Abstract
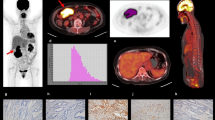
Background: Local recurrence, the most frequent pattern of recurrence of rectal carcinoma, is almost always fatal. The difficulty of diagnosing local recurrence contributes importantly to the poor prognosis. Methods: We coupled monoclonal antibody (Mab) A7, which reacts specifically with human colorectal carcinoma, to ferromagnetic lignosite (FML) particles to distinguish rectal carcinoma from other tissues by magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. We examined retention of immunoreactivity by the A7-FML complexes in vitro, and also their distribution in vivo according to radiolabeling and MR imaging when injected into nude mice bearing human colorectal carcinoma xenografts. Results: A7-FML retained binding activity nearly identical to that of Mab A7. Significantly more 125I-labeled A7-FML accumulated in engrafted tumors than did 125I-labeled normal mouse IgG-FML complexes (P<0.05). A7-FML disappeared rapidly from the blood. Normal tissues accumulated less 125I-labeled A7-FML than tumors; this accumulation decreased linearly with time. In MR imaging, signal intensity was reduced in the tumor by the injection of A7-FML. Conclusions: A7-FML is potentially useful as a MR contrast enhancing agent for human colorectal carcinoma xenografts implanted subcutaneously.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballou B, Levine G, Hakala TR, Solter D (1979) Tumor location detected with radioactively labeled monoclonal antibody and external scintigraphy. Science 206:844–847
Borris TJ, Weber CR (1999) Ferromagnetic MRI artifact secondary to a previous mandibular modified condylotomy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:104–105
Brouwers AH, Dorr U, Lang O, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Steffens MG, Oosterwijk E, Mergenthaler HG, Bihl H, Corstens FH (2002) 131I-cG250 monoclonal antibody immunoscintigraphy versus [18 F]FDG-PET imaging in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a comparative study. Nucl Med Commun 23:229–236
Bydder GM (1987) Clinical application of gadolinium-DTPA. In: Stark DD, Bradley WG (eds) Magnetic resonance imaging. Mosby, St Louis, pp 182–200
Condon B, Hadley DM, Hodgson R (2001) The ferromagnetic pillow: a potential MR hazard not detectable by a hand-held magnet. Br J Radiol 74:847–851
Del Sole A, Moncayo R, Tafuni G, Lucignani G (2004) Position of nuclear medicine techniques in the diagnostic work-up of brain tumors. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 48:76–81
Di Matteo G, Peparini N, Maturo A, Di Matteo FM, Zeri KP, Redler A, Mascagni D (2001) Lateral pelvic lymphadenectomy and total nerve sparing for locally advanced rectal cancer in Western patients. Panminerva Med 43:95–101
Hunter WM, Greenwood FC (1962) Preparation of iodine, 131I-labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature 194:495–496
Jani AB, Blend MJ, Hamilton R, Brendler C, Pelizzari C, Krauz L, Sapra B, Vijayakumar S, Awan A, Weichselbaum RR (2004) Radioimmunoscintigraphy for postprostatectomy radiotherapy: analysis of toxicity and biochemical control. J Nucl Med 45:1315–1322
Kitamura K, Takahashi T, Yamaguchi T, Yokota T, Noguchi A, Amagai T, Imanishi J (1989) Immunochemical characterization of the antigen recognized by the murine monoclonal antibody A7 against human colorectal cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 157:83–93
Mendonca-Diasand MH, Lauterbur PC (1986) Biological trace elements research. Magn Reson Med 3: 328–330
Molday RS, Yen SPS, Rembaum A (1977) Application of magnetic microspheres in labelling and separation of cells. Nature 268:437–438
Nakada K, Sakamoto J, Watanabe T, Itoh K, Akiyama S, Takagi H (1997) Imaging of recurrent intestinal carcinoma with indium-111-labeled anti-carcinoembrionic antigen CEA102. Jpn J Cancer Res 88:605–613
Oriuchi N, Watanabe N, Sugimachi S, Higuchi T, Imai K, Yamanaka H, Hashimoto M, Kanda H, Endo K (1996) Different biodistribution of 99mTc-labelled chimeric mouse-human monoclonal antibody between athymic mice model and human. Br J Cancer 73:1466–1472
Otsuji E, Yamaguchi Y, Yamaguchi N, Koyama K, Imanishi J, Yamaoka N, Takahashi T (1992) Expression of the cell surface antigen detected by the monoclonal antibody A7 in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Jpn J Surg 22:351–356
Otsuji E, Tsuruta H, Toma A, Kobayashi S, Okamoto K, Yata Y, Yamagishi H (2003) Effects of idiotypic human anti-mouse antibody against in vitro binding and antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate. Hepato Gasroenterol 50: 380–384
Phom H, Kumar A, Tripathi M, Chandrashekar N, Choudhry VP, Malhotra A, Bal CS (2004) Comparative evaluation of Tc-99 m-heat-denatured RBC and Tc-99 m-anti-D IgG opsonized RBC spleen planar and SPECT scintigraphy in the detection of accessory spleen in post splenectomy patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Clin Nucl Med 29:403–409
Renshaw PF, Owen CS, McLaughlin AC, Frey TG, Leigh JS (1986) Ferromagnetic contrast agents: a new approach. Magn Reson Med 3:217–225
Saini S, Stark DD, Hahn PF, Bousquet JC, Introcasso J, Wittenberg J, Brady TJ, Ferrucci JT (1987) Ferrite particles: A superparamagnetic MR contrast agent for enhanced detection of liver carcinoma. Radiology 162:217–222
Schoefl GI (1963) Studies on inflammation. III. Growing capillaries: their structure and permeability. Viwchow’s Arch Path Anat 337:97–141
Seneterre E, Weissleder R, Jaramillo D, Reimer P, Lee AS, Brady TJ, Wittenberg J (1991) Bone marrow: Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide for MR imaging. Radiology 179:529–533
Stark DD, Weissleder R, Elizondo G, Hahn PF, Saini S, Todd LE, Wittenberg J, Ferrucci JT (1988) Superparamagnetic iron oxide: clinical application as a contrast agent for MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 168:297–301
Takahashi T, Yamaguchi T, Kitamura K, Noguchi A, Honda M, Otsuji E (1993) Follow-up study of patients treated with monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate: report of 77 cases with colorectal cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 84:976–981
Weissleder R, Elizondo G, Wittenberg J, Rabiato CA, Bebgele HH, Josephson L (1990) Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide: An intravenous contrast agent for assessing lymph nodes with MR imaging. Radiology 175:494–498
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otsuji, E., Kuriu, Y., Okamoto, K. et al. Monoclonal antibody A7 coupled to magnetic particles as a contrast enhancing agent for magnetic resonance imaging of human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55, 728–733 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0067-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0067-9