Abstract
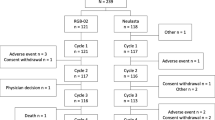
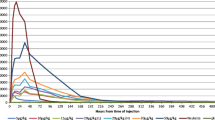
Recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is used in immunotherapy for correction of neutropoenia. The optimal dose for activation of immune functions and the pharmacokinetics following repeated administrations is less analysed in depth. In this study, the pharmacokinetics and the effects on haematological functions and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) were analysed in 50 patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma receiving monoclonal antibody based therapy in combination with Escherichia coli-derived GM-CSF (molgramostim) administered s.c. once daily for 10 days every month over a period of 4 months. Thirty-three patients received a GM-CSF dose of 200–250 μg/m2/day. Seventeen patients received GM-CSF doses varying between 65 and 325 μg/m2/day in the different treatment cycles. Serum GM-CSF concentration was measured (ELISA) before and 3–4 h after (peak serum concentration) GM-CSF administration days 1, 5 and 10. Prior to therapy, GM-CSF was not detectable in serum. Following repeated daily administrations, the peak serum concentration of GM-CSF gradually decreased on days 5 and 10 compared to day 1 (P < 0.05). During a 10-day treatment cycle, the total number of leukocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes and lymphocytes increased. A dose-dependent increment in total white blood cell count and neutrophils was observed. The total numbers of GM-CSF receptor (α-subunit) expressing cells (granulocytes and monocytes) increased significantly during treatment while a transient decline in expression intensity was observed at day 5, suggesting a receptor-mediated removal of GM-CSF as a mechanism for the elimination of GM-CSF from circulation. ADCC of peripheral mononuclear cells was decreased at day 10 compared to baseline. An inverse correlation between the dose and ADCC was noted. The data might indicate that high doses of GM-CSF may have a negative impact on ADCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JO (1998) Emerging applications of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood 92(12):4491–4508
Aweeka FT, Kwong M, Mak M, al-Uzri A, Affrime M, Cutler D, Kahn J, Gambertoglio JG (1996) Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: the effects of zidovudine. J Clin Pharmacol 36(12):1107–1113
Baselga J, Arteaga CL (2005) Critical update and emerging trends in epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(11):2445–2459
Bukowski RM, Budd GT, Gibbons JA, Bauer RJ, Childs A, Antal J, Finke J, uason L, Lorenzi V, McLain D, et al (1994) Phase I trial of subcutaneous recombinant macrophage colony-stimulating factor: clinical and immunomodulatory effects. J Clin Oncol 12(1):97–106
Burgess AW, Begley CG, Johnson GR, Lopez AF, Williamson DJ, Mermod JJ, Simpson RJ, Schmitz A, DeLamarter JF (1987) Purification and properties of bacterially synthesized human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Blood 69(1):43–51
Cannistra SA, Groshek P, Garlick R, Miller J, Griffin JD (1990) Regulation of surface expression of the granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor in normal human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(1):93–97
Cebon J, Dempsey P, Fox R, Kannourakis G, Bonnem E, Burgess AW, Morstyn G (1988) Pharmacokinetics of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor using a sensitive immunoassay. Blood 72(4):1340–1347
Cebon JS, Bury RW, Lieschke GJ, Morstyn G (1990) The effects of dose and route of administration on the pharmacokinetics of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Eur J Cancer 26(10):1064–1069
Chachoua A, Oratz R, Hoogmoed R, Caron D, Peace D, Liebes L, Blum RH, Vilcek J (1994) Monocyte activation following systemic administration of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 15(3):217–224
Collins TS, Hurwitz HI (2005) Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol 32(1):61–68
Gregory B, Kirchem A, Phipps S, Gevaert P, Pridgeon C, Rankin SM, Robinson DS (2003) Differential regulation of human eosinophil IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF receptor alpha-chain expression by cytokines: IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF down-regulate IL-5 receptor alpha expression with loss of IL-5 responsiveness, but up-regulate IL-3 receptor alpha expression. J Immunol 170(11):5359–5366
Gribben JG, Devereux S, Thomas NS, Keim M, Jones HM, Goldstone AH, Linch DC (1990) Development of antibodies to unprotected glycosylation sites on recombinant human GM-CSF. Lancet 335(8687):434–437
Hellman C, Lonnkvist K, Hedlin G, Hallden G, Lundahl J (2002) Down-regulated IL-5 receptor expression on peripheral blood eosinophils from budesonide-treated children with asthma. Allergy 57(4):323–328
Herlyn M, Steplewski Z, Herlyn D, Koprowski H (1979) Colorectal carcinoma-specific antigen: detection by means of monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76(3):1438–1442
Hovgaard D, Mortensen BT, Schifter S, Nissen NI (1993) Comparative pharmacokinetics of single-dose administration of mammalian and bacterially-derived recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Eur J Haematol 50(1):32–36
Kuwabara T, Kobayashi S, Sugiyama Y (1996) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Drug Metab Rev 28(4):625–658
Lieschke GJ, Burgess AW (1992) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (2). N Engl J Med 327(2):99–106
Liljefors M, Nilsson B, Fagerberg J, Ragnhammar P, Mellstedt H, Frodin J-E (2005) Clinical effects of a chimeric anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Int J Oncol 26(6):1581–1589
Liljefors M, Ragnhammar P, Nilsson B, Ullenhag G, Mellstedt H, Frodin J-E (2004) Anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody (MAb17-1A) based treatment combined with alpha-interferon, 5-fluorouracil and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Int J Oncol 25(3):703–711
Martinez-Moczygemba M, Huston DP (2003) Biology of common beta receptor-signaling cytokines: IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112(4):653–665; quiz 666
Masucci G, Wersall P, Ragnhammar P, Mellstedt H (1989) Granulocyte-monocyte-colony-stimulating factor augments the cytotoxic capacity of lymphocytes and monocytes in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 29(4):288–292
Mellstedt H (2003) Monoclonal antibodies in human cancer. Drugs Today (Barc) 39(Suppl C):1–16
Mellstedt H, Fagerberg J, Frodin J-E, Henriksson L, Hjelm-Skog A-L, Liljefors M, Ragnhammar P, Shetye J, Osterborg A (1999) Augmentation of the immune response with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other hematopoietic growth factors. Curr Opin Hematol 6(3):169–175
Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Mifsud S, Di Rago L (1999) Receptor clearance obscures the magnitude of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor responses in mice to endotoxin or local infections. Blood 93(5):1579–1585
Molineux G (2004) The design and development of pegfilgrastim (PEG-rmetHuG-CSF, Neulasta). Curr Pharm Des 10(11):1235–1244
Muller CE, Mukodzi S, Reddemann H (1999) Relationships of cytokine (GM-CSF) serum concentration to blood cell count and the inflammatory parameters in children with malignant diseases. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 16(6):509–518
Pardoll DM (2000) Therapeutic vaccination for cancer. Clin Immunol 95(1 Pt 2):S44–S62
Parmiani G, Castelli C, Pilla L, Santinami M, Colombo MP, Rivoltini L (2007) Opposite immune functions of GM-CSF administered as vaccine adjuvant in cancer patients. Ann Oncol 18:226–232
Ragnhammar P, Masucci G, Frodin J-E, Hjelm A-L, Mellstedt H (1992) Cytotoxic functions of blood mononuclear cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma treated with mAb 17-1A and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor. Cancer Immunol Immunother 35(3):158–164
Ragnhammar P, Fagerberg J, Frodin J-E, Hjelm A-L, Lindemalm C, Magnusson I, Masucci G, Mellstedt H (1993) Effect of monoclonal antibody 17-1A and GM-CSF in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma—long-lasting, complete remissions can be induced. Int J Cancer 53(5):751–758
Ragnhammar P, Friesen HJ, Frodin J-E, Lefvert AK, Hassan M, Osterborg A, Mellstedt H (1994) Induction of anti-recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (Escherichia coli-derived) antibodies and clinical effects in nonimmunocompromised patients. Blood 84(12):4078–4087
Ragnhammar P, Frodin J-E, Trotta PP, Mellstedt H (1994) Cytotoxicity of white blood cells activated by granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor and macrophage-colony-stimulating factor against tumor cells in the presence of various monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 39(4):254–262
Serafini P, Carbley R, Noonan KA, Tan G, Bronte V, Borrello I (2004) High-dose granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-producing vaccines impair the immune response through the recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells. Cancer Res 64(17):6337–6343
Shaw DR, Khazaeli MB, Sun LK, Ghrayeb J, Daddona PE, McKinney S, LoBuglio AF (1987) Characterization of a mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody (17-1A) to a colon cancer tumor-associated antigen. J Immunol 138(12):4534–4538
Stute N, Furman WL, Schell M, Evans WE (1995) Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in children after intravenous and subcutaneous administration. J Pharm Sci 84(7):824–828
Thompson JA, Lee DJ, Kidd P, Rubin E, Kaufmann J, Bonnem EM, Fefer A (1989) Subcutaneous granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and hematological effects. J Clin Oncol 7(5):629–637
Ullenhag G, Bird C, Ragnhammar P, Frodin J-E, Strigard K, Osterborg A, Thorpe R, Mellstedt H, Wadhwa M (2001) Incidence of GM-CSF antibodies in cancer patients receiving GM-CSF for immunostimulation. Clin Immunol 99(1):65–74
Wadhwa M, Skog A-L, Bird C, Ragnhammar P, Liljefors M, Gaines-Das R, Mellstedt H, Thorpe R (1999) Immunogenicity of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) products in patients undergoing combination therapy with GM-CSF. Clin Cancer Res 5(6):1353–1361
Weiner GJ, Link BK (2004) Antibody therapy of lymphoma. Adv Pharmacol 51:229–253
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society, Cancer Society in Stockholm, King Gustav V Jubilee Fund, Cancer and Allergy Foundation, Torsten and Ragnar Söderberg Foundation and Karolinska Institute Foundations. We thank Lena Virving, Birgitta Hagström and Juan Castro for skillful technical assistance and Leila Relander for excellent typing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liljefors, M., Nilsson, B., Mellstedt, H. et al. Influence of varying doses of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on pharmacokinetics and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57, 379–388 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0377-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0377-1