Abstract
Purpose: To assess the efficacy of intrapleural urokinase instillation through smll-caliber catheters for the treatment of loculate and/or septate effusions.
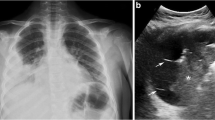
Methods: We inserted small-caliber catheters (8.2 Fr) in 102 patients with septate and/or loculate pleural effusions using ultrasonographic guidance. Urokinase (100,000 IU/2 hr, 3 times a day) was instilled through the catheter until the effusion resolved and D-dimer levels were <500 ng/ml. Patients were enrolled regardless of the etiology of the pleural effusion provided there were no contraindications for the use of urokinase. D-dimer levels were determined before and after treatment. Follow-up was performed by chest radiograph and sonography at 1 day, 7 days, and every 30 days thereafter for 6 months.
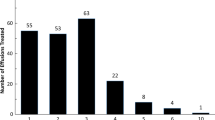
Results: Successful catheter placement was achieved in all cases. The mean time catheters stayed in place was 5.7 days and the mean dose of drug instilled was 690,000 IU. Pleural effusion drainage was complete at the first assessment in all patients. Failure of the treatment, with recurrent effusion at 30 days, occurred in six patients (5.8%). Complete resolution without sequelae was observed in 19 patients (19.6%). In 75 cases (73.5%) resolution was partial, with pleural thickening (>2 mm). Two patients died from unrelated causes within 30 days after catheter placement. Complications were seen in 13 patients (12.74%): hydropneumothorax, nine cases (8.82%); infection of the puncture point, three cases (2.94%); and adverse reaction, one case (0.98%). No further treatment was required.
Conclusions: The use of intrapleural fibrinolytic agents delivered through small-caliber catheters for the treatment of loculate and/or septate pleural effusion is a simple, effective, minimally invasive and inexpensive procedure that can prevent sequelae and shorten drainage time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wehr CJ, Adkins RB (1986) Empyema thoracis: A ten-year experience. South Med J 79:171–176
Lemmer JH, Botham MJ, Omnger MB (1989) Modern management of adult thoracic empyema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 90:849–855
Mandal AK, Thadepall H (1987) Treatment of spontaneous bacterial empyema thoracis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 94:414–418
van Sonnenberg E, Nakamoto SK, Mueller PR, Casola G, Neff CC, Friedman PJ, Ferrucci JT, Simeone JF (1984) CT- and ultrasound-guided catheter drainage of empyemas after chest-tube failure. Radiology 151:349–353
Westcott JL (1985) Percutaneous catheter drainage of pleural effusion and empyema. AJR 144:1189–1193
Merriam MA, Cronan JJ, Dorfman GS, Lambiase RE, Haas RA (1988) Radiographically guided percutaneous catheter drainage of pleural collections. AJR 151:1113–1116
Silverman SG, Muller PR, Saini S, Hahn PF, Simeone JF, Forman BH, Steiner E, Ferrucci JT (1988) Thoracic empyema: Management with image-guided catheter drainage. Radiology 169:5–9
Bergh NP, Ekroth R, Larsson S, Nagy P (1977) Intrapleural streptokinase in the treatment of hemothorax and empyema. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 11:265–268
Henke C, Leatherman J (1992) Intrapleurally administered streptokinase in the treatment of acute loculated nonpurulent parapneumonic effusions. Am Rev Respir Dis 145:680–684
Alfageme I, Moreno L, Muñoz E, Umbria S, Peña N (1993) Uso de la estreptoquinasa intrapleural en el tratamiento de empiemas y derrames pleurales paraneumónicos complicados. Arch Bronconeumol 29:12–15
Casanova J, Izquierdo JM, Pac J, Mariñan M, Rojo R, Rumbero JC, Vara F (1995) Utilidad de la urocinasa en derrames pleurales multiloculados. Arch Bronconeumol 31:51–55
Dubois R, Drieu C, Dubois C, Toulemonde F (1973) Décaillotage pleural par l’urokinase. Anesthes Franc 14(3):293–296
Vogelzang RL, Tobin RS, Burstein S, Amscheutz SL, Marzano M, Kozlowski JM (1987) Transcatheter intracavitary fibrinolysis of infected extravascular hematomas. AJR 148:378–380
Moulton JS, Moor PT, Mencini RA (1989) Treatment of loculated pleural effusions with transcatheter intracavity urokinase. AJR 153:941–945
Moulton JS, Benkert RE, Weisiger KH, Chambers JA (1995) Treatment of complicated pleural fluid collections with image-guided drainage and intracavitary urokinase. Chest 108:1252–1259
Lee KS, Im J-G, Kim YH, Hwang SH, Bae WK, Lee BH (1991) Treatment of thoracic multiloculated empyemas with intracavitary urokinase: A prospective study. Radiology 179:771–775
De Gregorio MA, Ruiz C, Alfonso ER, Fernández JA, Perez-Trullen A, Ariño I, Rodriguez-Panadero F (1996) Drainage of loculated and/or multiseptate pleural effusions using a small caliber catheter and urokinase (pleurofibrinolysis). Arch Bronconeumol 32:229–231
Light RW (1995) A new classification of parapneumonic effusions and empyema. Chest 108:299–301
Eibenberger KL, Dock WI, Ammann ME, Dorffner R, Hörmann M, Grabenwöger F (1994) Quantification of pleural effusions: Sonography versus radiography. Radiology 191:681–684
Yang PC, Luh KT, Chang DB, Wu HD, Yu CJ, Kuo SH (1992) Value of sonography in determining the nature of pleural effusion: Analysis of 320 cases. AJR 159:29–33
van Sonnenberg E, Ferrucci JT, Mueller PR, Wittenberg J, Simeone JF (1982) Percutaneous drainage of abscesses and fluid collections: Technique, results, and applications. Radiology 142:1–10
Mueller PR, van Sonnenberg E, Ferrucci JT (1984) Percutaneous drainage of 250 abdominal abscesses and fluid collections. II. Current procedural concepts. Radiology 151:343–346
van Sonnenberg E, Wing VW, Casola G (1984) Temporizing effect of percutaneous drainage of complicated abscesses in critically ill patients. AJR 142:821–826
Tillet WS, Sherry S (1949) The effect in patients of streptococcal fibrinolysin (streptokinase) and streptococcal desoxyribonuclease on fibrinous, purulent sagnuinous pleural exudations. J Clin Invest 28:173–179
Godley PJ, Bell RC (1984) Major hemorrhage following administration of intrapleural streptokinase. Chest 86:486–487
Lawrence DR, Ohri SK, Moxon RE, Townsend ER, Fountain SW (1997) Thoracoscopic debridement of empyema thoracis. Ann Thorac Surg 64:1448–1450
Mackinley TAA, Lyons GA, Chimondeguy DJ, Barboza Piedras MA, Angaramo G, Emery J (1996) VATS debridement versus thoracotomy in the treatment of loculated postpneumonia empyema. Ann Thorac Surg 61:1626–1630
Striffeler H, Gugger M, Im Hof V, Cerny A, Furrer M, Ris H (1998) Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for fibrinopurulent pleural empyema in 67 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 65:319–323
Lahorra JM, Haaga JR, Stellato T, Flanigan T, Graham R (1993) Safety of intracavitary urokinase with percutaneous abscess drainage. AJR 160:171–174
Ryan JM, Boland GW, Lee MJ, Mueller PR (1996) Intracavitary urokinase therapy as an adjunct to percutaneous drainage in a patient with a multiloculated empyema. AJR 167:643–647
Park CS, Chung WM, Lim MK, Cho CHH, Suh CHH, Chung WK (1996) Transcatheter instillation of urokinase into loculated pleural effusion: Analysis of treatment effect. AJR 167:649–652
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Gregorio, M.A., Ruiz, C., Alfonso, E.R. et al. Transcatheter intracavitary fibrinolysis of loculated pleural effusions: Experience in 102 patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22, 114–118 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002709900345
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002709900345