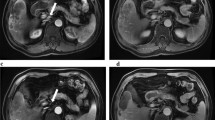
Abstract
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a rare life-threatening disease, whose only treatment with potential for cure is surgical resection. However, only 27% of patients at most are suitable for surgery when first diagnosed. For patients with unresectable disease, therapeutic options are chemotherapy or chemoradiation. We evaluated the feasibilty and safety of oxaliplatin-eluting microspheres transarterial chemoembolization (OEM-TACE) associated with chemotherapy (ChT) in patients affected by unresectable ICC. Between December 2005 and May 2008 we treated nine patients (six female and three male) with unresectable ICC. All patients had undergone OEM-TACE associated with chemotherapy with oxaliplatin and gemcitabine. A retrospective comparison was carried out with a historical group of 11 patients treated with ChT only, estimating the prevalence of adverse effects and the median survival of the two groups. A total of 30 TACEs were performed during the observational time (ranging from one to seven procedures per patient). OEM-TACEs were followed by few adverse effects (AEs), without G4 AEs, according to CTACAE 3.0. According to RECIST criteria, 44% (4/9) of patients achieved partial responses and 56% (5/9) stabililization of disease. Overall survival analysis in the two groups showed a significantly increased survival in patients treated with ChT and OEM-TACE, with respect to those treated with ChT (30 vs. 12.7 months; p = 0.004). In conclusion, in our experience OEM-TACE associated with ChT in the treatment of advanced unresectable ICC is a safe and feasible treatment causing no major adverse events. Although RECIST criteria can underestimate the rate of responses in patients treated with locoregional therapies, we achieved very encouraging results. A randomized multicentric trial is warranted to assess the actual superiority of OEM-TACE associated with ChT compared to conventional chemotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaib Y, El-Serag HB (2004) The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 24:115–125
Nakeeb A, Pitt HA, Sohn TA, Coleman J, Abrams RA, Piantadosi S, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL (1996) Cholangiocarcinoma. A spectrum of intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal tumors. Ann Surg 224:463–473
Burak K, Angulo P, Pasha TM, Egan K, Petz J, Lindor KD (2004) Incidence and risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:523–526
Berthiaume EP, Wands J (2004) The molecular pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 24:127–137
Tan JC, Coburn NG, Baxter NN, Kiss A, Law CH (2008) Surgical management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma—a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol 15:600–608
Shaib YH, Davila JA, Henderson L, McGlynn KA, El-Serag HB (2007) Endoscopic and surgical therapy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol 41:911–917
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y et al (2001) Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 234(4):507–519
Alberts SR, Gores GJ, Kim GP, Roberts LR, Kendrick ML, Rosen CB, Chari ST, Martenson JA (2007) Treatment options for hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer. Mayo Clin Proc 82:628–637
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X et al (2002) Arterial embolization or chemoembolization versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 359:1734–1739
Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK et al (2001) Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Is there room for a new studies? Clin Gastroenterol 32:383–389
Cammà C, Schepis F, Orlando A, Albanese M, Shahied L, Trevisani F, Andreone P, Craxì A, Cottone M (2002) Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology 224:47–54
Lewis AL, Taylor RR, Brenda H et al (2006) Pharmacokinetic and safety study of doxorubicin-eluting beads in a porcine model of hepatic arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:1335–1343
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V, Jaques D, Budach V, Langer C, Murphy B, Cumberlin R, Coleman CN, Rubin P (2003) CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13:176–181
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Non parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
R Development Core Team (2005) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC et al (2008) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg 248:84–96
Yonemoto N, Furuse J, Okusaka T, Yamao K, Funakoshi A, Ohkawa S, Boku N, Tanaka K, Nagase M, Saisho H, Sato T (2007) A multi-center retrospective analysis of survival benefits of chemotherapy for unresectable biliary tract cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:843–851
Charoentum C, Thongprasert S, Chewaskulyong B, Munprakan S (2007) Experience with gemcitabine and cisplatin in the therapy of inoperable and metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 13:2852–2854
Paule B, Herelle MO, Rage E, Ducreux M, Adam R, Guettier C, Bralet MP (2007) Cetuximab plus gemcitabine-oxaliplatin (GEMOX) in patients with refractory advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Oncology 72:105–110
Poggi G, Quaretti P, Minoia C et al (2008) Transhepatic arterial chemoembolization with oxaliplatin-eluting microsphere (OEM-TACE) for unresectable hepatic tumors. Anticancer Res 28:3835–3842
Burger I, Hong K, Schulick R, Georgiades C, Thuluvath P, Choti M, Kamel I, Geschwind JF (2005) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: initial experience in a single institution. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:353–361
Aliberti C, Benea G, Tilli M, Fiorentini G (2008) Chemoembolization (TACE) of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with slow-release doxorubicin-eluting beads: preliminary results. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 5:883–888
Tanaka N, Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Fujii A, Matsumura K, Takeda K (2002) Arterial chemoinfusion therapy through an implanted port system for patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma—initial experience. Eur J Radiol 41:42–48
Vogl TJ, Schwarz W, Eichler K, Hochmuth K, Hammerstingl R, Jacob U, Scheller A, Zangos S, Heller M (2006) Hepatic intraarterial chemotherapy with gemcitabine in patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinomas and liver metastases of pancreatic cancer: a clinical study on maximum tolerable dose and treatment efficacy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:745–755
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poggi, G., Amatu, A., Montagna, B. et al. OEM-TACE: A New Therapeutic Approach in Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 1187–1192 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9694-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9694-4