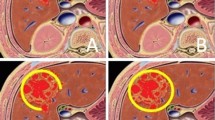
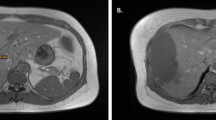
Abstract
Purpose
The management of patients with giant haemangioma of the liver remains controversial. Although the usual treatment method for symptomatic giant haemangioma is surgery, the classical paradigm of operative resection remains. In this study, we evaluated the symptomatic improvement and size-reduction effect of embolisation with bleomycin mixed with lipiodol for the treatment of symptomatic giant hepatic haemangioma.
Methods
This study included 26 patients [21 female, five male; age 41–65 years (mean 49.83 ± 1.53)] with symptomatic giant haemangioma unfit for surgery and treated with selective embolisation by bleomycin mixed with lipiodol. The patients were followed-up (mean 7.4 ± 0.81 months) clinically and using imaging methods. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 16.0, and p < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Embolisation of 32 lesions in 26 patients was performed. The mean volume of the haemangiomas was 446.28 ± 88 cm3 (range 3.39–1559 cm3) before intervention and 244.43 ± 54.38 cm3 (range 94–967 cm3) after intervention. No mortality or morbidity related to the treatment was identified. Symptomatic improvement was observed in all patients, and significant volume reduction was achieved (p = 0.001).
Conclusion
The morbidity of surgical treatment in patients with giant liver hemangioma were similar to those obtained in patients followed-up without treatment. Therefore, follow-up without treatment is preferred in most patients. Thus, minimally invasive embolisation is an alternative and effective treatment for giant symptomatic haemangioma of the liver.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi BY, Nguyen MH (2005) The diagnosis and management of benign hepatic tumors. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:401–412
Ishack KG, Rabin L (1975) Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am 59:995
Pietrabissa A, Giulianotti P, Campatelli A et al (1996) Management and follow-up of 78 giant haemangiomas of the liver. Br J Surg 83:915–918
Weimann A, Ringe B, Klempnauer J et al (1997) Benign liver tumors: differential diagnosis and indications for surgery. World J Surg 21:983–990
Trastec UF, van Heerden JA, Sheedy RF et al (1983) Cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: resect or observe? Am J Surg 145:49–53
Schnelldorfer T, Ware AL, Smoot R et al (2010) Management of giant hemangioma of the liver: resection versus observation. J Am Coll Surg 211(6):724–730
Tarazov PG, Polysalov VN, Ryzhkov VK (1990) Hemangiomatosis of the liver and spleen: successful treatment with embolization and spleenectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155:1235–1236
Althaus S, Ashdown B, Coldwell D et al (1996) Transcatheter arterial embolization of two symptomatic giant cavernous hemangiomas of the liver. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 19:364–367
Shrivastava DN, Gandhi D, Seith A et al (2001) Trans-catheter arterial embolization in the treatment of symptomatic cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: a prospective study. Abdom Imaging 26:510–514
Deutsch GS, Yeh KA, Bates WB III et al (2001) Embolization for management of hepatic hemangiomas. Am Surg 67:159–164
Giavroglou C, Economou H, Ioannidis I (2003) Arterial embolization of giant hepatic hemangiomas. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 26:92–96
Zeng Q, Li Y, Chen Y et al (2004) Gigantic cavernous hemangioma of the liver treated by intra-arterial embolization with pingyangmycin-lipiodol emulsion: a multi-center study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27(5):481–482
Herman P, Costa ML, Machado MA et al (2005) Management of hepatic hemangiomas: a 14-year experience. J Gastrointest Surg 9:853–859
Erdogan D, Busch OR, van Delden OM et al (2007) Management of liver hemangiomas according to size and symptoms. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(11):1953–1958
Ribeiro MAF Jr, Papaiordanou F, Gonçalves JM et al (2010) Spontaneous rupture of hepatic hemangiomas: a review of the literature. World J Hepatol 2(12):428–433
Yamamoto T, Kawarada Y, Yano T et al (1991) Spontaneous rupture of hemangioma of the liver: treatment with transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization. Am J Gastroenterol 86:1645–1649
Chen ZY, Qi QH, Dong ZL (2002) Etiology and management of hemmorrhage in spontaneous liver rupture: a report of 70 cases. World J Gastroenterol 8:1063–1066
Jain V, Ramachandran V, Garg R et al (2010) Spontaneous rupture of a giant hepatic hemangioma—Sequential management with transcatheter arterial embolization and resection. Saudi J Gastroenterol 16(2):116–119
Glinkova V, Shevah O, Boaz M et al (2004) Hepatic haemangiomas: possible association with female sex hormones. Gut 53(9):1352–1355
Mungovan JA, Cronan JJ, Vacarro J (1994) Hepatic cavernous hemangiomas: lack of enlargement over time. Radiology 191:111–113
Yamashita Y, Ogata I, Urata J et al (1997) Cavernous hemangioma of the liver: pathologic correlation with dynamic CT findings. Radiology 203:121–125
Ho HY, Wu TH, Yu MC et al (2012) Surgical management of giant hepatic hemangiomas: complications and review of the literature. Chang Gung Med J 35(1):70–78
Brouwers MA, Peeters PM, de Jong KP et al (1997) Surgical treatment of giant haemangioma of the liver. Br J Surg 84:314–316
Billio A, Pescosta N, Rosanelli C et al (2001) Treatment of Kasabach–Merritt syndrome by embolisation of a giant liver hemangioma. Am J Hematol 66:140–141
Malagari K, Alexopoulou E, Dourakis S et al (2007) Transarterial embolization of giant liver hemangiomas associated with Kasabach–Merritt syndrome: a case report. Acta Radiol 48(6):608–612
Soyer P, Levesque M (1995) Hemoperitoneum due to spontaneous rupture of hepatic haemangiomatosis: treatment by superselective arterial embolization and partial hepatectomy. Australas Radiol 39:90–92
Zhao ZR, Li GW, Wang GT (1994) Investigation on blood supply and embolization treatment of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Chin J Radiol 28:472–475
Bennett JM, Reich SD (1979) Bleomycin. Ann Intern Med 90:945–948
Oikawa T, Hirotani K, Ogasawara H et al (1990) Inhibition of angiogenesis by bleomycin and its copper complex. Chem Pharm Bull 38:1790–1792
Chen Y, Li Y, Zhu Q et al (2008) Fluoroscopic intralesional injection with pingyangmycin lipiodol emulsion for the treatment of orbital venous malformations.AJR Am J Roentgenol 190(4):966–971
Muir T, Kirstin M, Fourie P et al (2004) Intralesional bleomycin injection for hemangiomas and congenital vascular malformations. Paeditr Surg Int 19:766–773
Duncan IC, Van Der Nest L (2004) Intralesional bleomycin injections for the palliation of epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(7):1144–1146
Ohishi H, Uchida H, Yoshimura H et al (1985) Hepatocellular carcinoma detected by iodized oil. Use of anticancer agents. Radiology 154(1):25–29
Ouyang Y, Ouyang XH, Yu M, Gu SB (2001) Frequency of arterio-venous shunts in hepatic cavernous hemangiomas in adults as seen on selective arteriography and postembolization radiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 24:161–167
Leung DA, Goin JE, Sickles C et al (2001) Determinants of postembolization syndrome after hepatic chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12(3):321–326
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozkaya, H., Cinar, C., Besir, F.H. et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Giant Haemangiomas of the Liver: Embolisation With Bleomycin. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 101–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0618-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0618-y