Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to assess the reproducibility in healthy volunteers of α-[11C]methyl-l-tryptophan (α[11C]MT) brain trapping imaging with positron emission tomography (PET), using volumes of interest (VOIs) and voxel-based image analysis.
Methods
Six right-handed healthy male volunteers (34.3±10.9 years) with a negative family history for psychiatric disorders were scanned twice in the resting condition, 22±17 days apart. An unbiased semiautomatic segmentation of the brain was used to define VOIs. The trapping constant K* (ml g−1 min−1) for α[11C]MT was calculated for the whole brain and seven brain regions using the graphical method for irreversible tracers. In addition, parametric maps of K* were obtained from dynamic scans using the same method. Comparison of test and retest K* functional images was performed using SPM99. Student’s paired t statistic was applied for comparisons of α[11C]MT brain trapping in a priori selected VOIs.
Results
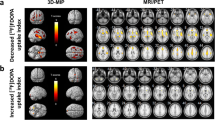
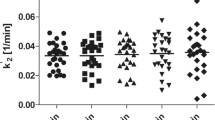
α[11C]MT brain trapping in VOIs showed a mean variability 2.6±1.8% (0.3–5%) for absolute and 1.5±2.1% (1.4–4.1%) for normalized K*. Intraclass correlations between test and retest conditions were 0.61±0.34 for absolute K* values and 0.73±0.20 for K* values normalized by global mean. SPM99 analysis using a height threshold of p=0.05 (two tailed) and an extent threshold of 100 voxels showed no significant differences between scans.
Conclusion
Rest measurements in healthy male volunteers of the trapping constant for α[11C]MT, using PET, appeared to be stable during an average interval of 3 weeks.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagberg GE, Torstenson R, Marteinsdottir I, Fredrikson M, Langstrom B, Blomqvist G. Kinetic compartment modeling of [11C]-5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan for positron emission tomography assessment of serotonin synthesis in human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002;22:1352–66
Frazer A, Hensler J. Serotonin. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, et al., eds. Basic neurochemistry, 5th edn. Vol. 3. New York: Raven Press; 1995
Diksic M, Nagahiro S, Sourkes TL, Yamamoto YL. A new method to measure brain serotonin synthesis in vivo. I. Theory and basic data for a biological model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1990;10:1–12
Muzik O, Chugani DC, Chakraborty P, Mangner T, Chugani HT. Analysis of [C-11]alpha-methyl-tryptophan kinetics for the estimation of serotonin synthesis rate in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1997;17:659–69
Diksic M, Young SN. Study of the brain serotonergic system with labeled alpha-methyl-L-tryptophan. J Neurochem 2001;78:1185–200
Cohen Z, Tsuiki K, Takada A, Beaudet A, Diksic M, Hamel E. In vivo-synthesized radioactively labelled alpha-methyl serotonin as a selective tracer for visualization of brain serotonin neurons. Synapse 1995;21:21–8
Missala K, Sourkes TL. Functional cerebral activity of an analogue of serotonin formed in situ. Neurochem Int 1988;12:209–14
WHO. Declaration of Helsinki: recommendations guiding physicians in biomedical research involving human subjects. In: 18th World Medical Assembly. Helsinki: World Medical Association; 1964
Nishizawa S, Leyton M, Okazawa H, Benkelfat C, Mzengeza S, Diksic M. Validation of a less-invasive method for measurement of serotonin synthesis rate with alpha-[11C]methyl-tryptophan. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1998;18:1121–9
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, William JBW. Structured clinical interview for the DSM-IV-TR axis I disorders—patient edition (SCID-I/P, version 2.0). New York: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute; 1998
Nurnberger JI Jr, Blehar MC, Kaufmann CA, York-Cooler C, Simpson SG, Harkavy-Friedman J, et al. Diagnostic interview for genetic studies. Rationale, unique features, and training. NIMH Genetics Initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1994;51:849–59; discussion 863–864
Patlak CS, Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD. Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1983;3:1–7
Diksic M, Tohyama Y, Takada A. Brain net unidirectional uptake of alpha-[14C]methyl-L-tryptophan (alpha-MTrp) and its correlation with regional serotonin synthesis, tryptophan incorporation into proteins, and permeability surface area products of tryptophan and alpha-MTrp. Neurochem Res 2000;25:1537–46
Chugani DC, Chugani HT. PET: mapping of serotonin synthesis. Adv Neurol 2000;83:165–71
Shoaf SE, Carson RE, Hommer D, Williams WA, Higley JD, Schmall B, et al. The suitability of [11C]-alpha-methyl-L-tryptophan as a tracer for serotonin synthesis: studies with dual administration of [11C] and [14C] labeled tracer. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2000;20:244–52
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JB, Frith CD, Frackoviak RS. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1995;2:189–210
Seibyl JP, Laruelle M, van Dyck CH, Wallace E, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi S, et al. Reproducibility of iodine-123-beta-CIT SPECT brain measurement of dopamine transporters. J Nucl Med 1996;37:222–8
Okazawa H, Diksic M. Image generation of serotonin synthesis rates using alpha-methyltryptophan and PET. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22:777–85
Okazawa H, Leyton M, Benkelfat C, Mzengeza S, Diksic M. Statistical mapping analysis of serotonin synthesis images generated in healthy volunteers using positron-emission tomography and alpha-[11C]methyl-L-tryptophan. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2000;25:359–70
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peters TM, Evans AC. Automatic 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1994;18:192–205
Okazawa H, Diksic M. Image generation of serotonin synthesis rates using alpha-methyltryptophan and PET. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22 5:777–85
Leyton M, Okazawa H, Diksic M, Paris J, Rosa P, Mzengeza S, et al. Brain regional [11C]methyl-L-tryptophan trapping in impulsive subjects with borderline personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2001;158:775–82
Collins LG, Evans AC. Animal: validation and applications of non-linear registration-based segmentation. Int J Pattern Recogn Art Intell 1997;11:1271–94
Collins DL, Zijdenbos AP, Barré WFC, Evans AC. ANIMAL+INSECT: inproved cortical structure segmentation. In: Kuba A, Samal M, Todd-Pokropek A, eds. Proc. of the annual symposium on information processing in medical imaging. Vol. 1613. Springer, 1999;210–23
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imag 1998;17:87–97
Zijdenbos A, Forghani R, Evans A. Automatic quantification of MS lesions in 3D MRI brain data sets: validation of INSECT. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI). Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; 1998
Maquet P, Dive D, Salmon E, von Frenckel R, Franck G. Reproducibility of cerebral glucose utilization measured by PET and the [18F]-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose method in resting, healthy human subjects. Eur J Nucl Med 1990;16:267–73
Melega WP, Raleigh MJ, Stout DB, DeSalles AA, Cherry SR, Blurton-Jones M, et al. Longitudinal behavioral and 6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA-PET assessment in MPTP-hemiparkinsonian monkeys. Exp Neurol 1996;141:318–29
Koeppe RA, Mangner T, Betz AL, Shulkin BL, Allen R, Kollros P, et al. Use of [11C]aminocyclohexanecarboxylate for the measurement of amino acid uptake and distribution volume in human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1990;10:727–39
Shoaf SE, Carson R, Hommer D, Williams W, Higley JD, Schmall B, et al. Brain serotonin synthesis rates in rhesus monkeys determined by [11C]alpha-methyl-L-tryptophan and positron emission tomography compared to CSF 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid concentrations. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;19:345–53
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by grants from the NIH, CIHR, and FRSQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosa-Neto, P., Diksic, M., Leyton, M. et al. Stability of α-[11C]methyl-l-tryptophan brain trapping in healthy male volunteers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32, 1199–1204 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1829-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1829-5