Abstract
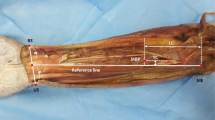
The aim of this study was to elucidate the anatomical location of nerve entry points of Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) and its implications for non-surgical neurolysis. A total of 21 amputated forearms of 11 Korean fresh cadavers were dissected. Two transverse x-axes joined the medial and lateral epicondyles and the radial and ulnar styloid processes. The longitudinal y-axis joined the midpoints of the proximal and distal transverse x-axes. The locations of the points were marked relative to the forearm length (x) and forearm width (y). The number of nerve entry points from median nerve and ulnar nerve were average 3.91 ± 0.62 (range 3–5, median 4) and 2.14 ± 0.65 (range 1–3, median 2) respectively. Most (82.9%) nerve entry points of FDP from the median nerve were within two circles, with 15 mm diameter. The two circles were on medial 1/10 of forearm width from the y-axis, and on proximal 1/3 (1:2) and 2/5 (2:3) of forearm length on x-axis. Most (80.0%) nerve entry points of the ulnar nerve innervating FDP were within a 15 × 30 mm rectangle. Its center was located at +26.5% on x-axis and −36.0% on y-axis. The nerve entry points used to be selected in performing non-surgical neurolysis with either ethyl alcohol (50%) or phenol (5–12%).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhadra N, Keith MW, Peckham PH (1999) Variations in innervation of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle. J Hand Surg(Am) 24:700–703
Canovas F, Mouilleron P, Bonnel F (1998) Biometry of the muscular branches of the median nerve to the forearm. Clin Anat 11:239–245
Glenn MB (1990) Nerve blocks. In: Glenn MB, Whyte J (eds) The practical management of spasticity in children and adults. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 227–258
Jang SH, Ahn SH, Park SM, Kim SH, Lee KH, Lee ZI (2004) Alcohol neurolysis of tibial nerve motor branches to the Gastrocnemius muscle to treat ankle spasticity in patients with hemiplegic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 85:506–508
Kong KH, Chua KSG (2005) Intramuscular neurolysis with alcohol to treat post-stroke finger flexor spasticity. Clin Rehabil 16:378–381
Lepage D, Parratte B, Tatu L, et al (2005) Extra- and intramuscular nerve supply of the muscles of the anterior antecubital compartment: applications for selective neurotomy and for botulinum toxin injection. Surg Radiol Anat 27:420–430
Marur T, Akkin SM, Alp M, et al (2005) The muscular branching patterns of the ulnar nerve to the flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus muscles. Surg Radiol Anat 27:322–326
Standring S (2005) Gray’s anatomy. Elsevier, Edinburgh, p 877
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to Dr Robert S. Chung, MD, FACS, Genetic Institute, Orange County, CA, for reviewing this manuscript. We are also grateful to Kwan Hyun Yoon, M.A. for his illustrations. This work was supported by grant (R01-2005-000-10018-0) from the Basic Research Program of the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, K., Jin, S., Hwang, SH. et al. Location of nerve entry points of flexor digitorum profundus. Surg Radiol Anat 29, 617–621 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-007-0260-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-007-0260-y