Abstract
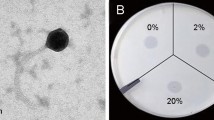
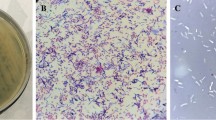
Lysinibacillus sphaericus has great application potential not only in the biocontrol of mosquitoes but also in the bioremediation of toxic metals. Phages contribute to the genetic diversity and niche adaptation of bacteria, playing essential roles in their life cycle, but may also cause economic damage for industrially important bacteria through phage contamination during fermentation. In this study, the L. sphaericus phage vB_LspM-01, which belongs to the Myoviridae family, was isolated and characterized. Results showed that vB_LspM-01 could specifically infect most tested L. sphaericus isolates but was not active against isolates belonging to other species. Furthermore, phage-born endolysin exhibited a broader antimicrobial spectrum than the host range of the phage. The vB_LspM-01 genome had no obvious similarity with that of its host, and ca. 22.6% of putative ORFs could not get a match with the public databases. Phylogenic analysis based on the putative terminase large subunit showed high similarity with the phages identified with pac-type headful packaging. The vB_LspM-01 encoding genes were only detected in a tiny percentage of L. sphaericus C3-41 individual cells in the wild population, whereas they showed much higher frequency in the resistant population grown within the plaques; however, the phage genes could not be stably inherited during host cell division. Additionally, the vB_LspM-01 encoding genes were only detected in the host population during the logarithmic growth phase. The mitomycin C induction helped the propagation and lysogeny-lysis switch of vB_LspM-01. The study demonstrated that vB_LspM-01 can be present in a pseudolysogenic state in L. sphaericus C3-41 populations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann H-W, DuBow MS (1987) Viruses of prokaryotes. in: general properties of bacteriophages, Vol. I. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 202
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang YJ, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W16–W21
Bertani G (1953) Lysogenic versus lytic cycle of phage multiplication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 18:65–70
Borek AL, Obszanska K, Hryniewicz W, Sitkiewicz I (2012) Typing of Streptococcus pyogenes strains using the phage profiling method. Virulence 3(6):534–538
Bott K, Strauss B (1965) The carrier state of Bacillus subtilis infected with the transducing bacteriophage Sp10. Virology 25:212–225
Catalano CE, Cue D, Feiss M (1995) Virus DNA packaging: the strategy used by phage lambda. Mol Microbiol 16(6):1075–1086
Cenens W, Mebrhatu MT, Makumi A, Ceyssens PJ, Lavigne R, Van Houdt R, Taddei F, Aertsen A (2013) Expression of a novel P22 ORFan gene reveals the phage carrier state in Salmonella typhimurium. PLoS Genet 9(2):e1003269
Chandry PS, Moore SC, Davidson BE, Hillier AJ (2002) Transduction of concatemeric plasmids containing the cos site of Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage sk1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 216(1):85–90
Chirakadze I, Perets A, Ahmed R (2009) Phage typing. Methods Mol Biol 502:293–305
Desiere F, Lucchini S, Brussow H (1999) Comparative sequence analysis of the DNA packaging, head, and tail morphogenesis modules in the temperate cos-site Streptococcus thermophilus bacteriophage Sfi21. Virology 260(2):244–253
Duffy C, Feiss M (2002) The large subunit of bacteriophage lambda’s terminase plays a role in DNA translocation and packaging termination. J Mol Biol 316(3):547–561
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics 5:1–19
Fortier LC, Sekulovic O (2013) Importance of prophages to evolution and virulence of bacterial pathogens. Virulence 4(5):354–365
Fu P, Ge Y, Wu YM, Zhao N, Yuan ZM, Hu XM (2017a) The LspC3-41I restriction-modification system is the major determinant for genetic manipulations of Lysinibacillus sphaericus C3-41. BMC Microbiol 17:116
Fu P, Xiang X, Ge Y, Yuan Z, Hu X (2017b) Differential expression of duplicated binary toxin genes binA/binB in Lysinibacillus sphaericus C3-41. Lett Appl Microbiol 65(1):90–97
Geng PL, Tian S, Yuan ZM, Hu XM (2017) Identification and genomic comparison of temperate bacteriophages derived from emetic Bacillus cereus. PLoS One 12(9):e0184572
Gillis A, Mahillon J (2014) Influence of lysogeny of tectiviruses GIL01 and GIL16 on Bacillus thuringiensis growth, biofilm formation, and swarming motility. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(24):7620–7630
Goh S (2016) Phage transduction. Methods Mol Biol 1476:177–185
Gomez-Garzon C, Hernandez-Santana A, Dussan J (2017) A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Lysinibacillus sphaericus unveils unexploited biotechnological potentials. PLoS One 12(6):e0179666
Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C (2007) CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server):W52–W57
Gual A, Camacho AG, Alonso JC (2000) Functional analysis of the terminase large subunit, G2P, of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPP1. J Biol Chem 275(45):35311–35319
Han B, Liu HZ, Hu XM, Cai YJ, Zheng DS, Yuan ZM (2007) Molecular characterization of a glucokinase with broad hexose specificity from Bacillus sphaericus strain C3-41. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(11):3581–3586
Hu XM, Hansen BM, Hendriksen NB, Yuan ZM (2006) Detection and phylogenic analysis of one anthrax virulence plasmid pXO1 conservative open reading frame ubiquitous presented within Bacillus cereus group strains. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 349(4):1214–1219
Hu XM, Fan W, Han B, Liu HZ, Zheng D, Li Q, Dong W, Yan J, Gao M, Berry C, Yuan Z (2008) Complete genome sequence of the mosquitocidal bacterium Bacillus sphaericus C3-41 and comparison with those of closely related bacillus species. J Bacteriol 190(8):2892–2902
Ikeda H, Tomizawa JI (1965) Transducing fragments in generalized transduction by phage P1. I Molecular origin of the fragments. J Mol Biol 14(1):85–109
Ivanova N, Sorokin A, Anderson I, Galleron N, Candelon B, Kapatral V, Bhattacharyya A, Reznik G, Mikhailova N, Lapidus A, Chu L, Mazur M, Goltsman E, Larsen N, D'Souza M, Walunas T, Grechkin Y, Pusch G, Haselkorn R, Fonstein M, Ehrlich SD, Overbeek R, Kyrpides N (2003) Genome sequence of Bacillus cereus and comparative analysis with Bacillus anthracis. Nature 423(6935):87–91
Khemayan K, Pasharawipas T, Puiprom O, Sriurairatana S, Suthienkul O, Flegel TW (2006) Unstable lysogeny and pseudolysogeny in Vibrio harveyi siphovirus-like phage 1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1355–1363
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35(9):3100–3108
Latino L, Midoux C, Hauck Y, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C (2016) Pseudolysogeny and sequential mutations build multiresistance to virulent bacteriophages in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology-Sgm 162:748–763
Liu G, Song L, Shu C, Wang P, Deng C, Peng Q, Lereclus D, Wang X, Huang D, Zhang J, Song F (2013) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki strain HD73. Genome Announc 1(2):e0008013
Lood R, Collin M (2011) Characterization and genome sequencing of two Propionibacterium acnes phages displaying pseudolysogeny. BMC Genomics 12
Los M, Wegrzyn G (2012) Pseudolysogeny. Adv Virus Res 82:339–349
Lowe TM, Chan PP (2016) tRNAscan-SE on-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W54–W57
Mahony J, Martel B, Tremblay DM, Neve H, Heller KJ, Moineau S, van Sinderen D (2013) Identification of a new P335 subgroup through molecular analysis of Lactococcal phages Q33 and BM13. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(14):4401–4409
Murphy J, Mahony J, Ainsworth S, Nauta A, van Sinderen D (2013) Bacteriophage orphan DNA methyltransferases: insights from their bacterial origin, function, and occurrence. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(24):7547–7555
Ogata S, Eguchi T, Doi K (2000) Protection against bacteriophage contamination in industrial fermentation processes--investigation and applications of phage resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Uirusu 50(1):17–26
Priest FG (1992) Biological-control of mosquitos and other biting flies by Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus thuringiensis. J Appl Bacteriol 72(5):357–369
Rabsch W (2007) Salmonella typhimurium phage typing for pathogens. Methods Mol Biol 394:177–211
Rasko DA, Ravel J, Okstad OA, Helgason E, Cer RZ, Jiang L, Shores KA, Fouts DE, Tourasse NJ, Angiuoli SV, Kolonay J, Nelson WC, Kolsto AB, Fraser CM, Read TD (2004) The genome sequence of Bacillus cereus ATCC 10987 reveals metabolic adaptations and a large plasmid related to Bacillus anthracis pXO1. Nucleic Acids Res 32(3):977–988
Ripp RVM a SA (2002) Pseudolysogeny: a bacteriophage strategy for increasing longevity in situ. Horizontal Gene Transfer:81–91
Schuch R, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2002) A bacteriolytic agent that detects and kills Bacillus anthracis. Nature 418(6900):884–889
Shaw DR, Dussan J (2018) Transcriptional analysis and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the mechanism of toxic metals removal and efflux pumps in Lysinibacillus sphaericus OT4b.31. Int Biodeterior Biodegr 127:46–61
Shin H, Bandara N, Shin E, Ryu S, Kim KP (2011) Prevalence of Bacillus cereus bacteriophages in fermented foods and characterization of phage JBP901. Res Microbiol 162(1016):791–797
Sicard N, Venema G (1969) Penetration of thymine-starved bacterial DNA during transformation of B. Subtilis 168 T. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 36(4):647–650
Szymczak P, Janzen T, Neves AR, Kot W, Hansen LH, Lametsch R, Neve H, Franz CMAP, Vogensen FK (2017) Novel variants of Streptococcus thermophilus bacteriophages are indicative of genetic recombination among phages from different bacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(5)
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Taylor LD, Burke WF (1990) Transformation of an entomopathic strain of Bacillus sphaericus by high-voltage electroporation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66(1–3):125–127
Thiéry I, Back C, Barbazan P, Sinègre G (1996) Applications de Bacillus thuringiensis et de B sphaericus dans la démoustication et la lutte contre les vecteurs de maladies tropicales
Tsourkas PK, Yost DG, Krohn A, LeBlanc L, Zhang A, Stamereilers C, Amy PS (2015) Complete genome sequences of nine phages capable of infecting Paenibacillus larvae, the causative agent of American foulbrood disease in honeybees. Genome Announc 3(5)
van Zyl LJ, Sunda F, Taylor MP, Cowan DA, Trindade MI (2015) Identification and characterization of a novel Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius bacteriophage, GVE3. Arch Virol 160(9):2269–2282
Weinbauer MG (2004) Ecology of prokaryotic viruses. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28(2):127–181
Wu DD, Yuan YH, Liu PM, Wu Y, Gao MY (2014) Cellular responses in Bacillus thuringiensis CS33 during bacteriophage BtCS33 infection. J Proteome 101:192–204
Xu K, Yuan ZM, Rayner S, Hu XM (2015) Genome comparison provides molecular insights into the phylogeny of the reassigned new genus Lysinibacillus. BMC Genomics 16:140
Yousten AA, de Barjac H, Hedrick J, Cosmao Dumanoir V, Myers P (1980) Comparison between bacteriophage typing and serotyping for the differentiation of Bacillus sphaericus strains. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 131B(3):297–308
Yuan ZM, Zhang YM, Cai QX, Liu EY (2000) High-level field resistance to Bacillus sphaericus C3-41 in Culex quinquefasciatus from southern China. Biocontrol Sci Tech 10(1):41–49
Yuan YH, Peng Q, Wu DD, Kou Z, Wu Y, Liu PM, Gao MY (2015) Effects of actin-like proteins encoded by two Bacillus pumilus phages on unstable lysogeny, revealed by genomic analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(1):339–350
Zahiri NS, Mulla MS (2005) Non-larvicidal effects of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus on oviposition and adult mortality of Culex quinquefasciatus Say (Diptera : Culicidae). J Vector Ecol 30(1):155–162
Zhang YM (1987) Isolation of two highly toxic Bacillus sphaericus strains. Insecticidal Microorg 1:98–99
Acknowledgments
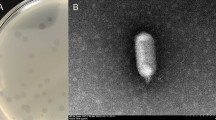
We would like to thank Pei Zhang from the Core Facility and Technical Support, Wuhan Institute of Virology, for her help with producing EM micrographs.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key R&D Programs of China (2016YFC1201000) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 31570007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 878 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, P., Wan, X., Cheng, J. et al. vB_LspM-01: a novel myovirus displaying pseudolysogeny in Lysinibacillus sphaericus C3-41. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 10691–10702 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9424-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9424-4