Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to describe topography of vessels and nerves in striated muscles to understand individual muscle function.
Materials and methods
Immunohistochemistry for nerve and artery was used to examine the thigh and gluteal muscles of six human midterm fetuses.
Results
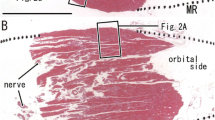
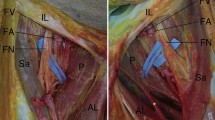
The supplying nerves often accompanied arteries along epimysium bundling muscle fibers as well as in the covering fascia surrounding the entire muscle mass. However, courses of nerve twigs were usually independent of those of vessels in muscle bundles. Notably, irrespective of whether or not the vascular bundle accompanied the nerves at the muscle surface or hilus, most of the motor endplate bands did not accompany the vessels.
Conclusion
Since the motor endplates were low vascularised, a chemical induction of vessels for nerve terminal development (or the reversed induction) seemed unlikely in striated muscles. In contrast to proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation, manual stimulation of the endplate bands may stimulate muscle activity without sympathetic reflexes through vessel-accompanying nerves.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADB:
-
Adductor brevis muscle
- ADL:
-
Adductor longus muscle
- ADM:
-
Adductor magnus muscle
- BF:
-
Biceps femoris muscle
- F:
-
Femur
- FA:
-
Femoral artery
- FN:
-
Femoral nerve
- GR:
-
Gracilis muscle
- GMD:
-
Gluteus medius muscle
- GMI:
-
Gluteus minimus muscle
- GMX:
-
Gluteus maximus muscle
- IL:
-
Ilium
- IP:
-
Iliopsoas muscle
- LCFA:
-
Lateral circumflexus femoris artery
- LFCN:
-
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- OE:
-
Obturator externus muscle
- PE:
-
Pectineus muscle
- PI:
-
Piriformis muscle
- QF:
-
Quadratus femoris muscle
- QI:
-
Obliquus internus abdominis muscle
- RA:
-
Rectus abdominis muscle
- RF:
-
Rectus femoris muscle
- SA:
-
Sartorius muscle
- SM:
-
Semimembranosus muscle
- SN:
-
Sciatic nerve
- ST:
-
Semitendinosus muscle (tendon)
- TFL:
-
Tensor fasciae latae muscle
- VL:
-
Vastus lateralis muscle
References
Abe S, Kikuchi R, Nakao T, Cho BH, Murakami G, Ide Y (2012) Nerve terminal distribution in the human tongue intrinsic muscles: an immunohistochemical study using midterm fetuses. Clin Anat 25:189–197. doi:10.1002/ca.21201
Abe S, Fukuda M, Yamane S, Saka H, Katori Y, Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Murakami G (2013) Fetal anatomy of the upper pharyngeal muscles with special reference to the nerve supply: is it an enteric plexus or simply an intramuscular nerve? Anat Cell Biol 46:141–148. doi:10.5115/acb.2013.46.2.141
Arese M, Serini G, Bussolino F (2011) Nervous vascular parallels: axon guidance and beyond. Int J Dev Biol 55:439–445. doi:10.1387/ijdb.103242ma
Chang H, Cho KH, Hayashi S, Kim JH, Abe H, Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Murakami G (2014) Site- and stage-dependent differences in vascular density of the human fetal brain. Childs Nerv Syst 30:399–409. doi:10.1007/s00381-013-2272-8
Chalmers G (2004) Re-examination of the possible role of Golgi tendon organ and muscle spindle reflexes in proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation muscle stretching. Sports Biomech 3:159–183
Eichmann A, Makinen T, Alitalo K (2005) Neural guidance molecules regulate vascular remodeling and vessel navigation. Genes Dev 19:1013–1021
Hayashi S, Murakami G, Ohtsuka A, Itoh M, Nakano T, Fukuzawa Y (2008) Connective tissue configuration in the human liver hilar region with special reference to the liver capsule and vascular sheath. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 15:640–647. doi:10.1007/s00534-008-1336-8
Hieda K, Cho KH, Arakawa T, Fujimiya M, Murakami G, Matsubara A (2013) Nerves in the intersphincteric space of the human anal canal with special reference to their continuation to the enteric nerve plexus of the rectum. Clin Anat 26:843–854. doi:10.1002/ca.22227
Homma T, Sakai T (1992) Thenar and hypothenar muscles and their innervation by the ulnar and median nerves in the human hand. Acta Anat (Basel) 145:44–49
Hosaka F, Katori Y, Kawase T, Fujimiya M, Ohguro H (2014) Site-dependent differences in density of sympathetic nerve fibers in muscle-innervating nerves of the human head and neck. Anat Sci Int 89:101–111
Ishizawa A, Hayashi S, Nasu H, Abe H, Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Murakami G (2013) An artery accompanying the sciatic nerve (arteria comitans nervi ischiadici) and the position of the hip joint: a comparative histological study using chick, mouse, and human foetal specimens. Folia Morphol (Warsz.) 72:41–50
Kato M, Niikura H, Yaegashi N, Murakami G, Tatsumi H, Matsubara A (2008) Histotopography of the female cavernous nerve: a study using donated fetuses and adult cadavers. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 19:1687–1695. doi:10.1007/s00192-008-0713-9
Kikuchi N, Murakami G, Kashiwa H, Homma K, Sato TJ, Ogino T (2001) Morphometrical study of the arterial perforators of the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. Surg Radiol Anat 23:375–381
Kanbayashi T, Takafuji T, Sato Y (1993) On the arterial supply in the human biceps brachii muscle. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 69:289–310
Larrieu-Lahargue F, Thomas KR, Li DY (2012) Netrin ligands and receptors: lessons from neurons to the endothelium. Trends Cardiovasc Med 22:44–47. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2012.06.010
Ljung BO, Forsgren S, Fridén J (1999) Sympathetic and sensory innervations are heterogeneously distributed in relation to the blood vessels at the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle origin of man. Cells Tissues Organs 165:45–54
Mackenzie F, Ruhrberg C (2012) Diverse roles for VEGF-A in the nervous system. Development 139:1371–1380. doi:10.1242/dev.072348
Maden CH, Gomes J, Schwarz Q, Davidson K, Tinker A, Ruhrberg C (2012) NRP1 and NRP2 cooperate to regulate gangliogenesis, axon guidance and target innervation in the sympathetic nervous system. Dev Biol 369:277–285. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.026
Miyake N, Hayashi S, Kawase T, Cho BH, Murakami G, Fujimiya M, Kitano H (2010) Fetal anatomy of the human carotid sheath and structures in and around it. Anat Rec 293:438–445. doi:10.1002/ar.21089
Moriya A, Takafuji T, Sato Y (1993) Arterial supply in the human pectoralis minor muscle. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 69:321–333
Mu L, Sanders I (2010) Human tongue neuroanatomy: nerve supply and motor endplates. Clin Anat 23:777–791. doi:10.1002/ca.21011
Nakao T, Cho KH, Yamamoto M, Yamane S, Murakami G, Ide Y, Abe S (2012) Site-dependent difference in the density of sympathetic nerve fibers in muscle-innervating nerves: a histologic study using human cadavers. Eur J Anat 16:33–42
Niikura H, Jin ZW, Cho BH, Murakami G, Yaegashi N, Lee JK, Lee NH, Li CA (2010) Human fetal anatomy of the coccygeal attachments of the levator ani muscle. Clin Anat 23:566–574. doi:10.1002/ca.20983
Rubini EC, Souza AC, Mello ML, Bacurau RF, Cabral LF, Farinatti PT (2011) Immediate effect of static and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching on hip adductor flexibility in female ballet dancers. J Dance Med Sci 15:177–181
Standring S (2005) Gray’s anatomy, 39th edn. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, London, p 121
Tsujihata M, Yoshimura T, Satoh A, Kinoshita I, Matsuo H, Mori M, Nagataki S (1989) Diagnostic significance of IgG, C3, and C9 at the limb muscle motor end-plate in minimal myasthenia gravis. Neurology 39(10):1359–1363
Weinstein BM (2005) Vessels and nerves: marching to the same tune. Cell 120:299–302
Youdas JW, Haeflinger KM, Kreun MK, Holloway AM, Kramer CM, Hollman JH (2010) The efficacy of two modified proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching techniques in subjects with reduced hamstring muscle length. Physiother Theory Pract 26:240–250. doi:10.3109/09593980903015292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, H.S., Cho, K.H., Murakami, G. et al. Topographical relationships of intramuscular nerves and vessels of the motor endplates in the thigh and gluteal regions of human fetuses: an immunohistochemical study. Surg Radiol Anat 38, 587–596 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-015-1586-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-015-1586-5