Abstract
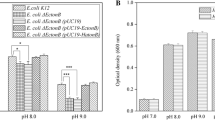
The six- and seven-subunit Na+/H+ antiporters (Mrp) are widely distributed in bacteria. They are reported to be integral for pH homeostasis in alkaliphilic bacteria when adapting to high pH environments. In this study, operons encoding for the six-subunit Na+/H+ antiporters were found in the genomes of all studied Dietzia strains, which have different alkaline-resistant abilities. Disruption of the operon in the strain Dietzia sp. DQ12-45-1b which leads to declined growth in presence of hypersaline and alkaline conditions suggested that the six-subunit Na+/H+ antiporter played an important role in hypersaline and alkaline resistance. Although the complexes DqMrp from DQ12-45-1b (strain with high alkaline resistance) and DaMrp from D. alimentaria 72T (strain with low alkaline resistance) displayed Na+(Li+)/H+ antiport activities, they functioned optimally at different pH levels (9.0 for DQ12-45-1b and 8.0 for 72T). While both antiporters functioned properly to protect Escherichia coli cells from salt shock, only the DqMrp-containing strain survived the high alkaline shock. Furthermore, real-time PCR results showed that the expression of mrpA and mrpD induced only immediately after DQ12-45-1b cells were subjected to the alkaline shock. These results suggested that the expression of DqMrp might be induced by a pH gradient across the cell membrane, and DqMrp mainly functioned at an early stage to respond to the alkaline shock.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco-Rivero A, Leganes F, Fernandez-Valiente E, Calle P, Fernandez-Pinas F (2005) mrpA, a gene with roles in resistance to Na+ and adaptation to alkaline pH in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC7120. Microbiology 151(5):1671–1682. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27848-0
Duckworth AW, Grant S, Grant WD, Jones BE, Meijer D (1998) Dietzia natronolimnaios sp. nov., a new member of the genus Dietzia isolated from an East African soda lake. Extremophiles 2(3):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007920050079
Dzioba-Winogrodzki J, Winogrodzki O, Krulwich TA, Boin MA, Hase CC, Dibrov P (2009) The Vibrio cholerae Mrp system: cation/proton antiport properties and enhancement of bile salt resistance in a heterologous host. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 16(3–4):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1159/000119547
Hamamoto T, Hashimoto M, Hino M, Kitada M, Seto Y, Kudo T, Horikoshi K (1994) Characterization of a gene responsible for the Na+/H+ antiporter system of alkalophilic Bacillus species strain C-125. Mol Microbiol 14(5):939–946. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01329.x
Hunte C, Screpanti E, Venturi M, Rimon A, Padan E, Michel H (2005) Structure of a Na+/H+ antiporter and insights into mechanism of action and regulation by pH. Nature 435(7046):1197–1202. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03692
Ito M, Guffanti AA, Oudega B (1999) mrp, a multigene, multifunctional locus in Bacillus subtilis with roles in resistance to cholate and to NA+ and in pH homeostasis. J Bacteriol 181(8):2394–2402
Jasso-Chavez R, Diaz-Perez C, Rodriguez-Zavala JS, Ferry JG (2017) Functional role of MrpA in the MrpABCDEFG Na+/H+ antiporter complex from the archaeon Methanosarcina acetivorans. J Bacteriol 199(2):e00662-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00662-16
Jiang J, Wang L, Zhang H, Wu H, Huang H, Yang L (2013a) Putative paired small multidrug resistance family proteins PsmrAB, the homolog of YvdSR, actually function as a novel two-component Na+/H+ antiporter. FEMS Microbiol Lett 338(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12008
Jiang J, Wang L, Zou Y (2013b) Identification of important charged residues for alkali cation exchange or pH regulation of NhaH, a Na+/H+ antiporter of Halobacillus dabanensis. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1823(3):997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.11.015
Kajiyama Y, Otagiri M, Sekiguchi J, Kosono S, Kudo T (2007) Complex formation by the mrpABCDEFG gene products, which constitute a principal Na+/H+ antiporter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 189(20):7511–7514. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00968-07
Kashyap DR, Botero LM, Lehr C, Hassett DJ, McDermott TR (2006) A Na+:H+ antiporter and a molybdate transporter are essential for arsenite oxidation in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 188(4):1577–1584. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.4.1577-1584.2006
Kim J, Roh SW, Choi JH, Jung MJ, Nam YD, Kim MS, Park EJ, Shin KS, Bae JW (2011) Dietzia alimentaria sp. nov., isolated from a traditional Korean food. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(9):2254–2258. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.021501-0
Kosono S, Haga K, Tomizawa R, Kajiyama Y, Hatano K, Takeda S, Wakai Y, Hino M, Kudo T (2005) Characterization of a multigene-encoded sodium/hydrogen antiporter (Sha) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its involvement in pathogenesis. J Bacteriol 187(15):5242–5248. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.15.5242-5248.2005
Kozachkov L, Padan E (2013) Conformational changes in NhaA Na+/H+ antiporter. Mol Membr Biol 30(1):90–100. https://doi.org/10.3109/09687688.2012.693209
Krulwich TA, Hicks DB, Ito M (2009) Cation/proton antiporter complements of bacteria: why so large and diverse? Mol Microbiol 74(2):257–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06842.x
Krulwich TA, Sachs G, Padan E (2011) Molecular aspects of bacterial pH sensing and homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(5):330–343. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2549
Kudo T, Hino M, Kitada M, Horikoshi K (1990) DNA sequences required for the alkalophily of Bacillus sp. strain C-125 are located close together on its chromosomal DNA. J Bacteriol 172(12):7282–7283. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.12.7282-7283.1990
Lee C, Kang HJ, von Ballmoos C, Newstead S, Uzdavinys P, Dotson DL, Iwata S, Beckstein O, Cameron AD, Drew D (2013) A two-domain elevator mechanism for sodium/proton antiport. Nature 501(7468):573–577. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12484
Lu S, Nie Y, Tang YQ, Xiong G, Wu XL (2014) A critical combination of operating parameters can significantly increase the electrotransformation efficiency of a gram-positive Dietzia strain. J Microbiol Methods 103:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2014.05.015
Morino M, Natsui S, Swartz TH, Krulwich TA, Ito M (2008) Single gene deletions of mrpA to mrpG and mrpE point mutations affect activity of the Mrp Na+/H+ antiporter of alkaliphilic Bacillus and formation of hetero-oligomeric Mrp complexes. J Bacteriol 190(12):4162–4172. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00294-08
Morino M, Suzuki T, Ito M, Krulwich TA (2014) Purification and functional reconstitution of a seven-subunit Mrp-type Na+/H+ antiporter. J Bacteriol 196(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01029-13
Nie Y, Liang J, Fang H, Tang YQ, Wu XL (2011) Two novel alkane hydroxylase-rubredoxin fusion genes isolated from a Dietzia bacterium and the functions of fused rubredoxin domains in long-chain n-alkane degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(20):7279–7288. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00203-11
Padan E (2008) The enlightening encounter between structure and function in the NhaA Na+–H+ antiporter. Trends Biochem Sci 33(9):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2008.06.007
Putnoky P, Kereszt A, Nakamura T (1998) The pha gene cluster of Rhizobium meliloti involved in pH adaptation and symbiosis encodes a novel type of K+ efflux system. Mol Microbiol 28(6):1091–1101. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00868.x
Sperling E, Górecki K, Drakenberg T (2016) Functional differentiation of antiporter-like polypeptides in complex I; a site-directed mutagenesis study of residues conserved in MrpA and NuoL but not in MrpD, NuoM, and NuoN. PLoS One 11(7):e0158972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158972
Swartz TH, Ikewada S, Ishikawa O, Ito M, Krulwich TA (2005) The Mrp system: a giant among monovalent cation/proton antiporters? Extremophiles 9(5):345–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0451-6
Szvetnik A, Bihari Z, Szabo Z, Kelemen O, Kiss I (2010) Genetic manipulation tools for Dietzia spp. J Appl Microbiol 109(5):1845–1852. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04818.x
Teruo K, Toshi S, Kei I, Masaaki T, Tomofusa T (1994) Properties and sequence of the NhaA Na+/H+ antiporter of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Biochem 116(5):1030–1038. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124624
Toshiaki H, Kazuyo K, Teruo K, Tohru M, Tomofusa T (1998) A putative multisubunit Na+/H+ antiporter from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 180(24):6642–6648
Van K, Julia C, Hatfull GF (2007) Recombineering in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Methods 4(2):147–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth996
Wang XB, Chi CQ, Nie Y, Tang YQ, Tan Y, Wu G, Wu XL (2011) Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons (C6-C40) and crude oil by a novel Dietzia strain. Bioresour Technol 102(17):7755–7761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.009
Williams KA (2000) Three-dimensional structure of the ion-coupled transport protein NhaA. Nature 403(6765):112–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/47534
Yamaguchi T, Tsutsumi F, Putnoky P, Fukuhara M, Nakamura T (2009) pH-dependent regulation of the multi-subunit cation/proton antiporter Pha1 system from Sinorhizobium meliloti. Microbiology 155(8):2750–2756. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.028563-0
Yang L, Jiang J, Wei W, Zhang B, Wang L, Yang S (2006) The pha2 gene cluster involved in Na+ resistance and adaption to alkaline pH in Sinorhizobium fredii RT19 encodes a monovalent cation/proton antiporter. FEMS Microbiol Lett 262(2):172–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00385.x
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Lei Wang from China Agricultural University for kindly providing E. coli KNabc.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31225001 to XLW, and 31300108 to YN) and the National Basic Research Program of China (“973” Program, 2014CB846002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 710 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Qin, XY., Zhang, KD. et al. Role of the Group 2 Mrp sodium/proton antiporter in rapid response to high alkaline shock in the alkaline- and salt-tolerant Dietzia sp. DQ12-45-1b. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 3765–3777 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8846-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8846-3