Abstract
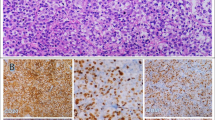
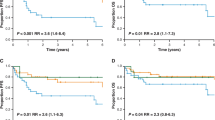
Cell-of-origin (COO) classification of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is increasingly important due to its prognostic significance and the development of subtype-specific therapeutics. We compared the clinical utility of the Lymph2Cx assay against four widely used immunohistochemical algorithms in 150 R-CHOP-treated DLBCL patients using archival tissue. In contrast to the predominance of germinal center B cell-like (GCB) subtype in Western populations, Lymph2Cx assay classified more than half of the Korean cases as the activated B cell-like (ABC) subtype (ABC, 83/150 [55.3%]; GCB, 51/150 [34.0%]; unclassifiable, 16/150 [10.7%]). Predominance of ABC subtype tended to be more pronounced in the nodal lymphomas than in the extranodal lymphomas. However, among the primary extranodal sites, ABC subgroups predominated in primary testicular, breast, and adrenal gland lymphomas. The classification of COO by Lymph2Cx assay did not show any significant association with clinical parameters. The overall concordance rates of the immunohistochemical algorithms with the Lymph2Cx ranged from 78.0 to 84.3%. However, 47.1–66.7% of the cases of the Lymph2Cx-defined GCB subgroup were misclassified as the non-GCB class by the IHC algorithms. The survival of Lymph2Cx-classified COO subtypes was not significantly different in the present cohort. In conclusion, ABC subtype predominated over GCB in Korean patients. There are significant discrepancies between the immunohistochemistry and Lymph2Cx classifications, especially in GCB subtype.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/35000501
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, Gascoyne RD, Muller-Hermelink HK, Smeland EB, Giltnane JM, Hurt EM, Zhao H, Averett L, Yang L, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES, Simon R, Klausner RD, Powell J, Duffey PL, Longo DL, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Sanger WG, Dave BJ, Lynch JC, Vose J, Armitage JO, Montserrat E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Grogan TM, Miller TP, LeBlanc M, Ott G, Kvaloy S, Delabie J, Holte H, Krajci P, Stokke T, Staudt LM, Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:1937–1947. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012914
Schneider C, Pasqualucci L, Dalla-Favera R (2011) Molecular pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Diagn Pathol 28:167–177
Young RM, Shaffer AL 3rd, Phelan JD, Staudt LM (2015) B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol 52:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminhematol.2015.01.008
Lenz G, Wright G, Dave SS, Xiao W, Powell J, Zhao H, Xu W, Tan B, Goldschmidt N, Iqbal J, Vose J, Bast M, Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Armitage JO, Kyle A, May L, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Troen G, Holte H, Kvaloy S, Dierickx D, Verhoef G, Delabie J, Smeland EB, Jares P, Martinez A, Lopez-Guillermo A, Montserrat E, Campo E, Braziel RM, Miller TP, Rimsza LM, Cook JR, Pohlman B, Sweetenham J, Tubbs RR, Fisher RI, Hartmann E, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Wrench D, Lister TA, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH, Chan WC, Staudt LM, Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project (2008) Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med 359:2313–2323. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0802885
Younes A (2015) Prognostic significance of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell of origin: seeing the forest and the trees. J Clin Oncol 33:2835–2836. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.61.9288
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, Pan Z, Farinha P, Smith LM, Falini B, Banham AH, Rosenwald A, Staudt LM, Connors JM, Armitage JO, Chan WC (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-05-1545
Choi WW, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Piris MA, Banham AH, Delabie J, Braziel RM, Geng H, Iqbal J, Lenz G, Vose JM, Hans CP, Fu K, Smith LM, Li M, Liu Z, Gascoyne RD, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Rimsza LM, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Jaye DL, Staudt LM, Chan WC (2009) A new immunostain algorithm classifies diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Clin Cancer Res 15:5494–5502. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0113
Meyer PN, Fu K, Greiner TC, Smith LM, Delabie J, Gascoyne RD, Ott G, Rosenwald A, Braziel RM, Campo E, Vose JM, Lenz G, Staudt LM, Chan WC, Weisenburger DD (2011) Immunohistochemical methods for predicting cell of origin and survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab. J Clin Oncol 29:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.0368
Visco C, Li Y, Xu-Monette ZY, Miranda RN, Green TM, Li Y, Tzankov A, Wen W, Liu WM, Kahl BS, d’Amore ES, Montes-Moreno S, Dybkaer K, Chiu A, Tam W, Orazi A, Zu Y, Bhagat G, Winter JN, Wang HY, O’Neill S, Dunphy CH, Hsi ED, Zhao XF, Go RS, Choi WW, Zhou F, Czader M, Tong J, Zhao X, van Krieken JH, Huang Q, Ai W, Etzell J, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJ, Piris MA, Moller MB, Bueso-Ramos CE, Medeiros LJ, Wu L, Young KH (2012) Comprehensive gene expression profiling and immunohistochemical studies support application of immunophenotypic algorithm for molecular subtype classification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Leukemia 26:2103–2113. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.83
Gutierrez-Garcia G, Cardesa-Salzmann T, Climent F, Gonzalez-Barca E, Mercadal S, Mate JL, Sancho JM, Arenillas L, Serrano S, Escoda L, Martinez S, Valera A, Martinez A, Jares P, Pinyol M, Garcia-Herrera A, Martinez-Trillos A, Gine E, Villamor N, Campo E, Colomo L, Lopez-Guillermo A, l’Estudi dels Limfomes de Catalunya G p, Balears I (2011) Gene-expression profiling and not immunophenotypic algorithms predicts prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 117:4836–4843. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-12-322362
Hwang HS, Park CS, Yoon DH, Suh C, Huh J (2014) High concordance of gene expression profiling-correlated immunohistochemistry algorithms in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. Am J Surg Pathol 38:1046–1057. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000211
Read JA, Koff JL, Nastoupil LJ, Williams JN, Cohen JB, Flowers CR (2014) Evaluating cell-of-origin subtype methods for predicting diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival: a meta-analysis of gene expression profiling and immunohistochemistry algorithms. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 14:460–467 e462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2014.05.002
Scott DW, Wright GW, Williams PM, Lih CJ, Walsh W, Jaffe ES, Rosenwald A, Campo E, Chan WC, Connors JM, Smeland EB, Mottok A, Braziel RM, Ott G, Delabie J, Tubbs RR, Cook JR, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Glinsmann-Gibson BJ, Fu K, Staudt LM, Gascoyne RD, Rimsza LM (2014) Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 123:1214–1217. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-11-536433
Scott DW, Mottok A, Ennishi D, Wright GW, Farinha P, Ben-Neriah S, Kridel R, Barry GS, Hother C, Abrisqueta P, Boyle M, Meissner B, Telenius A, Savage KJ, Sehn LH, Slack GW, Steidl C, Staudt LM, Connors JM, Rimsza LM, Gascoyne RD (2015) Prognostic significance of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell of origin determined by digital gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue biopsies. J Clin Oncol 33:2848–2856. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.60.2383
Nowakowski GS, Chiappella A, Witzig TE, Spina M, Gascoyne RD, Zhang L, Flament J, Repici J, Vitolo U (2016) ROBUST: Lenalidomide-R-CHOP versus placebo-R-CHOP in previously untreated ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Future Oncol 12:1553–1563. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2016-0130
Hwang HS, Yoon DH, Suh C, Park CS, Huh J (2013) Prognostic value of immunohistochemical algorithms in gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Res 48:266–273. https://doi.org/10.5045/br.2013.48.4.266
Lu TX, Gong QX, Wang L, Fan L, Zhang XY, Chen YY, Wang Z, Xu W, Zhang ZH, Li JY (2015) Immunohistochemical algorithm alone is not enough for predicting the outcome of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:275–286
Xu Q, Tan C, Ni S, Wang Q, Wu F, Liu F, Ye X, Meng X, Sheng W, Du X (2015) Identification and validation of a two-gene expression index for subtype classification and prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep 5(10006). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10006
Yoon N, Ahn S, Yong Yoo H, Jin Kim S, Seog Kim W, Hyeh Ko Y (2017) Cell-of-origin of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas determined by the Lymph2Cx assay: better prognostic indicator than Hans algorithm. Oncotarget 8:22014–22022. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15782
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW (2008) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th edn. IARC, Lyon
Lister TA, Crowther D, Sutcliffe SB, Glatstein E, Canellos GP, Young RC, Rosenberg SA, Coltman CA, Tubiana M (1989) Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin’s disease: Cotswolds meeting. J Clin Oncol 7:1630–1636. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1989.7.11.1630
International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors P (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329:987–994. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199309303291402
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca E, Rosen ST, Stroobants S, Lister TA, Hoppe RT, Dreyling M, Tobinai K, Vose JM, Connors JM, Federico M, Diehl V, International Harmonization Project on Lymphoma (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2403
McHugh ML (2012) Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 22:276–282
Frick M, Dorken B, Lenz G (2011) The molecular biology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ther Adv Hematol 2:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040620711419001
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB, Kohlhammer H, Lamy L, Zhao H, Yang Y, Xu W, Shaffer AL, Wright G, Xiao W, Powell J, Jiang JK, Thomas CJ, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Johnson NA, Rimsza LM, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH, Delabie J, Smeland EB, Fisher RI, Braziel RM, Tubbs RR, Cook JR, Weisenburger DD, Chan WC, Pierce SK, Staudt LM (2010) Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 463:88–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08638
Wilson WH, Young RM, Schmitz R, Yang Y, Pittaluga S, Wright G, Lih CJ, Williams PM, Shaffer AL, Gerecitano J, de Vos S, Goy A, Kenkre VP, Barr PM, Blum KA, Shustov A, Advani R, Fowler NH, Vose JM, Elstrom RL, Habermann TM, Barrientos JC, McGreivy J, Fardis M, Chang BY, Clow F, Munneke B, Moussa D, Beaupre DM, Staudt LM (2015) Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Med 21:922–926. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3884
Nowakowski GS, LaPlant B, Macon WR, Reeder CB, Foran JM, Nelson GD, Thompson CA, Rivera CE, Inwards DJ, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Porrata LF, Ansell SM, Gascoyne RD, Habermann TM, Witzig TE (2015) Lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP overcomes negative prognostic impact of non-germinal center B-cell phenotype in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 33:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.55.5714
Clarke CA, Glaser SL, Gomez SL, Wang SS, Keegan TH, Yang J, Chang ET (2011) Lymphoid malignancies in U.S. Asians: incidence rate differences by birthplace and acculturation. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 20:1064–1077. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0038
Sun J, Yang Q, Lu Z, He M, Gao L, Zhu M, Sun L, Wei L, Li M, Liu C, Zheng J, Liu W, Li G, Chen J (2012) Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in China: analysis of 4,638 cases according to the World Health Organization classification. Am J Clin Pathol 138:429–434. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCP7YLTQPUSDQ5C
Chang ST, Chen SW, Ho CH, Kuo CC, Sakata S, Takeuchi K, Chuang SS (2016) Immunophenotypic and genetic characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc 115:961–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2016.09.006
Staiger AM, Ziepert M, Horn H, Scott DW, Barth TFE, Bernd HW, Feller AC, Klapper W, Szczepanowski M, Hummel M, Stein H, Lenze D, Hansmann ML, Hartmann S, Moller P, Cogliatti S, Lenz G, Trumper L, Loffler M, Schmitz N, Pfreundschuh M, Rosenwald A, Ott G, German High-Grade Lymphoma Study G (2017) Clinical impact of the cell-of-origin classification and the MYC/ BCL2 dual expresser status in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated within prospective clinical trials of the German high-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma study group. J Clin Oncol 35:2515–2526. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.70.3660
Czuczman MS, Trneny M, Davies A, Rule SA, Linton K, Wagner-Johnston N, Gascoyne RD, Slack G, Brousset P, Eberhard DA, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Salles G, Witzig TE, Zinzani PL, Wright GW, Staudt LM, Yang Y, Williams PM, Lih CJ, Russo J, Thakurta A, Hagner P, Fustier P, Song D, Lewis ID (2017) A phase 2/3 multicenter, randomized, open-label study of lenalidomide vs investigator’s choice in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 23:4127–4137. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2818
Fletcher CD, Kahl BS (2014) Central nervous system involvement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: an analysis of risks and prevention strategies in the post-rituximab era. Leuk Lymphoma 55:2228–2240. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2013.869326
Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Nickelsen M, Kansara R, Villa D, Sehn LH, Glass B, Scott DW, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Ziepert M, Pfreundschuh M, Loeffler M, Savage KJ (2016) CNS international prognostic index: a risk model for CNS relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J Clin Oncol 34:3150–3156. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.65.6520
Cheah CY, Wirth A, Seymour JF (2014) Primary testicular lymphoma. Blood 123:486–493. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-10-530659
Hu S, Song Y, Li Y, Sun X, Su L, Zhang W, Jia J, Bai O, Liang R, Li X, Zhang H, Gao Y, Zhang W, Xiao X, Bao H, Wang N, Ren H, Cen X, Yang S, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Liu A, Wang J, Shi Y, Yuan M, He X (2016) Primary breast diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: outcomes of a multicenter retrospective study by the Lymphoma and Leukemia Committee of Chinese Geriatric Oncology Society (LLC-CGOS). Blood 128:4228
Sohn BS, Kim SM, Yoon DH, Kim S, Lee DH, Kim JH, Lee SW, Huh J, Suh C (2012) The comparison between CHOP and R-CHOP in primary gastric diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 91:1731–1739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1512-4
Huang J, Jiang W, Xu R, Huang H, Lv Y, Xia Z, Sun X, Guan Z, Lin T, Li Z (2010) Primary gastric non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Chinese patients: clinical characteristics and prognostic factors. BMC Cancer 10(358). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-358
Li X, Xia B, Guo S, Zhan Z, Zhang L, Zhao D, Wu X, Zhang Y (2013) A retrospective analysis of primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with or without concomitant mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma components. Ann Hematol 92:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1701-9
Hu S, Xu-Monette ZY, Tzankov A, Green T, Wu L, Balasubramanyam A, Liu WM, Visco C, Li Y, Miranda RN, Montes-Moreno S, Dybkaer K, Chiu A, Orazi A, Zu Y, Bhagat G, Richards KL, Hsi ED, Choi WW, Zhao X, van Krieken JH, Huang Q, Huh J, Ai W, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJ, Zhou F, Slack GW, Gascoyne RD, Tu M, Variakojis D, Chen W, Go RS, Piris MA, Moller MB, Medeiros LJ, Young KH (2013) MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: a report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood 121:4021–4031; quiz 4250. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-10-460063
Ennishi D, Mottok A, Ben-Neriah S, Shulha HP, Farinha P, Chan FC, Meissner B, Boyle M, Hother C, Kridel R, Lai D, Saberi S, Bashashati A, Shah SP, Morin RD, Marra MA, Savage KJ, Sehn LH, Steidl C, Connors JM, Gascoyne RD, Scott DW (2017) Genetic profiling of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma determines cell-of-origin-specific clinical impact. Blood 129:2760–2770. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-747022
de Jong D, Rosenwald A, Chhanabhai M, Gaulard P, Klapper W, Lee A, Sander B, Thorns C, Campo E, Molina T, Norton A, Hagenbeek A, Horning S, Lister A, Raemaekers J, Gascoyne RD, Salles G, Weller E, Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium (2007) Immunohistochemical prognostic markers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: validation of tissue microarray as a prerequisite for broad clinical applications--a study from the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J Clin Oncol 25:805–812. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.09.4490
Linderoth J, Ehinger M, Akerman M, Cavallin-Stahl E, Enblad G, Erlanson M, Jerkeman M (2007) Tissue microarray is inappropriate for analysis of BCL6 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 79:146–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2007.00892.x
Funding
This study was supported by a grant (2016-705, contributed by Namkyo Chung) from the Asan Institute for Life Sciences and Corporate Relations of Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants
For the retrospective type of the study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, H.S., Yoon, D.H., Hong, J.Y. et al. The cell-of-origin classification of diffuse large B cell lymphoma in a Korean population by the Lymph2Cx assay and its correlation with immunohistochemical algorithms. Ann Hematol 97, 2363–2372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3442-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3442-2