Abstract
Objective
To describe the normal MR anatomy and variations of the distal semimembranosus tendinous arms and the posterior oblique ligament as seen in the three orthogonal planes, to review the biomechanics of this complex and to illustrate pathologic examples.
Results and conclusion
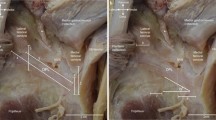
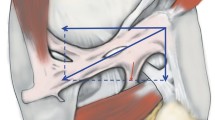
The distal semimembranosus tendon divides into five tendinous arms named the anterior, direct, capsular, inferior and the oblique popliteal ligament. These arms intertwine with the branches of the posterior oblique ligament in the posterior medial aspect of the knee, providing stability. This tendon-ligamentous complex also acts synergistically with the popliteus muscle and actively pulls the posterior horn of the medial meniscus during knee flexion. Pathologic conditions involving this complex include complete and partial tears, insertional tendinosis, avulsion fractures and bursitis.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan EB. Some aspects of functional anatomy of the human knee joint. Clin Orthop 1962; 23:18–29.
Hughston JC, Eilers AF. The role of the posterior oblique ligament in repairs of acute medial (collateral) ligament tears of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1973; 55:923–940.
Hassine D, Rougereau G, Feron JM, Henry-Feugeas MC, Fabre V, et al. MR imaging of posteromedial and posterolateral stabilizers of the knee: anatomic basis and patterns of lesions in knee injuries. Surg Radiol Anat 1994; 16:293–301.
Loredo R, Hodler J, Pedowitz R, Yeh LR, Trudell D, Resnick D. Posteromedial corner of the knee: MR imaging with gross anatomic correlation. Skeletal Radiol 1999; 28:305–311.
Warren LF, Marshall JL. The supporting structures and layers on the medial side of the knee: an anatomical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1979; 61:56–62.
Hughston JC. Knee ligaments. Injury and repair. St Louis: Mosby, 1993:3–70.
Kim YC, Yoo WK, Chung IH, Seo JS, Tanaka S. Tendinous insertion of semimembranosus muscle into the lateral meniscus. Surg Radiol Anat 1997; 19:365–369.
Hughston JC. The importance of the posterior oblique ligament in repairs of acute tears of the medial ligaments in knees with and without an associated rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994; 76:1328–1344.
Brantigan OC, Voshell AF. The tibial collateral ligament: its function, its bursae, and its relation to the medial meniscus. J Bone Joint Surg 1943; 25:121–131.
Brantigan OC, Voshell AF. The mechanics of the ligaments and menisci of the knee joint. J Bone Joint Surg 1941; 23:44–66.
Renstrom P, Johnson RJ. Anatomy and biomechanics of the menisci. Clin Sports Med 1990; 9:523–538.
Torreggiani WC, Al-Ismail K, Munk PL, Roche C, Keogh C, Nicolau S, Marchinkow LP. The imaging spectrum of Baker's (popliteal) cysts. Clin Radiol 2002; 57:681–691.
Rothstein CP, Laorr A, Helms CA, Tirman P. Semimembranosus-tibial collateral ligament bursitis: MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 166:875–877.
Varela JR, Rodriguez E, Soler R, Gonzalez J, Pombo S. Complete rupture of the distal semimembranosus tendon with secondary hamstring muscles atrophy: MR findings in two cases. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29:362–364.
Alioto RJ, Browne JE, Barnthouse CD, Scott AR. Complete rupture of the distal semimembranosus complex in a professional athlete. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1997; 336:162–165.
DeSmet AA, Best TM. MR imaging of the distribution and location of acute hamstring injuries in athletes. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000; 174:393–399.
Yao L, Lee JK. Avulsion of the posteromedial tibial plateau by the semimembranosus tendon: diagnosis with MR imaging. Radiology 1989; 172:513–514.
Chan KK, Resnick D, Goodwin D, Seeger LL. Posteromedial tibial plateau injury including avulsion fracture of the semimembranosus tendon insertion site: ancillary sign of anterior cruciate ligament tear at MR imaging. Radiology 1999; 211:754–758.
Bencardino JT, Rosenberg ZS, Brown R, Hassakhani A, Lustrin E, Beltran J. Traumatic musculotendinous injuries of the knee: diagnosis with MR imaging. RadioGraphics 2000; 20:S103-S120.
Vanek J. Posteromedial fracture of the tibial plateau is not an avulsion injury. A case report and experimental study. J Bone Joint Surg 1994; 76:290–292.
Andersen-Ranberg F, Hejgaard N. Ruptured semimembranosus bursa: an unusual complication following sports injury of the knee. J Sports Med 1986; 20:23–24.
Bunker TD, Thomas E. Ruptured semimembranosus bursa: a complication of arthroscopy. A short case report. Injury 1983; 15:182–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beltran, J., Matityahu, A., Hwang, K. et al. The distal semimembranosus complex: normal MR anatomy, variants, biomechanics and pathology. Skeletal Radiol 32, 435–445 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-003-0641-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-003-0641-1