Abstract
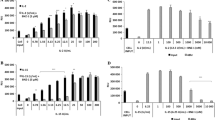
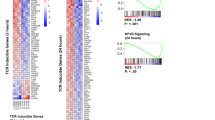
Large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia is a chronic lymphoproliferative disease in which T-bet [T-box transcription factor 21 gene (tbx21)] overexpression may play a pathogenic role. T-bet orchestrates the differentiation of mature peripheral T-cells into interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α producing CD4+ T-helper type I (Th1) and CD8+ T cytotoxic cells that are necessary for antiviral responses. When IL-12 is produced by antigen–presenting cells, T-bet expression is induced, causing direct stimulation of ifng gene transcription while simultaneously acting as a transcriptional repressor of the IL4 gene, which then leads to Th1 dominance and T-helper type 2 differentiation blockade. Additionally, T-bet has been shown to regulate histone acetylation of the ifng promoter and enhancer to loosen condensed DNA, creating greater accessibility for other transcription factor binding, which further amplifies IFNγ production. We found that treatment with a farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib reduced Th1 cytokines in LGL leukemia patient T-cells and blocked T-bet protein expression and IL-12 responsiveness in T-cells from healthy donors. The mechanism of suppression was based on modulation of histone acetylation of the ifng gene, which culminated in Th1 blockade.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nash R, McSweeney P, Zambello R, Semenzato G, Loughran TP Jr (1993) Clonal studies of CD3-lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes. Blood 81:2363–2368
Loughran TP Jr (1993) Clonal diseases of large granular lymphocytes. Blood 82:1–14
Epling-Burnette PK, Sokol L, Chen X, Bai F, Zhou J et al (2008) Clinical improvement by farnesyltransferase inhibition in NK large granular lymphocyte leukemia associated with imbalanced NK receptor signaling. Blood 112:4694–4698
Zhang R, Shah MV, Yang J, Nyland SB, Liu X et al (2008) Network model of survival signaling in large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16308–16313
Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG et al (2000) A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 100:655–669
Rengarajan J, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH (2000) Transcriptional regulation of Th1/Th2 polarization. Immunol Today 21:479–483
Sullivan BM, Juedes A, Szabo SJ, von Herrath M, Glimcher LH (2003) Antigen-driven effector CD8 T cell function regulated by T-bet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15818–15823
Avni O, Lee D, Macian F, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH et al (2002) T(H) cell differentiation is accompanied by dynamic changes in histone acetylation of cytokine genes. Nat Immunol 3:643–651
Agarwal S, Rao A (1998) Modulation of chromatin structure regulates cytokine gene expression during T cell differentiation. Immunity 9:765–775
Valapour M, Guo J, Schroeder JT, Keen J, Cianferoni A et al (2002) Histone deacetylation inhibits IL4 gene expression in T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 109:238–245
Mullen AC, High FA, Hutchins AS, Lee HW, Villarino AV et al (2001) Role of T-bet in commitment of TH1 cells before IL-12-dependent selection. Science 292:1907–1910
Afkarian M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Jacobson NG, Cereb N et al (2002) T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 3:549–557
O’Shea JJ, Paul WE (2010) Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of helper CD4+ T cells. Science 327:1098–1102
Zeiser R, Youssef S, Baker J, Kambham N, Steinman L et al (2007) Preemptive HMG-CoA reductase inhibition provides graft-versus-host disease protection by Th-2 polarization while sparing graft-versus-leukemia activity. Blood 110:4588–4598
Dunn SE, Youssef S, Goldstein MJ, Prod’homme T, Weber MS et al (2006) Isoprenoids determine Th1/Th2 fate in pathogenic T cells, providing a mechanism of modulation of autoimmunity by atorvastatin. J Exp Med 203:401–412
Youssef S, Stuve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL et al (2002) The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 420:78–84
Lerner EC, Zhang TT, Knowles DB, Qian Y, Hamilton AD et al (1997) Inhibition of the prenylation of K-Ras, but not H- or N-Ras, is highly resistant to CAAX peptidomimetics and requires both a farnesyltransferase and a geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitor in human tumor cell lines. Oncogene 15:1283–1288
Miquel K, Pradines A, Sun J, Qian Y, Hamilton AD et al (1997) GGTI-298 induces G0-G1 block and apoptosis whereas FTI-277 causes G2-M enrichment in A549 cells. Cancer Res 57:1846–1850
Epling-Burnette PK, Loughran TP Jr (2010) Suppression of farnesyltransferase activity in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: current understanding and recommended use of tipifarnib. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:689–698
Kurzrock R, Cortes J, Kantarjian H (2002) Clinical development of farnesyltransferase inhibitors in leukemias and myelodysplastic syndrome. Semin Hematol 39:20–24
Reid TS, Beese LS (2004) Crystal structures of the anticancer clinical candidates R115777 (Tipifarnib) and BMS-214662 complexed with protein farnesyltransferase suggest a mechanism of FTI selectivity. Biochemistry 43:6877–6884
Raponi M, Lancet JE, Fan H, Dossey L, Lee G et al (2008) A 2-gene classifier for predicting response to the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111:2589–2596
Raponi M, Belly RT, Karp JE, Lancet JE, Atkins D et al (2004) Microarray analysis reveals genetic pathways modulated by tipifarnib in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer 4:56
Karp JE, Lancet JE (2008) Tipifarnib in the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia. Biologics 2:491–500
Brandwein JM, Leber BF, Howson-Jan K, Schimmer AD, Schuh AC et al (2009) A phase I study of tipifarnib combined with conventional induction and consolidation therapy for previously untreated patients with acute myeloid leukemia aged 60 years and over. Leukemia 23:631–634
Harousseau JL (2007) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors in hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev 21:173–182
Harousseau JL, Lancet JE, Reiffers J, Lowenberg B, Thomas X et al (2007) A phase 2 study of the oral farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 109:5151–5156
Goemans BF, Zwaan CM, Harlow A, Loonen AH, Gibson BE et al (2005) In vitro profiling of the sensitivity of pediatric leukemia cells to tipifarnib: identification of T-cell ALL and FAB M5 AML as the most sensitive subsets. Blood 106:3532–3537
Biagi C, Astolfi A, Masetti R, Serravalle S, Franzoni M et al (2010) Pediatric early T-cell precursor leukemia with NF1 deletion and high-sensitivity in vitro to tipifarnib. Leukemia 24:1230–1233
Witzig TE, Tang H, Micallef IN, Ansell SM, Link BK et al (2011) Multi-institutional phase II of the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib (R115777) in patients with relapsed and refractory lymphomas. Blood [Epub ahead of print]
Marks RE, Ho AW, Robbel C, Kuna T, Berk S et al (2007) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors inhibit T-cell cytokine production at the posttranscriptional level. Blood 110:1982–1988
Epling-Burnette PK, Painter JS, Rollison DE, Ku E, Vendron D et al (2007) Prevalence and clinical association of clonal T-cell expansions in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Leukemia 21:659–667
Epling-Burnette PK, Bai F, Wei S, Chaurasia P, Painter JS et al (2004) ERK couples chronic survival of NK cells to constitutively activated Ras in lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes (LDGL). Oncogene 23:9220–9229
Chen X, Bai F, Sokol L, Zhou J, Ren A et al (2009) A critical role for DAP10 and DAP12 in CD8+ cell-mediated tissue damage in large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood 113:3226–3234
Zou JX, Rollison DE, Boulware D, Chen DT, Sloand EM et al (2009) Altered naive and memory CD4+ T-cell homeostasis and immunosenescence characterize younger patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 23:1288–1296
Villagra A, Cheng F, Wang HW, Suarez I, Glozak M et al (2009) The histone deacetylase HDAC11 regulates the expression of interleukin 10 and immune tolerance. Nat Immunol 10:92–100
Morinobu A, Kanno Y, O’Shea JJ (2004) Discrete roles for histone acetylation in human T helper 1 cell-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 279:40640–40646
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Yang J, Epling-Burnette PK, Painter JS, Zou J, Bai F et al (2008) Antigen activation and impaired Fas-induced death-inducing signaling complex formation in T-large-granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood 111:1610–1616
Sebti SM, Hamilton AD (1996) Rational design of Ras prenyltransferase inhibitors as potential anticancer drugs. Biochem Soc Trans 24:692–699
Magram J, Sfarra J, Connaughton S, Faherty D, Warrier R et al (1996) IL-12-deficient mice are defective but not devoid of type 1 cytokine responses. Ann NY Acad Sci 795:60–70
Zhang S, Lukacs NW, Lawless VA, Kunkel SL, Kaplan MH (2000) Cutting edge: differential expression of chemokines in Th1 and Th2 cells is dependent on Stat6 but not Stat4. J Immunol 165:10–14
Mingari MC, Maggi E, Cambiaggi A, Annunziato F, Schiavetti F et al (1996) Development in vitro of human CD4+ thymocytes into functionally mature Th2 cells. Exogenous interleukin-12 is required for priming thymocytes to produce both Th1 cytokines and interleukin-10. Eur J Immunol 26:1083–1087
Collins JT, Dunnick WA (1999) Cutting edge: IFN-gamma regulated germline transcripts are expressed from gamma2a transgenes independently of the heavy chain 3′ enhancers. J Immunol 163:5758–5762
Spilianakis CG, Lee GR, Flavell RA (2005) Twisting the Th1/Th2 immune response via the retinoid × receptor: lessons from a genetic approach. Eur J Immunol 35:3400–3404
Chen X, Vodanovic-Jankovic S, Johnson B, Keller M, Komorowski R et al (2007) Absence of regulatory T-cell control of TH1 and TH17 cells is responsible for the autoimmune-mediated pathology in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 110:3804–3813
Esensten JH, Lee MR, Glimcher LH, Bluestone JA (2009) T-bet-deficient NOD mice are protected from diabetes due to defects in both T cell and innate immune system function. J Immunol 183:75–82
Gocke AR, Cravens PD, Ben LH, Hussain RZ, Northrop SC et al (2007) T-bet regulates the fate of Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes in autoimmunity. J Immunol 178:1341–1348
Ji N, Sosa RA, Forsthuber TG (2011) More than just a T-box: the role of T-bet as a possible biomarker and therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases. Immunotherapy 3:435–441
Liu R, Hao J, Dayao CS, Shi FD, Campagnolo DI (2009) T-bet deficiency decreases susceptibility to experimental myasthenia gravis. Exp Neurol 220:366–373
Shi Y, Wang H, Su Z, Chen J, Xue Y et al (2010) Differentiation imbalance of Th1/Th17 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells might contribute to pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Scand J Immunol 72:250–255
You Y, Zhao W, Chen S, Tan W, Dan Y et al (2010) Association of TBX21 gene haplotypes in a Chinese population with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol 39:254–258
Shi M, Lin TH, Appell KC, Berg LJ (2008) Janus-kinase-3-dependent signals induce chromatin remodeling at the Ifng locus during T helper 1 cell differentiation. Immunity 28:763–773
Oliveira JB, Bidere N, Niemela JE, Zheng L, Sakai K et al (2007) NRAS mutation causes a human autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8953–8958
Bolick SC, Landowski TH, Boulware D, Oshiro MM, Ohkanda J et al (2003) The farnesyl transferase inhibitor, FTI-277, inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in drug-resistant myeloma tumor cells. Leukemia 17:451–457
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the NCI R01CA11211201, the NIH AI056213 and U54RR019397-05. Tipifarnib was provided by the Cancer Therapies Evaluation Program (CTEP). Flow cytometry support was provided by the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center Flow Cytometry Core Facility.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, F., Villagra, A.V., Zou, J. et al. Tipifarnib-mediated suppression of T-bet-dependent signaling pathways. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61, 523–533 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1109-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1109-0