Abstract
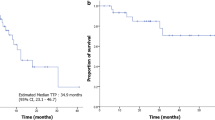
Ovarian cancer patients with persistent (platinum-resistant) or progressive (platinum-refractory) disease respond poorly to second line chemotherapy and have low survival expectancy. New and improved therapeutic approaches are needed and immune biologics are one possibility. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a T-cell growth factor believed to be important in anti-tumor immunity. We performed a phase II clinical trial with intraperitoneal (IP) recombinant IL-2 administered in weekly infusions of 6 × 105 IU/m2. Thirty-one subjects were sequentially entered into the study and clinical responses were surgically confirmed in 24 patients. The primary end point of this study was clinical response with immunologic measurements as secondary end points. The IP regimen was generally well tolerated. Of the 24 patients assessed for response, there were 6 (4 complete, 2 partial) responses for an overall response rate of 25.0% [95% confidence interval (CI) of 11–45]. The median survival of the 31 patient cohort was 2.1 years (95% CI of 1.3–4.4), but for the 6 patients with responses the median survival has not been reached (range 24–120+ months). Eosinophil and lymphocyte numbers were continuously monitored during treatment. Peripheral blood eosinophils were markedly increased at the completion of treatment (p < 0.0001) and associated with increased circulating eotaxin (p = 0.03). We also found significant associations between changes in CD3 counts and survival (p = 0.05) and between IFNγ-secreting CD8 T cells at early time points and survival (p = 0.04). This study provides important evidence for IP IL-2 in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer and identifies several immune correlates of survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ (2005) Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 55:10–30
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Cannistra SA (2004) Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med 351:2519–2529
Gordon AN, Fleagle JT, Guthrie D, Parkin DE, Gore ME, Lacave AJ (2001) Recurrent epithelial ovarian carcinoma: a randomized phase III study of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin versus topotecan. J Clin Oncol 19:3312–3322
Alberts DS, Liu PY, Hannigan EV, O’Toole R, Williams SD, Young JA, Franklin EW, Clarke-Pearson DL, Malviya VK, DuBeshter B (1996) Intraperitoneal cisplatin plus intravenous cyclophosphamide versus intravenous cisplatin plus intravenous cyclophosphamide for stage III ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 335:1950–1955
Markman M, Blessing JA, Moore D, Ball H, Lentz SS (1998) Altretamine (hexamethylmelamine) in platinum-resistant and platinum-refractory ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group phase II trial. Gynecol Oncol 69:226–229
Armstrong DK, Bundy B, Wenzel L, Huang HQ, Baergen R, Lele S, Copeland LJ, Walker JL, Burger RA (2006) Intraperitoneal cisplatin and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 354:34–43
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Matory YL, Skibber JM, Shiloni E, Vetto JT et al (1985) Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med 313:1485–1492
Elias L, Hunt WC (2001) A literature analysis of prognostic factors for response and quality of response of patients with renal cell carcinoma to interleukin-2-based therapy. Oncology 61:91–101
Grande C, Firvida JL, Navas V, Casal J (2006) Interleukin-2 for the treatment of solid tumors other than melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 17:1–12
Edwards RP, Gooding W, Lembersky BC, Colonello K, Hammond R, Paradise C, Kowal CD, Kunschner AJ, Baldisseri M, Kirkwood JM, Herberman RB (1997) Comparison of toxicity and survival following intraperitoneal recombinant interleukin-2 for persistent ovarian cancer after platinum: twenty-four-hour versus 7-day infusion. J Clin Oncol 15:3399–3407
Markman M, Reichman B, Hakes T, Lewis JL Jr, Jones W, Rubin S, Barakat R, Curtin J, Almadrones L, Hoskins W (1992) Impact on survival of surgically defined favorable responses to salvage intraperitoneal chemotherapy in small-volume residual ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 10:1479–1484
Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, Abrams J, Sznol M, Parkinson D, Hawkins M, Paradise C, Kunkel L, Rosenberg SA (1999) High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol 17:2105–2116
Fyfe G, Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Sznol M, Parkinson DR, Louie AC (1995) Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol 13:688–696
Donskov F, Bennedsgaard KM, Von Der Maase H, Marcussen N, Fisker R, Jensen JJ, Naredi P, Hokland M (2002) Intratumoural and peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma undergoing interleukin-2 based immunotherapy: association to objective response and survival. Br J Cancer 87:194–201
Fumagalli L, Lissoni P, Di Felice G, Meregalli S, Valsuani G, Mengo S, Rovelli F (1999) Pretreatment serum markers and lymphocyte response to interleukin-2 therapy. Br J Cancer 80:407–411
Jeong IG, Han KS, Joung JY, Choi WS, Hwang SS, Yang SO, Seo HK, Chung J, Lee KH (2007) Analysis of changes in the total lymphocyte and eosinophil count during immunotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: correlation with response and survival. J Korean Med Sci 22:S122–S128
Markman M, Bundy BN, Alberts DS, Fowler JM, Clark-Pearson DL, Carson LF, Wadler S, Sickel J (2001) Phase III trial of standard-dose intravenous cisplatin plus paclitaxel versus moderately high-dose carboplatin followed by intravenous paclitaxel and intraperitoneal cisplatin in small-volume stage III ovarian carcinoma: an intergroup study of the Gynecologic Oncology Group, Southwestern Oncology Group, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 19:1001–1007
Bordin V, Giani L, Meregalli S, Bukovec R, Vaghi MM, Mandala M, Paolorossi F, Ardizzoia A, Tancini G, Barni S, Frigerio F, Fumagalli L, Bordoni A, Valsuani G, Di Felice G, Lissoni P (2000) Five-year survival results of subcutaneous low-dose immunotherapy with interleukin-2 alone in metastatic renal cell cancer patients. Urol Int 64:3–8
Lissoni P, Barni S, Ardizzoia A, Crispino S, Paolorossi F, Andres M, Scardino E, Tancini G (1994) Prognostic factors of the clinical response to subcutaneous immunotherapy with interleukin-2 alone in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncology 51:59–62
Palmer PA, Atzpodien J, Philip T, Negrier S, Kirchner H, Von der Maase H, Geertsen P, Evers P, Loriaux E, Oskam R et al (1993) A comparison of 2 modes of administration of recombinant interleukin-2: continuous intravenous infusion alone versus subcutaneous administration plus interferon alpha in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biother 8:123–136
von Rohr A, Ghosh AK, Thatcher N, Stern PL (1993) Immunomodulation during prolonged treatment with combined interleukin-2 and interferon-alpha in patients with advanced malignancy. Br J Cancer 67:163–171
Wersall P, Mellstedt H (1995) Increased LAK and T cell activation in responding renal cell carcinoma patients after low dose cyclophosphamide, IL-2 and alpha-IFN. Med Oncol 12:69–77
Degrate L, Nobili C, Franciosi C, Caprotti R, Brivio F, Romano F, Leone BE, Trezzi R, Uggeri F (2009) Interleukin-2 immunotherapy action on innate immunity cells in peripheral blood and tumoral tissue of pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg 394:115–121
Rand TH, Silberstein DS, Kornfeld H, Weller PF (1991) Human eosinophils express functional interleukin 2 receptors. J Clin Invest 88:825–832
Lamkhioued B, Renzi PM, Abi-Younes S, Garcia-Zepada EA, Allakhverdi Z, Ghaffar O, Rothenberg MD, Luster AD, Hamid Q (1997) Increased expression of eotaxin in bronchoalveolar lavage and airways of asthmatics contributes to the chemotaxis of eosinophils to the site of inflammation. J Immunol 159:4593–4601
Mattoli S, Stacey MA, Sun G, Bellini A, Marini M (1997) Eotaxin expression and eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236:299–301
Ying S, Robinson DS, Meng Q, Rottman J, Kennedy R, Ringler DJ, Mackay CR, Daugherty BL, Springer MS, Durham SR, Williams TJ, Kay AB (1997) Enhanced expression of eotaxin and CCR3 mRNA and protein in atopic asthma Association with airway hyperresponsiveness and predominant co-localization of eotaxin mRNA to bronchial epithelial and endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol 27:3507–3516
Fernandez-Acenero MJ, Galindo-Gallego M, Sanz J, Aljama A (2000) Prognostic influence of tumor-associated eosinophilic infiltrate in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 88:1544–1548
Rivoltini L, Viggiano V, Spinazze S, Santoro A, Colombo MP, Takatsu K, Parmiani G (1993) In vitro anti-tumor activity of eosinophils from cancer patients treated with subcutaneous administration of interleukin 2. Role of interleukin 5. Int J Cancer 54:8–15
Samoszuk M (1997) Eosinophils and human cancer. Histol Histopathol 12:807–812
Leighton SE, Teo JG, Leung SF, Cheung AY, Lee JC, van Hasselt CA (1996) Prevalence and prognostic significance of tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 77:436–440
Moroni M, Porta C, De Amici M, Quaglini S, Cattabiani MA, Buzio C (2000) Eosinophils and C4 predict clinical failure of combination immunotherapy with very low dose subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon in renal cell carcinoma patients. Haematologica 85:298–303
van Driel WJ, Hogendoorn PC, Jansen FW, Zwinderman AH, Trimbos JB, Fleuren GJ (1996) Tumor-associated eosinophilic infiltrate of cervical cancer is indicative for a less effective immune response. Hum Pathol 27:904–911
Karagiannis SN, Bracher MG, Hunt J, McCloskey N, Beavil RL, Beavil AJ, Fear DJ, Thompson RG, East N, Burke F, Moore RJ, Dombrowicz DD, Balkwill FR, Gould HJ (2007) IgE-antibody-dependent immunotherapy of solid tumors: cytotoxic and phagocytic mechanisms of eradication of ovarian cancer cells. J Immunol 179:2832–2843
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2001) Inflammatory cells and cancer: think different. J Exp Med 193:F23–F26
Cesana GC, Romano F, Piacentini G, Scotti M, Brenna A, Bovo G, Vaghi M, Aletti G, Caprotti R, Kaufman H, Uggeri F (2007) Low-dose interleukin-2 administered pre-operatively to patients with gastric cancer activates peripheral and peritumoral lymphocytes but does not affect prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 14:1295–1304
Donskov F, Bennedsgaard KM, Hokland M, Marcussen N, Fisker R, Madsen HH, Fode K, von der Maase H (2004) Leukocyte orchestration in blood and tumour tissue following interleukin-2 based immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:729–739
Clarke B, Tinker AV, Lee CH, Subramanian S, van de Rijn M, Turbin D, Kalloger S, Han G, Ceballos K, Cadungog MG, Huntsman DG, Coukos G, Gilks CB (2008) Intraepithelial T cells and prognosis in ovarian carcinoma: novel associations with stage, tumor type, and BRCA1 loss. Mod Pathol 22:393–402
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, Jungbluth AA, Frosina D, Gnjatic S, Ambrosone C, Kepner J, Odunsi T, Ritter G, Lele S, Chen YT, Ohtani H, Old LJ, Odunsi K (2005) Intraepithelial CD8 + tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8 +/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18538–18543
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, Makrigiannakis A, Gray H, Schlienger K, Liebman MN, Rubin SC, Coukos G (2003) Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 348:203–213
Egeter O, Mocikat R, Ghoreschi K, Dieckmann A, Rocken M (2000) Eradication of disseminated lymphomas with CpG-DNA activated T helper type 1 cells from nontransgenic mice. Cancer Res 60:1515–1520
Hunder NN, Wallen H, Cao J, Hendricks DW, Reilly JZ, Rodmyre R, Jungbluth A, Gnjatic S, Thompson JA, Yee C (2008) Treatment of metastatic melanoma with autologous CD4+ T cells against NY-ESO-1. N Engl J Med 358:2698–2703
Muller-Hermelink N, Braumuller H, Pichler B, Wieder T, Mailhammer R, Schaak K, Ghoreschi K, Yazdi A, Haubner R, Sander CA, Mocikat R, Schwaiger M, Forster I, Huss R, Weber WA, Kneilling M, Rocken M (2008) TNFR1 signaling and IFN-gamma signaling determine whether T cells induce tumor dormancy or promote multistage carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 13:507–518
Grange JM, Bottasso O, Stanford CA, Stanford JL (2008) The use of mycobacterial adjuvant-based agents for immunotherapy of cancer. Vaccine 26:4984–4990
Schon MP, Schon M (2008) TLR7 and TLR8 as targets in cancer therapy. Oncogene 27:190–199
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8:579–591
Longo R, Gasparini G (2008) Anti-VEGF therapy: the search for clinical biomarkers. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 8:301–314
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH R21 CA74105-02S1, American Cancer Society, Chiron Therapeutics, PA Department of Health and the Magee-Womens Health Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vlad, A.M., Budiu, R.A., Lenzner, D.E. et al. A phase II trial of intraperitoneal interleukin-2 in patients with platinum-resistant or platinum-refractory ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59, 293–301 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0750-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0750-3