ≥ 31,381 μg/L (8.273, 1.855–36.883, p = 0.006), and IL-6 ≥ 18.59 pg/mL (19.446, 1.527–247.642, p = 0.022) were independent risk factor of mortality. A nomogram included the four prediction factors mentioned above was also tabled to help clinicians evaluate the probability of poor outcome. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) analysis, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA) certify the accuracy and the clinical usefulness of the nomogram. Our research reveals that male, altered mental status, serum ferritin ≥ 31,381 µg/L, and IL-6 ≥ 18.59 pg/mL are four independent predictors for poor prognosis. Doctors should pay more attention to patients with altered mental status, high serum ferritin, and IL-6 level, who have a higher risk of death.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HLH:
-
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- HPS:
-
Hemophagocytic syndrome
- MAS:
-
Macrophage activation symptoms
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- TBil:
-
Total bilirubin
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- TT:
-
Thrombin time
- sIL-2R:
-
Soluble IL-2 receptor
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- hsCRP:
-
High sensitive C-reactive protein
- PCT:
-
Procalcitonin
- SF:
-
Serum ferritin
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- ESR:
-
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- AMS:
-
Altered mental status
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
Zhang Q, Li L, Zhu L, Zhu J, Yang X, Zhou ZY, Zhu M, Xie M, Sun J, Li X, Wu Y, Wei Z, Xie W, Ye X (2018) Adult onset haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis prognosis is affected by underlying disease: analysis of a single-institution series of 174 patients. Swiss Med Wkly 148:w14641. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2018.14641
Janka GE, Lehmberg K (2013) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2013:605–611. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2013.1.605
Larroche C (2012) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: diagnosis and treatment. Joint Bone Spine 79(4):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.10.015
Song Y, Wang Z, Hao Z, Li L, Lu J, Kang H, Lu Y, You Y, Li L, Chen Q, Chen B (2019) Requirement for etoposide in the treatment of pregnancy related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a multicenter retrospective study. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1033-5
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, López-Guillermo A, Khamashta MA, Bosch X (2014) Adult haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet 383(9927):1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61048-x
Grange S, Buchonnet G, Besnier E, Artaud-Macari E, Beduneau G, Carpentier D, Dehay J, Girault C, Marchalot A, Guerrot D, Tamion F (2016) The use of ferritin to identify critically ill patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Crit Care Med 44(11):e1045–e1053. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001878
Yoon JH, Park SS, Jeon YW, Lee SE, Cho BS, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee S, Min CK, Cho SG, Lee JW (2019) Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors in adult patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis not associated with malignancy. Haematologica 104(2):269–276. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.198655
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, Janka G (2007) HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48(2):124–131. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.21039
Shah AR, Muzzafar T, Assi R, Schellingerhout D, Estrov Z, Tamamyan G, Kantarjian H, Daver N (2017) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: an under recognized entity. BBA clinical 7:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.12.002
Zhang Z, Wang J, Ji B, Greenwood T, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Kong D, Li A, Jiang Y, Guo Y, Liu X, Wang Y, Dou A, Li N, Henter J, Sun G, Zheng C (2016) Clinical presentation of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults is less typical than in children. Clinics 71(4):205–209. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2016(04)05
Hu T, Wang S, Huang L, Wang J, Shi D, Li Y, Tong T, Peng W (2019) A clinical-radiomics nomogram for the preoperative prediction of lung metastasis in colorectal cancer patients with indeterminate pulmonary nodules. Eur Radiol 29(1):439–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5539-3
Chen X, Tang Y, Mo Y, Li S, Lin D, Yang Z, Yang Z, Sun H, Qiu J, Liao Y, Xiao J, Chen X, Wu X, Wu R, Dai Z (2020) A diagnostic model for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on radiological semantic and clinical features: a multi-center study. Eur Radiol 30(9):4893–4902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06829-2
Otrock ZK, Eby CS (2015) Clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and outcomes of adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am J Hematol 90(3):220–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.23911
Brisse E, Wouters CH, Matthys P (2015) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): a heterogeneous spectrum of cytokine-driven immune disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26(3):263–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.10.001
Trottestam H, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, Webb D, Janka G, Henter JI, Histiocyte S (2011) Chemoimmunotherapy for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: long-term results of the HLH-94 treatment protocol. Blood 118(17):4577–4584. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-06-356261
Okano M, Gross TG (1996) Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome and fatal infectious mononucleosis. Am J Hematol 53(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-8652(199610)53:2%3c111::AID-AJH8%3e3.0.CO;2-2
La Rosée P, Horne A, Hines M, von Bahr GT, Machowicz R, Berliner N, Birndt S, Gil-Herrera J, Girschikofsky M, Jordan MB, Kumar A, van Laar JAM, Lachmann G, Nichols KE, Ramanan AV, Wang Y, Wang Z, Janka G, Henter J-I (2019) Recommendations for the management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Blood 133(23):2465–2477. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2018894618
Zhang L, Zhou J, Sokol L (2014) Hereditary and acquired hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cancer Control 21(4):301–312. https://doi.org/10.1177/107327481402100406
Janka G (2009) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: when the immune system runs amok. Klin Padiatr 221(5):278–285. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1237386
Parikh SA, Kapoor P, Letendre L, Kumar S, Wolanskyj AP (2014) Prognostic factors and outcomes of adults with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Mayo Clin Proc 89(4):484–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.12.012
Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C (2007) Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis 7(12):814–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(07)70290-6
Hayden A, Park S, Giustini D, Lee AY, Chen LY (2016) Hemophagocytic syndromes (HPSs) including hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in adults: a systematic scoping review. Blood Rev 30(6):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2016.05.001
Zhao Y, Lu D, Ma S, Li L, Zhu J, Zhou ZY, Yang X, Zhu L, Zhu M, Xie M, Sun J, Ye X, Xie W (2019) Risk factors of early death in adult patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-institution study of 171 Chinese patients. Hematology 24(1):606–612. https://doi.org/10.1080/16078454.2019.1660458
Riviere S, Galicier L, Coppo P, Marzac C, Aumont C, Lambotte O, Fardet L (2014) Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: a retrospective analysis of 162 patients. Am J Med 127(11):1118–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.04.034
Otrock ZK, Hock KG, Riley SB, de Witte T, Eby CS, Scott MG (2017) Elevated serum ferritin is not specific for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Ann Hematol 96(10):1667–1672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3072-0
Schulert GS, Grom AA (2015) Pathogenesis of macrophage activation syndrome and potential for cytokine- directed therapies. Annu Rev Med 66:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-061813-012806
Akashi K, Hayashi S, Gondo H, Mizuno S, Harada M, Tamura K, Yamasaki K, Shibuya T, Uike N, Okamura T et al (1994) Involvement of interferon-gamma and macrophage colony-stimulating factor in pathogenesis of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Br J Haematol 87(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb04905.x
Gupta A, Tyrrell P, Valani R, Benseler S, Weitzman S, Abdelhaleem M (2008) The role of the initial bone marrow aspirate in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 51(3):402–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.21564
Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, Bhawan S, Certain S, Mathew PA, Henter JI, Bennett M, Fischer A, de Saint BG, Kumar V (1999) Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science 286(5446):1957–1959. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5446.1957
Naymagon L, Tremblay D, Mascarenhas J (2020) Reevaluating the role of ferritin in the diagnosis of adult secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Eur J Haematol 104(4):344–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13391
Fardet L, Galicier L, Lambotte O, Marzac C, Aumont C, Chahwan D, Coppo P, Hejblum G (2014) Development and validation of the HScore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive hemophagocytic syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(9):2613–2620. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38690
Henter JI, Samuelsson-Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Elinder G, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Komp D, Ladisch S, Webb D, Janka G, Histocyte S (2002) Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood 100(7):2367–2373. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-01-0172
Ehl S, Astigarraga I, von Bahr GT, Hines M, Horne A, Ishii E, Janka G, Jordan MB, La Rosee P, Lehmberg K, Machowicz R, Nichols KE, Sieni E, Wang Z, Henter JI (2018) Recommendations for the use of etoposide-based therapy and bone marrow transplantation for the treatment of HLH: consensus statements by the HLH Steering Committee of the Histiocyte Society. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 6(5):1508–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2018.05.031
Otrock ZK, Grossman BJ, Eby CS (2018) Transfusion requirements and 30-day mortality predictors for adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int J Hematol 108(5):485–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-018-2504-5
Li F, Yang Y, Jin F, Dehoedt C, Rao J, Zhou Y, Li P, Yang G, Wang M, Zhang R, Yang Y (2015) Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of adult hemophagocytic syndrome patients: a retrospective study of increasing awareness of a disease from a single-center in China. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-015-0224-y
Nabergoj M, Marinova M, Binotto G, Brugnaro L, Zaninotto M, Plebani M, Semenzato G, Vianello F (2017) Diagnostic and prognostic value of low percentage of glycosylated ferritin in acquired hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-center study. Int J Lab Hematol 39(6):620–624. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12713
Cai G, Wang Y, Liu X, Han Y, Wang Z (2017) Central nervous system involvement in adults with haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-center study. Ann Hematol 96(8):1279–1285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3035-5
Luttrull MD, Boulter DJ, Kirsch CFE, Aulino JM, Broder JS, Chakraborty S, Choudhri AF, Ducruet AF, Kendi AT, Lee RK, Liebeskind DS, Mack W, Moritani T, Roca RP, Shah LM, Sharma A, Shih RY, Symko SC, Bykowski J (2019) ACR Appropriateness Criteria® acute mental status change, delirium, and new onset psychosis. J Am Coll Radiol 16(5):S26–S37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2019.02.024
Han JH, Wilber ST (2013) Altered mental status in older patients in the emergency department. Clin Geriatr Med 29(1):101–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2012.09.005
Xiao HY, Wang YX, Xu TD, Zhu HD, Guo SB, Wang Z, Yu XZ (2012) Evaluation and treatment of altered mental status patients in the emergency department: life in the fast lane. World J Emerg Med 3(4):270–277. https://doi.org/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2012.04.006
Acknowledgements
Authors expressed their gratitude for all persons who were involved in reporting patients and gathering data.
Funding
This work is funded by the Chinese National Thirteenth Five Years Project in Science and Technology (2017ZX10202201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M-X L and X-X G designed the study. All the authors contributed to the generation, collection, assembly, analysis of the data. M-X L and Y-H X wrote the manuscript; M-F H and Q N revised the manuscript. All the authors have read manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This retrospective chart review study was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Ethical Committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China approved this study, as retrospective design Ethical Committee abandoned the need for informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Mengxin Lu and Yanghao Xie are co-first authors; they contributed equally to the work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1108 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Xie, Y., Guan, X. et al. Clinical analysis and a novel risk predictive nomogram for 155 adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Ann Hematol 100, 2181–2193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04551-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04551-7