Abstract
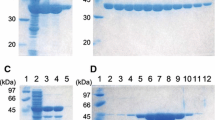
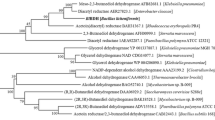
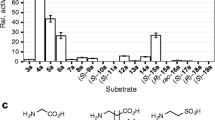
Acetoin is an important physiological metabolite excreted by microbes. Its functions include avoiding acidification, participating in regulation of the NAD+/NADH ratio, and storing carbon. Acetolactate decarboxylase is a well-characterized anabolic enzyme involved with 3-hydroxy butanone (acetoin). It catalyzes conversion of the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of acetolactate to generate the single product, (R)-acetoin. In addition to the X-ray crystal structure of acetolactate decarboxylase from Bacillus brevis, although the enzyme is widely present in microorganisms, very few atomic structures of acetolactate decarboxylase are reported. In this paper, we solved and reported a 1.5 Å resolution crystal structure of acetolactate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis. Dimeric assembly is observed in the solved structure, which is consistent with the elution profile conducted by molecular filtration. A zinc ion is coordinated by highly conserved histidines (191, 193, and 204) and conserved glutamates (62 and 251). We performed kinetic studies on acetolactate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis using circular dichroism, allowing the conversion of acetolactate to chiral acetoin for real-time tracking, yielding a Km value of 21 mM and a kcat value of 2.2 s−1. Using the two enantiomers of acetolactate as substrates, we further investigated the substrate preference of acetolactate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis by means of molecular docking and dynamic simulation in silico. The binding free energy of (S)-acetolactate was found to be ~ 30 kcal/mol greater than that of (R)-acetolactate, indicating a more stable binding for (S)-acetolactate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Pall S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E (2015) GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr, Sect D: Biol Crystallogr 66(2):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444909052925
Anand R, Dorrestein PC, Kinsland C, Begley TP, Ealick SE (2002) Structure of oxalate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis at 1.75 angstrom resolution. Biochemistry 41(24):765–7669. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0200965
Buckel W (1986) Biotin-dependent decarboxylases as bacterial sodium pumps: Purification and reconstitution of glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase from Acidaminococcus fermentans. Methods Enzymol 125:547–558
Chen D, Menche G, Td SL, Peterson J, Schein C (2007) Accounting for ligand-bound metal ions in docking small molecules on adenylyl cyclase toxins. Proteins 67(3):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21249
Crout DHG, Lee ER, Rathbone DL (1990) Absolute configuration of the product of the acetolactate synthase reaction by a novel method of analysis using acetolactate decarboxylase. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1(5):1367–1369. https://doi.org/10.1039/p19900001367
Crout DHG, Littlechild J, Mitchell MB, Morrey SM (1985) Cheminform abstract: stereochemistry of the decarboxylation of α-acetolactate (2- hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate) by the acetolactate decarboxylase. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1 16(4):2271–2276
Crout DHG, Rathbone DL (1988) Biotransformations with acetolactate decarboxylase: unusual conversions of both substrate enantiomers into products of high optical purity. J Chem Soc, Chem Commun 2:98–99. https://doi.org/10.1039/c39880000098
Davis IW, Leaver-Fay A, Chen VB, Block JN, Kapral GJ, Wang X, Murray LW, Arendall WB III, Snoeyink J, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2007) MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W375–W383. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm216
Dolin MI, Gunsalus IC (1951) Pyruvic acid metabolism. II. An acetoinforming enzyme system in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 62(2):199–214
Drake AF, Siligardi G, Crout DHG, Rathbone DL (1987) Applications of vibrational infrared circular-dichroism to biological problems-stereochemistry of proton-exchange in acetoin (3-hydroxybutan-2-one) catalyzed by acetolactate decarboxylase. J Chem Soc, Chem Commun 24:1834–1835. https://doi.org/10.1039/c39870001834
Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K (2010) Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr, Sect D: Biol Crystallogr 66(4):486–501. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444910007493
Falsafi-Zadeh S, Karimi Z, Galehdari H (2012) VMD DisRg: New User-Friendly Implement for calculation distance and radius of gyration in VMD program. Bioinformation 8(7):341. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630008341
Fisher Z, Prada JAH, Tu C, Duda D, Yoshioka C, An HQ, Govindasamy L, Silverman DN, McKenna R (2005) Structural and kinetic characterization of active-site histidine as a proton shuttle in catalysis by human carbonic anhydrase II. Biochemistry 44(4):1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0480279
Fusetti F, Schroter KH, Steiner RA, van Noort PI, Pijning T, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Egmond MR, Dijkstra BW (2002) Crystal structure of the copper-containing quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase from Aspergillus japonicus. Structure 10(2):259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00704-9
Goupil Feuillerat N, CocaignBousquet M, Godon JJ, Ehrlich SD, Renault P (1997) Dual role of alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. J Bacteriol 179(20):6285–6293. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.20.6285-6293.1997
Guo Y, Pan D, Ding H, Wu Z, Sun Y, Zeng X (2015) Purification and characterization of α‐acetolactate decarboxylase (ALDC) from newly isolated Lactococcus lactis DX. J Sci Food Agric 95(8):1655–1661
Hess B (2008) P-LINCS: A parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(1):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct700200b
Hornak V, Abel R, Okur A, Strockbine B, Roitberg A, Simmerling C (2006) Comparison of multiple amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 65(3):712–725. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21123
Hu X, Shelver WH (2003) Docking studies of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: zinc parameter optimization to improve the binding free energy prediction. J. Mol. Graph. Model 22(2):115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-3263(03)00153-0
Jorgensen WL (1983) Erratum: Monte Carlo simulation of n‐butane in water. Conformational evidence for the hydrophobic effect [J. Chem. Phys. 77, 5757 (1982)]. J Chem Phys 78(9):5846–5846. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.445502
Juni E (1952) Mechanisms of formation of acetoin by bacteria. J Biol Chem 195(2):715–726
Kantardjieff KA, Rupp B (2003) Matthews coefficient probabilities: Improved estimates for unit cell contents of proteins, DNA, and protein-nucleic acid complex crystals. Protein Sci 12(9):1865–1871. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.0350503
Kisrieva YS, Serebrennikov VM, Zagustina NA, Bezborodov AM (2000) Isolation and purification of acetolactate synthase and acetolactate decarboxylase from the culture of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Biochem Microbiol 36(2):109–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02737903
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Liu Z, Qin J, Gao C, Hua D, Ma C, Li L, Wang Y, Xu P (2011) Production of (2S,3S)-2,3-butanediol and (3S)-acetoin from glucose using resting cells of Klebsiella pneumonia and Bacillus subtilis. Bioresour Technol 102(22):10741–10744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.110
Marlow VA, Rea D, Najmudin S, Wills M, Fueloep V (2013) Structure and mechanism of acetolactate decarboxylase. ACS Chem Biol 8(10):2339–2344. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb400429h
McCoy AJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Adams PD, Winn MD, Storoni LC, Read RJ (2007) Phaser crystallographic software. J Appl Crystallogr 40(4):658–674. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807021206
Monnet C, Nardi M, Hols P, Gulea M, Corrieu G, Monnet V (2003) Regulation of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis by alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase in Streptococcus thermophilus. Lett Appl Microbiol 36(6):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765X.2003.01326.x
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19(14):1639–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14<1639::AID-JCC10>3.0.CO;2-B
Najmudin S, Andersen JT, Patkar SA, Borchert TV, Crout DHG, Fulop V (2003) Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies on acetolactate decarboxylase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59:1073-1075. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444903006978
Niedzwiecka N, Gronczewska J, Skorkowski EF (2017) NAD-preferring malic enzyme: localization, regulation and its potential role in herring (Clupea harengus) sperm cells. Fish Physiol Biochem 43(2):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0291-6
O'Sullivan SM, Condon S, Cogan TM, Sheehan D (2001) Purification and characterisation of acetolactate decarboxylase from Leuconostoc lactis NCW1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 194(2):245–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1097(00)00499-7
Otwinowski Z, Minor W (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 276(97):307–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(97)76066-x
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera-A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Phalip V, Monnet C, Schmitt P, Renault P, Godon JJ, Divies C (1994) Purification and properties of the alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase from Lactococcus lactis subsp. FEBS Lett 351(1):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(94)00820-5
Rasmussen AM, Gibson RM, Godtfredsen SE, Ottesen M (1985) Purification of α-acetolactate decarboxylase from Lactobacillus casei DSM 2547. Carlsberg Res Commun 50(2):73–82
Sanner MF (1999) Python: a programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model 17(1):57–61
Schrodinger, LLC (2015) The PyMOL molecular graphics system, version 1.8. Schrodinger, LLC, New York
Sousa da Silva AW, Vranken WF (2012) ACPYPE-AnteChamber PYthon Parser interfacE. BMC Res Notes 5(1):367. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-367
Sun JA, Zhang LY, Rao B, Shen YL, Wei DZ (2012) Enhanced acetoin production by Serratia marcescens H32 with expression of a water-forming NADH oxidase. Bioresour Technol 119(7):94–98
Szafir JJ, Bennett EO (1953) The adaptation of the Voges-Proskauer reaction for the quantitative assay of streptomycin. Science 117(3052):717–718. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.117.3052.717
Vinogradov M, Kaplun A, Vyazmensky M, Engel S, Golbik R, Tittmann K, Uhlemann K, Meshalkina L, Barak Z, Hübner G, Chipman DM (2005) Monitoring the acetohydroxy acid synthase reaction and related carboligations by circular dichroism spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 342(1):126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.049
Vivijs B, Moons P, Geeraerd AH, Aertsen A, Michiels CW (2014) 2,3-Butanediol fermentation promotes growth of Serratia plymuthica at low pH but not survival of extreme acid challenge. Int J Food Microbiol 175(2):36–44
Vogel C, Pleiss J (2014) The modular structure of ThDP-dependent enzymes. PROTEINS 82(10):2523–2537. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24615
Wang T (2015) Recombinant expression and enzymatic characterization of acetolactate decarboxylase in vitro. Dalian University of Technology, Dalian
Wechsler C, Meyer D, Loschonsky S, Funk LM, Neumann P, Ficner R, Brodhun F, Müller M, Tittmann K (2015) Tuning and Switching Enantioselectivity of Asymmetric Carboligation in an Enzyme through Mutational Analysis of a Single Hot Spot. ChemBioChem 16(18):2580–2584. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201500529
Werpy TA, Holladay JE, White JF (2004) Top value added chemicals from biomass: I. Results of screening for potential candidates from sugars and synthesis gas. U.S. Department of Energy, Washington, DC
Winn MD, Ballard CC, Cowtan KD, Dodson EJ, Emsley P, Evans PR, Keegan RM, Krissinel EB, Leslie AGW, McCoy A, McNicholas SJ, Murshudov GN, Pannu NS, Potterton EA, Powell HR, Read RJ, Vagin A, Wilson KS (2011) Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr, Sect D: Biol Crystallogr 67(4):235–242. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444910045749
Xiao Z, Lu JR (2014) Strategies for enhancing fermentative production of acetoin: A review. Biotechnol Adv 32(2):492–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.01.002
Xiao Z, Qiao S, Ma C, Xu P (2010) Acetoin production associated with the increase of cell biomass in Bacillus pumilus ATCC 14884. Afr J Microbiol Res 4(19):1997–2003
Xiao Z, Xu P (2007) Acetoin metabolism in bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 33(2):127–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408410701364604
Zbinden M, Marque L, Gaudron SM, Ravaux J, Leger N, Duperron S (2015) Epsilonproteobacteria as gill epibionts of the hydrothermal vent gastropod Cyathermia naticoides (North East-Pacific Rise). Mar Biol 162(2):435–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2591-7
Zhang X, Rao Z, Li J, Zhou J, Yang T, Xu M, Bao T, Zhao X (2015) Improving the acidic stability of Staphylococcus aureus α-acetolactate decarboxylase in Bacillus subtilis by changing basic residues to acidic residues. Amino Acids 47(4):707–717
Zhang X, Yang T, Lin Q, Xu M, Xia H, Xu Z, Li H, Rao Z (2011) Isolation and identification of an acetoin high production bacterium that can reverse transform 2,3-butanediol to acetoin at the decline phase of fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(12):2785–2790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0754-y
Zhao C, Su H, Liu Y (2016) Catalytic mechanism of acetolactate decarboxylase from Brevibacillus brevis towards both enantiomers of alpha-acetolactate. RSC Adv 6(84):80621–80629. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra18264j
Zhuang C, Zheng Q (2016) QM/MM calculations and MD simulations of acetolactate decarboxylase to reveal substrate R/S-acetolactate binding mode and stereoselective catalytic mechansim. RSC Adv 6(94):91852–91859. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra19346c
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (grant number 21506025) and Dalian University of Technology Science Foundation (grant number DUT16RC(4)12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(PDF 88 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, F., Li, M., Feng, Y. et al. Structural and enzymatic characterization of acetolactate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 6479–6491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9049-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9049-7