Abstract
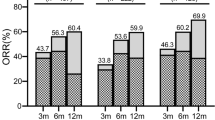
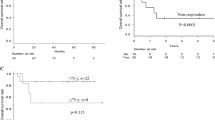
This study retrospectively analyzed the clinical outcome of 172 children with newly diagnosed severe aplastic anemia (SAA) between January 2008 and April 2018, who received rabbit antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine (CsA) as first-line treatment. The median age at diagnosis was 5 years (range, 1–14). The overall response rates were 22.7%, 45.3%, and 61% at 40 days, 3 months, and 6 months, respectively, after rabbit ATG. In multivariate analysis, mild disease severity was the only predictor of favorable response at 6 months (P = 0.006). In the present study, median follow-up period was 63 months (range, 1–135). The 5-year overall survival (OS) and failure-free survival (FFS) rates were 90.5% and 70.4%. Multivariate analysis showed that erythroid burst-forming units (BFU-E) > 2/105 bone marrow mononuclear cell (BMMNC) (P = 0.037) and time interval before IST ≤ 30 days (P = 0.017) were independent positive predictors for OS, meanwhile BFU-E > 2/105BMMNC (P = 0.029) was the only favorable prognostic factor for FFS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
07 November 2020
This article was revised because of the track changes present in the supplementary file.
Abbreviations
- IST:
-
Immunosuppressive therapy
- ATG:
-
Antithymocyte globulin
- CsA:
-
Cyclosporine
- SAA:
-
Severe aplastic anemia
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- vSAA:
-
Very severe aplastic anemia
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- FFS:
-
Failure-free survival
- BFU-E:
-
Erythroid burst-forming units
- BMMNC:
-
Bone marrow mononuclear cell
- PB:
-
Peripheral blood
- BM:
-
Bone marrow
- aAA:
-
Acquired aplastic anemia
- HSCs:
-
Hematopoietic stem cells
- HSCT:
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- ALG:
-
Antilymphocyte globulin
- AA:
-
Aplastic anemia
- ANC:
-
Absolute neutrophil count
- PLT:
-
Platelet
- ARC:
-
Absolute reticulocyte count
- CR:
-
Complete response
- HGB:
-
Hemoglobin
- NR:
-
Nonresponse
- PR:
-
Partial response
- IMDM:
-
Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PNH:
-
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- CFU-GM:
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming units
- AML:
-
Acute myelogenous leukemia
- MDS:
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome
- CFU-E:
-
Erythroid colony-forming units
- NIH:
-
National Institutes of Health
- WBC:
-
White blood cell
- ALC:
-
Absolute lymphocyte count
- CFU-GEMM:
-
Granulocyte erythrocyte macrophage megakaryocyte colony-forming units
References
Scheinberg P, Young NS (2012) How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 120(6):1185–1196. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-12-274019
Young NS, Calado RT, Scheinberg P (2006) Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Blood 108(8):2509–2519. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-03-010777
Frickhofen N, Heimpel H, Kaltwasser JP, Schrezenmeier H (2003) Antithymocyte globulin with or without cyclosporin A: 11-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing treatments of aplastic anemia. Blood 101(4):1236–1242. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-04-1134
Peslak SA, Olson T, Babushok DV (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of aplastic anemia. Curr Treat Options in Oncol 18(12):70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-017-0511-z
Luzzatto L, Risitano AM (2018) Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of acquired aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 182(6):758–776. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.15443
Liu LP, Chen XJ, Yang WY, Yi MH, Zhou K, Ruan M, Liu F, Chen X, Chang LX, Liu TF, Zhang L, Zou Y, Chen YM, Zhang FK, Zhu XF, Guo Y (2019) Predicting response to porcine antilymphocyte globulin plus cyclosporine A in children with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Pediatr Res 86(3):360–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0437-1
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Weinstein B, Scheinberg P, Biancotto A, Wu CO, Young NS (2011) Horse versus rabbit antithymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med 365(5):430–438. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1103975
Atta EH, Dias DS, Marra VL, de Azevedo AM (2010) Comparison between horse and rabbit antithymocyte globulin as first-line treatment for patients with severe aplastic anemia: a single-center retrospective study. Ann Hematol 89(9):851–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0944-y
Jeong DC, Chung NG, Cho B, Zou Y, Ruan M, Takahashi Y, Muramatsu H, Ohara A, Kosaka Y, Yang W, Kim HK, Zhu X, Kojima S (2014) Long-term outcome after immunosuppressive therapy with horse or rabbit antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for severe aplastic anemia in children. Haematologica 99(4):664–671. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2013.089268
Camitta BM, Rappeport JM, Parkman R, Nathan DG (1975) Selection of patients for bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood 45(3):355–363
Bacigalupo A, Hows J, Gluckman E, Nissen C, Marsh J, Van Lint MT, Congiu M, De Planque MM, Ernst P, McCann S et al (1988) Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) versus immunosuppression for the treatment of severe aplastic anaemia (SAA): a report of the EBMT SAA working party. Br J Haematol 70(2):177–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02460.x
Subspecialty Group of H, Society of P, Chinese Medical Association The Editorial B, Chinese Journal of P (2014) Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of acquired aplastic anemia in children. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 52(2):103–106
Camitta BM (2000) What is the definition of cure for aplastic anemia? Acta Haematol 103(1):16–18. https://doi.org/10.1159/000040999
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Scheinberg P, Boss C, Sloand EM, Young NS (2009) Treatment of severe aplastic anemia with a combination of horse antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine, with or without sirolimus: a prospective randomized study. Haematologica 94(3):348–354. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.13829
Nishikawa E, Yagasaki H, Hama A, Yabe H, Ohara A, Kosaka Y, Kudo K, Kobayashi R, Ohga S, Morimoto A, Watanabe KI, Yoshida N, Muramatsu H, Takahashi Y, Kojima S (2017) Long-term outcomes of 95 children with moderate aplastic anemia treated with horse antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine. Pediatr Blood Cancer 64(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.26305
Tichelli A, Schrezenmeier H, Socie G, Marsh J, Bacigalupo A, Duhrsen U, Franzke A, Hallek M, Thiel E, Wilhelm M, Hochsmann B, Barrois A, Champion K, Passweg JR (2011) A randomized controlled study in patients with newly diagnosed severe aplastic anemia receiving antithymocyte globulin (ATG), cyclosporine, with or without G-CSF: a study of the SAA Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 117(17):4434–4441. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-08-304071
Chen C, Xue HM, Xu HG, Li Y, Huang K, Zhou DH, Guo HX, Fang JP, Huang SL (2012) Rabbit-antithymocyte globulin combined with cyclosporin A as a first-line therapy: improved, effective, and safe for children with acquired severe aplastic anemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138(7):1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1184-4
Rogers ZR, Nakano TA, Olson TS, Bertuch AA, Wang W, Gillio A, Coates TD, Chawla A, Castillo P, Kurre P, Gamper C, Bennett CM, Joshi S, Geddis AE, Boklan J, Nalepa G, Rothman JA, Huang JN, Kupfer GM, Cada M, Glader B, Walkovich KJ, Thompson AA, Hanna R, Vlachos A, Malsch M, Weller EA, Williams DA, Shimamura A (2019) Immunosuppressive therapy for pediatric aplastic anemia: a North American Pediatric Aplastic Anemia Consortium study. Haematologica 104(10):1974–1983. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.206540
Tutelman PR, Aubert G, Milner RA, Dalal BI, Schultz KR, Deyell RJ (2014) Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria phenotype cells and leucocyte subset telomere length in childhood acquired aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 164(5):717–721. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12656
Kulagin A, Lisukov I, Ivanova M, Golubovskaya I, Kruchkova I, Bondarenko S, Vavilov V, Stancheva N, Babenko E, Sipol A, Pronkina N, Kozlov V, Afanasyev B (2014) Prognostic value of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria clone presence in aplastic anaemia patients treated with combined immunosuppression: results of two-Centre prospective study. Br J Haematol 164(4):546–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12661
Scheinberg P, Marte M, Nunez O, Young NS (2010) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in severe aplastic anemia patients treated with horse anti-thymocyte globulin plus cyclosporine. Haematologica 95(7):1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.017889
Yoshida N, Yagasaki H, Takahashi Y, Yamamoto T, Liang J, Wang Y, Tanaka M, Hama A, Nishio N, Kobayashi R, Hotta N, Asami K, Kikuta A, Fukushima T, Hirano N, Kojima S (2008) Clinical impact of HLA-DR15, a minor population of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria-type cells, and an aplastic anaemia-associated autoantibody in children with acquired aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 142(3):427–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07182.x
Bacigalupo A (2017) How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 129(11):1428–1436. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-693481
Yoshida N, Yagasaki H, Hama A, Takahashi Y, Kosaka Y, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, Kaneko T, Tsuchida M, Ohara A, Nakahata T, Kojima S (2011) Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy in childhood aplastic anemia. Haematologica 96(5):771–774. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2010.032805
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Young NS (2009) Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy and survival in severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 144(2):206–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07450.x
Fuhrer M, Rampf U, Baumann I, Faldum A, Niemeyer C, Janka-Schaub G, Friedrich W, Ebell W, Borkhardt A, Bender-Goetze C (2005) Immunosuppressive therapy for aplastic anemia in children: a more severe disease predicts better survival. Blood 106(6):2102–2104. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-03-0874
Chang MH, Kim KH, Kim HS, Jun HJ, Kim DH, Jang JH, Kim K, Jung CW (2010) Predictors of response to immunosuppressive therapy with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine and prognostic factors for survival in patients with severe aplastic anemia. Eur J Haematol 84(2):154–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2009.01378.x
Marsh JC, Hows JM, Bryett KA, Al-Hashimi S, Fairhead SM, Gordon-Smith EC (1987) Survival after antilymphocyte globulin therapy for aplastic anemia depends on disease severity. Blood 70(4):1046–1052
Bacigalupo A, Oneto R, Schrezenmeier H, Hochsmann B, Dufour C, Kojima S, Zhu X, Chen X, Issaragrisil S, Chuncharunee S, Jeong DC, Giammarco S, Van Lint MT, Zheng Y, Vallejo C (2018) First line treatment of aplastic anemia with thymoglobuline in Europe and Asia: outcome of 955 patients treated 2001-2012. Am J Hematol 93(5):643–648. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25081
Saracco P, Quarello P, Iori AP, Zecca M, Longoni D, Svahn J, Varotto S, Del Vecchio GC, Dufour C, Ramenghi U, Bacigalupo A, Locasciulli A (2008) Cyclosporin A response and dependence in children with acquired aplastic anaemia: a multicentre retrospective study with long-term observation follow-up. Br J Haematol 140(2):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06903.x
Calado RT, Cooper JN, Padilla-Nash HM, Sloand EM, Wu CO, Scheinberg P, Ried T, Young NS (2012) Short telomeres result in chromosomal instability in hematopoietic cells and precede malignant evolution in human aplastic anemia. Leukemia 26(4):700–707. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.272
Jeong D-C, Chung NG, Lee JW, P-s J, Cho B, Kim H-K (2011) Long-term outcome of immunosuppressive therapy with rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) for childhood severe aplastic anemia for 15 years. Blood 118(21):1346–1346. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V118.21.1346.1346
Jain R, Trehan A, Bansal D, Varma N (2019) Aplastic anemia in children: how good is immunosuppressive therapy? Pediatr Hematol Oncol 36(4):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/08880018.2019.1621970
Issaragrisil S, Up Y, Yimyam M, Pakdeesuwan K, Khuhapinant A, Muangsup W, Pattanapanyasat K (1998) Hematopoietic progenitor cells in the blood and bone marrow in various hematologic disorders. Stem Cells 16(Suppl 1):123–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.5530160815
Rosenfeld S, Follmann D, Nunez O, Young NS (2003) Antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for severe aplastic anemia: association between hematologic response and long-term outcome. Jama 289(9):1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.9.1130
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to sincerely thank the patients that participated in the follow-up and the support of AiYou Foundation.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant No.2016YFC0901503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Lan designed the study, collected and analyzed the data, and wrote the article; Lixian Chang designed the study, collected the data, and reviewed the article; Meihui Yi, Yuli Cai, and Jing Feng collected and analyzed the data; Chao Liu, Xiaoyan Chen, Aoli Zhang, and Lipeng Liu analyzed the data; Yuanyuan Ren, Shuchun Wang, Ye Guo, and Jingliao Zhang collected the data; Xiaofan Zhu designed the study and reviewed the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee and Institutional Review Board of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from legal guardians.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 24.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Y., Chang, L., Yi, M. et al. Long-term outcomes of 172 children with severe aplastic anemia treated with rabbit antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine. Ann Hematol 100, 53–61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04296-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04296-9