Abstract
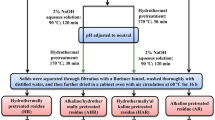
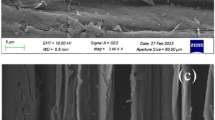
Wheat straws (WS) were pretreated by a two-step pretreatment for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. The raw wheat straw (RWS) was firstly soaked in microwave-assisted NaOH solution at the presence of a mixed solution of H2O2 and hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (HTAC), and the residue was put into methyl orange (MO) solution to obtain the final substrate for enzymatic hydrolysis. It was interesting to find that the WS after the first step of the pretreatment could effectively remove MO in the second step of the pretreatment with the highest removal efficiency of 98.86% at the MO concentration of 25 mg/L and at the adsorbent-adsorbate ratio of 0.8%. Meanwhile, the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of the WS that was pretreated by the two steps was higher than that of the RWS as well as the first-step-pretreated WS. Enzymatic hydrolysis experiment showed that the glucose concentration after 48-h hydrolysis was 4.85 g/L at the solid loading of 5%, compared with the RWS of 0.90 g/L and the first-step-pretreated WS of 4.33 g/L. This suggested that the two-step pretreatment method could not only make WS as a good adsorbent but also a more biodegradable lignocellulosic material. Characterization analysis showed that the specific surface area and the cellulose content of the WS were both increased after the two-step pretreatment, indicating that the pretreatment method was significant to properly utilizing WS as biosorbent and biofuel. Besides, a possible mechanism for the effect of the pretreatment on the WS was proposed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abubackar HN, Veiga MC, Kennes C (2015) Ethanol and acetic acid production from carbon monoxide in a Clostridium strain in batch and continuous gas-fed bioreactors. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:1029–1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120101029
Abubackar HN, Bengelsdorf FR, Dürre P, Veiga MC, Kennes C (2016) Improved operating strategy for continuous fermentation of carbon monoxide to fuel-ethanol by clostridia. Appl Energy 169:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.02.021
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.02.003
Chen HM, Jia Z, Hu TH, Zhao XB, Liu DH (2015) A comparison of several organosolv pretreatments for improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw: substrate digestibility, fermentability and structural features. Appl Energy 150:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.030
Chen YJ, He HJ, Liu HY, Zeng GM, Xia X, Yang CP (2018) Effect of salinity on removal performance and activated sludge characteristics in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour Technol 249:890–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.092
Cheng Y, He HJ, Yang CP, Zeng GM, Li X, Chen H, Yu GL (2016a) Challenges and solutions for biofiltration of hydrophobic volatile organic compounds. Biotechnol Adv 34:1091–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.06.007
Cheng Y, Yang CP, He HJ, Zeng GM, Zhao K, Yan Y (2016b) Biosorption of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by waste biomass from biotrickling filters: kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. J Environ Eng 142:C4015001–C4015007. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000956
Haruta S, Cui Z, Huang Z, Li M, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2002) Construction of a stable microbial community with high cellulose-degradation ability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1026-4
Hassan EBM, Shukry N (2008) Polyhydric alcohol liquefaction of some lignocellulosic agricultural residues. Ind Crop Prod 27:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2014.12.007
He HJ, Chen YJ, Li X, Cheng Y, Yang CP, Zeng GM (2017) Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:520–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.10.007
He HJ, Xiang ZH, Chen XJ, Chen H, Huang H, Wen M, Yang CP (2018) Biosorption of Cd(II) from synthetic wastewater using dry biofilms from biotrickling filters. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:1491–1500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1507-8
Huang YQ, Yang CP, Sun ZC, Zeng GM, He HJ (2015) Removal of cadmium and lead from aqueous solutions using nitrilotriacetic acid anhydride modified ligno-cellulosic material. RSC Adv 5:11475–11484. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA14859B
Inglesby MK, Zeronian SH (1996) The accessibility of cellulose as determined by dye adsorption. Cellulose 3:165–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02228799
Jalc D (2002) Effect of Tween 80 and monensin on ruminal fermentation of the diet containing 70% wheat straw treated by white-rot fungus in artificial rumen. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 115:453–457
Kabel MA, Jurak E, Mäkelä MR, Vries RPD (2017) Occurrence and function of enzymes for lignocellulose degradation in commercial Agaricus bisporus cultivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:4363–4369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8294-5
Kim JS, Lee YY, Kim TH (2016) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 199:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.085
Larsson S, Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Tengborg C, Stenberg K, Zacchi G, Nilvebrant NO (1999) The generation of fermentation inhibitors during dilute acid hydrolysis of softwood. Enzym Microb Technol 24:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(98)00101-X
Lin Y, Wu SH, Li X, Wu X, Yang CP, Zeng GM, Peng YR, Zhou Q, Lu L (2018) Microstructure and performance of Z-scheme photocatalyst of silver phosphate modified by MWCNTs and Cr-doped SrTiO3 for malachite green degradation. Appl Catal B Environ 227:557–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.054
Mcintosh S, Vancov T (2011) Optimisation of dilute alkaline pretreatment for enzymatic saccharification of wheat straw. Biomass Bioenergy 35:3094–3103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.04.018
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.06.025
Pan R, Cao L, Huang H, Zhang R, Mo Y (2010) Biosorption of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn from aqueous solutions by the fruiting bodies of jelly fungi (Tremella fuciformis and Auricularia polytricha). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:997–1005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2821-y
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007) Biological approaches for treatment of distillery wastewater: a review. Bioresour Technol 98:2321–2334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.027
Pant D, Adholeya A (2009) Nitrogen removal from biomethanated spentwash using hydroponic treatment followed by fungal decolorization. Environ Eng Sci 26:559–565. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2007.0328
Pant D, Singh A, Bogaert GV, Olsen SI, Nigam PS, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2012) Bioelectrochemical systems (BES) for sustainable energy production and product recovery from organic wastes and industrial wastewaters. RSC Adv 2:1248–1263. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1RA00839K
Pirbazari AE, Kisom BF, Khararoodi MG (2015) Anionic surfactant-modified rice straw for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 57:18202–18216. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1090919
Qi B, Chen X, Fei S, Yi S, Wan Y (2009) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw pretreated by alkaline peroxide using response surface methodology. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(15):7346–7353. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie8016863
Rossana L, Valeria V, Olimpia P, Vincenza F (2016) Bioreactors for lignocellulose conversion into fermentable sugars for production of high added value products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:597–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7125-9
Saha BC, Cotta MA (2011) Continuous ethanol production from wheat straw hydrolysate by recombinant ethanologenic Escherichia coli strain FBR5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3082-5
Saini JK, Saini R, Tewari L (2014) Lignocellulosic agriculture wastes as biomass feedstocks for second-generation bioethanol production: concepts and recent developments. 3 Biotech 5:337–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-014-0246-5
Satpathy SK, Tabil LG, Meda V, Naik SN, Prasad R (2014) Torrefaction of wheat and barley straw after microwave heating. Fuel 124:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.01.102
Sitepu IR, Jin MJ, Fernandez JE, Sousa LDC, Balan V, Boundymill KL (2014) Identification of oleaginous yeast strains able to accumulate high intracellular lipids when cultivated in alkaline pretreated corn stover. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7645–7657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5944-8
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templaton D, Crocker D (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Laboratory analytical procedure. Technical report NREL/TP-510-42618
Thomsen MH, Thygesen A, Thomsen AB (2009) Identification and characterization of fermentation inhibitors formed during hydrothermal treatment and following SSF of wheat straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1867-1
Unrean P, Khajeeram S, Laoteng K (2015) Systematic optimization of fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation at high-solid loading based on enzymatic hydrolysis and dynamic metabolic modeling of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2459–2470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7173-1
Wang JL, Chen C (2006) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review. Biotechnol Adv 24:427–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.03.001
Wang JL, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27:195–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.11.002
Wang W, Kang L, Wei H, Arora R, Lee YY (2011) Study on the decreased sugar yield in enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic substrate at high solid loading. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9200-8
Wang H, Yuan XZ, Wu ZB, Wang LL, Peng X, Leng LJ, Zeng GM (2014) Removal of basic dye from aqueous solution using Cinnamomum camphora sawdust: kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, and mass-transfer processes. Sep Sci Technol 49:2689–2699. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.940590
Wu SH, Shen ZQ, Yang CP, Zhou YX, Li X, Zeng GM, Ai SJ, He HJ (2017) Effects of C/N ratio and bulking agent on speciation of Zn and Cu and enzymatic activity during pig manure composting. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.09.016
Wu X, He HJ, Yang WL, Yu JP, Yang CP (2018) Efficient removal of atrazine from aqueous solutions using magnetic Saccharomyces cerevisiae bionanomaterial. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:7597–7610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9143-x
Xu J, Thomsen MH, Thomsen AB (2010) Investigation of acetic acid-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment on corn stover. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:509–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2340-x
Yang CP, Wang JQ, Lei M, Xie GX, Zeng GM, Luo SL (2010) Biosorption of zinc(II) from aqueous solution by dried activated sludge. J Environ Sci 22:675–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60162-5
Yang CP, Qian H, Li X, Cheng Y, He HJ, Zeng GM, Xi JY (2018) Simultaneous removal of multi-component VOCs in biofilters. Trends Biotechnol 36:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.02.004
Yu T, Deng YH, Liu HY, Yang CP, Wu BW, Zeng GM, Lu L, Nishimura F (2017) Effect of alkaline microwaving pretreatment on anaerobic digestion and biogas production of swine manure. Sci Rep 7:1668. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01706-3
Yu JP, He HJ, Yang WL, Yang CP, Zeng GM, Wu X (2018) Magnetic bionanoparticles of Penicillium sp. yz11-22N2 doped with Fe3O4 and encapsulated within PVA-SA gel beads for atrazine removal. Bioresour Technol 260:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.103
Zeng XY, Ma YT, Ma LR (2007) Utilization of straw in biomass energy in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 11:976–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2005.10.003
Zhang X, Xu J, Cheng JJ (2011) Pretreatment of corn stover for sugar production with combined alkaline reagents. Energy Fuel 25:4796–4802. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef201130d
Zhao X, Cheng K, Liu D (2009) Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:815–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1883-1
Zhou BW, Seunggu S, Kwanghyun H, Johnghwa A, Seokhwan H (2010a) Effect of microwave irradiation on cellular disintegration of gram positive and negative cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:765–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2574-7
Zhou Y, Stuartwilliams H, Farquhar GD, Hocart CH (2010b) The use of natural abundance stable isotopic ratios to indicate the presence of oxygen-containing chemical linkages between cellulose and lignin in plant cell walls. Phytochemistry 71:982–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.03.001
Zhou Q, Lin Y, Li X, Yang CP, Han ZF, Zeng GM, Lu L, He SY (2018) Effect of zinc ions on nutrient removal and growth of Lemna aequinoctialis from anaerobically digested swine wastewater. Bioresour Technol 249:457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.044
Zhu CY, Yang WL, He HJ, Yang CP, Yu JP, Wu X, Zeng GM, Tarre S, Green M (2018) Preparation, performance and mechanisms of magnetic Saccharomyces cerevisiae bionanocomposites for atrazine removal. Chemosphere 200:380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.020
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51478172, 51278464, 51521006), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (Grant No. LY17E080002), and Department of Science and Technology of Hunan Province of China (Grant No. 2017JJ2029), and the International S&T Cooperation Program of China (Grant No. 2015DFG92750).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animal or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Liu, H., Guo, J. et al. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw by two-step pretreatment combining alkalization and adsorption. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 9831–9842 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9335-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9335-4