Abstract
Objective
Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABC) rarely present in soft tissue locations (STABC). The 30 cases of STABC reported in the English literature were reviewed. Six new cases retrieved from the files of the Netherlands Committee on Bone Tumors were compared to the six cases described in the radiological literature.
Materials and methods
Imaging studies and histopathology of six new STABC cases were reviewed. Follow-up was recorded with respect to local recurrence. FISH for USP6 rearrangement and/or anchored multiplex PCR-based targeted NGS using Archer FusionPlex Sarcoma Panel were attempted.
Results
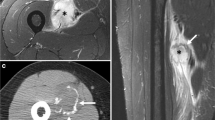
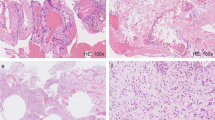
On imaging, the six STABC cases presented as a solid or multicystic intramuscular soft tissue mass, usually with thin peripheral mineralized bone shell. On MRI, perilesional edema was visualized in nearly all cases. Fluid-fluid levels were observed in one case. All lesions had the distinct histologic features of STABC. In three cases suitable for NGS, the diagnosis of STABC was confirmed by a COL1A1–USP6 fusion gene. In one additional case, USP6 gene rearrangement was detected by FISH. After marginal excision, none of the six STABC recurred after a mean follow-up period of 50 months (range, 39–187 months).
Conclusions
On imaging, it can be difficult to discriminate between STABC and myositis ossificans. The presence of a thin bony shell and fluid-fluid levels can be helpful in discriminating these two entities. STABC is readily diagnosed after histopathologic examination of the resection specimen. STABC belongs to the spectrum of tumors with USP6 rearrangements, which includes ABC, myositis ossificans, and nodular fasciitis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe HL, Lichtenstein L. Solitary unicameral bone cyst with emphasis on the roentgen picture, the pathologic picture and the pathogenesis. Arch Surg. 1942;46:1004–25.
Salm R, Sissons HA. Giant-cell tumours of soft tissues. J Pathol. 1972;107:27–39.
Ajilogba KA, Kaur H, Duncan R, McFarlane JH, Watt AJ. Extraosseous aneurysmal bone cyst in a 12-year-old girl. Pediatr Radiol. 2005;35:1240–2.
Amir G, Mogle P, Sucher E. Case report 729. Myositis ossificans and aneurysmal bone cyst. Skelet Radiol. 1992;21:257–9.
Baker KS, Gould ES, Patel HB, Hwang SJ. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst: a rare case in a middle aged patient. J Radiol Case Rep. 2015;9:26–35.
Jacquot C, Szymanska J, Nemana LJ, Steinbach LS, Horvai AE. Soft-tissue aneurysmal bone cyst with translocation t(17;17)(p13;q21) corresponding to COL1A1 and USP6 loci. Skelet Radiol. 2015;44:1695–9.
Samura H, Shiraishi M, Tokashiki H, Nosato E, Miyazato H, Muto Y. An extraosseous aneurysmal cyst in the pelvic cavity: report of a case. Clin Imaging. 2000;24:68–71.
Wang XL, Gielen JL, Salgado R, Delrue F, De Schepper AM. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst. Skelet Radiol. 2004;33:477–80.
Van Eijk R, Stevens L, Morreau H, van Wezel T. Assessment of a fully automated high-throughput DNA extraction method from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue for KRAS, and BRAF somatic mutation analysis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2013;94:121–5.
Meyers SP. MRI of bone and soft tissue tumors and tumorlike lesions—differential diagnosis and atlas. Stuttgart: Thieme Medical Publishers; 2008. p. 814.
Kransdorf MJ, Sweet DE. Aneurysmal bone cyst: concept, controversy, clinical presentation, and imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;164:573–80.
Martinez V, Sissons HA. Aneurysmal bone cyst. A review of 123 cases including primary lesions and those secondary to other bone pathology. Cancer. 1988;61:2291–304.
Hao Y, Wang L, Yan M, Jin F, Ge S, Dai K. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst in a 10-year-old girl. Oncol Lett. 2012;3:545–8.
McCann KM, Clifford CE, Salton HL. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst: a case report. FAOJ. 2011;4(6):No. 1.
Dal Cin P, Kozakewich HP, Goumnerova L, Mankin HJ, Rosenberg AE, Fletcher JA. Variant translocations involving 16q22 and 17p13 in solid variant and extraosseous forms of aneurysmal bone cyst. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2000;28:233–4.
Karkuzhali P, Bhattacharyya M, Sumitha P. Multiple soft tissue aneurysmal cysts: an occurrence after resection of primary aneurysmal bone cyst of fibula. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41:246–9.
Lopez-Barea F, Rodriguez-Peralto JL, Burgos-Lizaldez E, Alvarez-Linera J, Sanchez-Herrera S. Primary aneurysmal cyst of soft tissue. Report of a case with ultrastructural and MRI studies. Virchows Arch. 1996;428:125–9.
Nielsen GP, Fletcher CD, Smith MA, Rybak L, Rosenberg AE. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst: a clinicopathologic study of five cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:64–9.
Petrik PK, Findlay JM, Sherlock RA. Aneurysmal cyst, bone type, primary in an artery. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17:1062–6.
Riccioni L, Foschini MP. Extraosseous aneurysmal bone cyst. Tumori. 1996;82:485–7.
Rodriguez-Peralto JL, Lopez-Barea F, Sanchez-Herrera S, Atienza M. Primary aneurysmal cyst of soft tissues (extraosseous aneurysmal cyst). Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:632–6.
Shannon P, Bedard Y, Bell R, Kandel R. Aneurysmal cyst of soft tissue: report of a case with serial magnetic resonance imaging and biopsy. Hum Pathol. 1997;28:255–7.
D'Costa GF, Hastak MS, Patil YV. Primary aneurysmal cyst: bone type in the breast. Indian J Surg. 2007;69:248–50.
Della Libera D, Redlich G, Bittesini L, Falconieri G. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the larynx presenting with hypoglottic obstruction. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001;125:673–6.
Ellison DA, Sawyer JR, Parham DM, Nicholas R Jr. Soft-tissue aneurysmal bone cyst: report of a case with t(5;17)(q33;p13). Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2007;10:46–9.
Fellig Y, Oliveira AM, Margolin E, Gomori JM, Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, et al. Extraosseous aneurysmal bone cyst of cerebello-pontine angle with USP6 rearrangement. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:579–81.
Lopez LV, Rodriguez MG, Siegal GP, Wei S. Extraskeletal aneurysmal bone cyst: report of a case and review of the literature. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213:1445–9.
Pietschmann MF, Oliveira AM, Chou MM, Ihrler S, Niederhagen M, Baur-Melnyk A, et al. Aneurysmal bone cysts of soft tissue represent true neoplasms: a report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:e45.
Sahu A, Gujral SS, Gaur S. Extraosseous aneurysmal cyst in hand: a case report. Cases J. 2008;1:268.
Kao YC, Sung YS, Zhang L, Chen CL, Huang SC, Antonescu CR. Expanding the molecular signature of ossifying fibromyxoid tumors with two novel gene fusions: CREBBP-BCORL1 and KDM2A-WWTR1. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2017;56:42–50.
Sukov WR, Franco MF, Erickson-Johnson M, Chou MM, Unni KK, Wenger DE, et al. Frequency of USP6 rearrangements in myositis ossificans, brown tumor, and cherubism: molecular cytogenetic evidence that a subset of “myositis ossificans-like lesions” are the early phases in the formation of soft-tissue aneurysmal bone cyst. Skelet Radiol. 2008;37:321–7.
Oliveira AM, Perez-Atayde AR, Dal Cin P, Gebhardt MC, Chen CJ, Neff JR, et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst variant translocations upregulate USP6 transcription by promoter swapping with the ZNF9, COL1A1, TRAP150, and OMD genes. Oncogene. 2005;24:3419–26.
Bekers EM, Eijkelenboom A, Grünberg K, Roverts RC, de Rooy JWJ, van der Geest ICM, et al. Myositis ossificans—another condition with USP6 rearrangement, providing evidence of a relationship with nodular fasciitis and aneurysmal bone cyst. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018;34:56–9.
Flucke U, Bekers EM, Creytens D, van Gorp JM. COL1A1 is a fusionpartner of USP6 in myositis ossificans—FISH analysis of six cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2018.06.009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wangzhao Song studied the pathology specimens and drafted the manuscript with Stijn M. Bollen. Albert J. H. Suurmeijer conceived the study, participated in its design, and supervised this article. Anne-Marie Cleton-Jansen performed FISH and next-generation sequencing. Judith V.M.G. Bovée studied the pathology specimens and participated in the study design. Herman M. Kroon conceived the study, interpreted imaging features, designed, supervised, and finally approved this article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No funds were received in support of this work. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Sources of support
W. Song receives funding from the China Scholarship Council (CSC) program (grant no: 201606940023).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Suurmeijer, A.J.H., Bollen, S.M. et al. Soft tissue aneurysmal bone cyst: six new cases with imaging details, molecular pathology, and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol 48, 1059–1067 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3135-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3135-x