Abstract
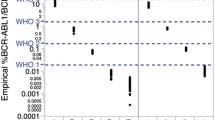
The level of BCR-ABL1 reached after treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors is an effective marker of the therapeutic response and a good survival predictor in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients. However, no agreement has yet been achieved about either the standardization of the technique to determine BCR-ABL1 or the interpretation of the results. The aim of this study was to compare the method currently recommended by the European Leukemia Net, which includes the application of a conversion factor to express the results in international scale, with an automated method (Xpert BCR-ABL™, Cepheid). BCR-ABL1 transcript quantification was performed in 117 samples from CML patients in two different laboratories by both methods, and the results were compared by statistical procedures. A high linear correlation was obtained in the results between the two methods. The concordance at logarithmic intervals reached 62 %. When the major molecular response (MMR) was analyzed, 85 % agreement was achieved. The automated method provides reproducible results and does not show significant differences compared with the traditional method. As a clinical tool, Xpert correctly classified the patients in MMR and can be considered a useful alternative for the molecular follow-up of CML patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branford S, Hughes TP (2010) Practical considerations for monitoring patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol 47:327–334
Hughes TP, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Müller MC, Kaeda JS, Foroni L et al (2010) Long-term prognostic significance of early molecular response to imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia: an analysis from the International Randomized Study of Interferon and STI571 (IRIS). Blood 116:3758–3765
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J et al (2006) Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 108:28–37
Branford S, Fletcher L, Cross NC, Müller MC, Hochhaus A, Kim DW et al (2008) Desirable performance characteristics for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response rates between clinical trials. Blood 112:3330–3338
Winn-Deen ES, Helton B, Van Atta R, Wong W, Peralta J, Wang J et al (2007) Development of an integrated assay for detection of BCR-ABL RNA. Clin Chem 53:1593–1600
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N et al (2003) Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia—a Europe Against Cancer Program. Leukemia 17:2318–2357
Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden VHJ, Bi W, Dee R et al (2003) Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR)—a Europe Against Cancer Program. Leukemia 17:2474–2486
Muller MC, Cross NCP, Erben P, Schenk T, Hanfstein B, Ernst T et al (2009) Harmonization of molecular monitoring of CML therapy in Europe. Leukemia 23:1957–1963
Jobbagy Z, Van Atta R, Murphy KM, Eshleman JR, Gocke CD (2007) Evaluation of the Cepheid GeneXpert BCR-ABL assay. J Mol Diagn 9:220–227
Dufresne SD, Belloni DR, Levy NB, Tsongalis G (2007) Quantitative assessment of the BCR-ABL transcript using the Cepheid Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor assay. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131:947–950
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J et al (2009) Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 27:6041–6051
Press RD, Galderisi C, Yang R, Rempfer C, Willis SG, Mauro MJ et al (2007) A half-log increase in BCR-ABL RNA predicts a higher risk of relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with an imatinib-induced complete cytogenetic response. Cli Can Res 13:6136–6143
White HE, Matejtschuk P, Rigsby P, Gabert J, Lin F, Lynn Wang Y et al (2010) Establishment of the first World Health Organization International Genetic Reference Panel for quantitation of BCR-ABL mRNA. Blood 116:e111–e117
Cayuela JM, Macintyre E, Darlington M, Abdelali RB, Fund X, Villarese P et al (2011) Cartridge-based automated BCR-ABL1 mRNA quantification: solving the issues of standardization, at what cost? Haematologica 96:664–671
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Beca “Carmen Lavigne’ AECC 2010 and Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS, Spain) PI-07/0608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 21.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Jorge, C.E., Gómez-Casares, M.T., Jiménez-Velasco, A. et al. Comparative study of BCR-ABL1 quantification: Xpert assay, a feasible solution to standardization concerns. Ann Hematol 91, 1245–1250 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1468-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1468-4