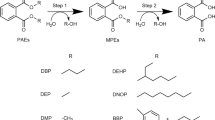
Abstract
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) have long been known as the most widely used plasticizer with a broad range of industrial application. PAEs are ubiquitous in different environments and our daily life due to their large and widespread application. Recent PAEs research mainly focused on their environmental fate (including leaching, migration, transformation) and toxicology and risk assessment. With the comprehensive recognition of their potential hazard, the elimination of PAEs has attracted worldwide concerns. Although many factors may contribute to the degradation of PAEs, the dominant role of biodegradation was widely reported. Many PAEs-degrading bacteria were isolated, metabolites and metabolic pathways were proposed, and enzymes involved in the degradation were identified. The current paper presents an overview of available reports about PAEs-degrading bacteria and related molecular mechanisms. The metabolic pathways deduced from the identified intermediates were presented. The upstream and downstream pathways of PAEs metabolism were summarized, including the aerobic and anaerobic pathways of phthalic acid (PA) degradation. Known enzymes involved in the hydrolysis of ester bonds were characterized according to their properties. Based on phylogenetic analysis, all these enzymes were distributed in four families of esterases and one unknown family. For these five families, conserved sequence motifs were identified and the biological properties of these motifs were characterized. Challenges and emerging opportunities are also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir S, Hafidi M, Merlina G, Hamdi H, Jouraiphy A, El Gharous M, Revel JC (2005) Fate of phthalic acid esters during composting of both lagooning and activated sludges. Process Biochem 40(6):2183–2190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.08.012
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343(1):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3430177
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Web Server):W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Cadogan DF, Papez M, Popp AC, Scheubel J (1993) An assessment of the release, occurrence and possible effects of plasticizers in the environment. Prog Rubber Plast Re 1:1–19
Chang BV, Liao CS, Yuan SY (2005) Anaerobic degradation of diethyl phthalate, di-n-butyl phthalate, and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate from river sediment in Taiwan. Chemosphere 58(11):1601–1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.031
Chang HK, Zylstra GJ (1998) Novel organization of the genes for phthalate degradation from Burkholderia cepacia DBO1. J Bacteriol 180(24):6529–6537
Chatterjee S, Dutta TK (2008) Metabolic cooperation of Gordonia sp. strain MTCC 4818 and Arthrobacter sp. strain WY in the utilization of butyl benzyl phthalate: effect of a novel co-culture in the degradation of a mixture of phthalates. Microbiology 154(11):3338–3346. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2008/021881-0
Chen CY (2004) Biosynthesis of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) from red alga—Bangia atropurpurea. Water Res 38(4):1014–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.029
Chen JA, Li X, Li J, Cao J, Qiu Z, Zhao Q, Xu C, Shu W (2007) Degradation of environmental endocrine disruptor di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate by a newly discovered bacterium, Microbacterium sp. strain CQ0110Y. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(3):676–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0700-3
Chen X, Xu S, Tan T, Lee ST, Cheng SH, Lee FW, Xu SJ, Ho KC (2014) Toxicity and estrogenic endocrine disrupting activity of phthalates and their mixtures. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(3):3156–3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303156
Chen X, Zhang X, Yang Y, Yue D, Xiao L, Yang L (2015) Biodegradation of an endocrine-disrupting chemical di-n-butyl phthalate by newly isolated Camelimonas sp. and enzymatic properties of its hydrolase. Biodegradation 26(2):171–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-015-9725-6
Cheung JKH, Lam RKW, Shi MY, Gu JD (2007) Environmental fate of endocrine-disrupting dimethyl phthalate esters (DMPE) under sulfate-reducing condition. Sci Total Environ 381(1-3):126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.030
Ding J, Wang C, Xie Z, Li J, Yang Y, Mu Y, Tang X, Xu B, Zhou J, Huang Z (2015) Properties of a newly identified esterase from Bacillus sp. K91 and its novel function in diisobutyl phthalate degradation. PLoS One 10(3):e0119216. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119216
Eaton RW (2001) Plasmid-encoded phthalate catabolic pathway in Arthrobacter keyseri 12B. J Bacteriol 183(12):3689–3703. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.12.3689-3703.2001
Eaton RW, Ribbons DW (1982) Metabolism of dibutylphthalate and phthalate by Micrococcus sp. strain 12b. J Bacteriol 151(1):48–57
Elder DJE, Kelly DJ (1994) The bacterial degradation of benzoic-acid and benzenoid compounds under anaerobic conditions—unifying trends and new perspectives. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13(4):441–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00061.x
Engelhardt G, Wallnofer PR, Hutzinger O (1975) The microbial metabolism of di-n-butyl phthalate and related dialkyl phthalates. B Environ Contam Tox 13(3):342–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01685348
Fenner K, Canonica S, Wackett LP, Elsner M (2013) Evaluating pesticide degradation in the environment: blind spots and emerging opportunities. Science 341(6147):752–758. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1236281
Hara H, Stewart GR, Mohn WW (2010) Involvement of a novel ABC transporter and monoalkyl phthalate ester hydrolase in phthalate ester catabolism by Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Appl Environ Microb 76(5):1516–1523. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02621-09
Hong DK, Jang S, Lee CW (2016) Gene cloning and characterization of a psychrophilic phthalate esterase with organic solvent tolerance from an Arctic bacterium Sphingomonas glacialis PAMC 26605. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 133: S337-S345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2017.02.004
Hsu P, Kuo Y, Leon Guo Y, Chen J, Tsai S, Chao H, Teng Y, Pan M (2016) The adverse effects of low-dose exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate during adolescence on sperm function in adult rats. Environ Toxicol 31:706–712
Hu J, Yang Q, Wang JL (2015) Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate in sequencing batch reactor bioaugmented with Micrococcus sp. and the bacterial community analysis. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(9):2819–2828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0683-z
Iwaki H, Nishimura A, Hasegawa Y (2012) Isolation and characterization of marine bacteria capable of utilizing phthalate. World J Microb Biot 28(3):1321–1325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0925-x
Iwata M, Imaoka T, Nishiyama T, Fujii T (2016) Re-characterization of mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate hydrolase belonging to the serine hydrolase family. J Biosci Bioeng 122(2): 140-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.01.008
Jiao Y, Chen X, Wang X, Liao X, Xiao L, Miao A, Wu J, Yang L (2013) Identification and characterization of a cold-active phthalate esters hydrolase by screening a metagenomic library derived from biofilms of a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS One 8(10):e75977. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075977
Jin D, Kong X, Cui B, Bai Z, Zhang H (2013) Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by a newly isolated halotolerant Sphingobium sp. Int J Mol Sci 14(12):24046–24054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224046
Jin D, Zhu Y, Wang X, Kong X, Liu H, Wang Y, Deng Y, Jia M (2016) Draft genome sequence of Sphingobium yanoikuyae TJ, a halotolerant di-n-butyl-phthalatedegrading bacterium. Genome Announc 4(3):e00569–e00516
Katsikantami I, Sifakis S, Tzatzarakis MN, Vakonaki E, Kalantzi O, Tsatsakis AM, Rizos AK (2016) A global assessment of phthalates burden and related links to health effects. Environ Int 97:212–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.09.013
Kimber I, Dearman RJ (2010) An assessment of the ability of phthalates to influence immune and allergic responses. Toxicology 271(3):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2010.03.020
Kleerebezem R, Pol LWH, Lettinga G (1999) Anaerobic biodegradability of phthalic acid isomers and related compounds. Biodegradation 10(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008321015498
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kumar V, Maitra SS (2016) Biodegradation of endocrine disruptor dibutyl phthalate (DBP) by a newly isolated Methylobacillus sp. V29 and the DBP degradation pathway. 3. Biotech 6:200
Kumar V, Sharma N, Maitra SS (2017) Comparative study on the degradation of dibutyl phthalate by two newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. V21b and Comamonas sp. 51F. Biot R 15:1–10
Kurane R (1986) Microbial degradation of phthalate esters. Microb Sci 3:92–95
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Latini G, Del Vecchio A, Massaro M, Verrotti A, De Felice C (2006) Phthalate exposure and male infertility. Toxicology 226(2-3):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2006.07.011
Liang D, Zhang T, Fang HHP, He J (2008) Phthalates biodegradation in the environment. Appl Microbiol Biot 80(2):183–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1548-5
Liu SM, Chi WC (2003) CO2-H2 dependent anaerobic biotransformation of phthalic acid isomers in sediment slurries. Chemosphere 52(6):951–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00326-6
Lobkovsky E, Moews PC, Liu H, Zhao H, Frere JM, Knox JR (1993) Evolution of an enzyme activity: crystallographic structure at 2-A resolution of cephalosporinase from the ampC gene of Enterobacter cloacae P99 and comparison with a class A penicillinase. P Natl Acad Sci USA 90 (23): 11257-11261.
Luo Z, Ding J, Xu W, Zheng T, Zhong T (2015) Purification and characterization of an intracellular esterase from a marine Fusarium fungal species showing phthalate diesterase activity. Int Biodeter Biodegr 97:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.10.006
Ma D, Hao Z, Sun R, Bartlam M, Wang Y (2016) Genome sequence of a typical ultramicrobacterium, Curvibacter sp. strain PAE-UM, capable of phthalate ester degradation. Genome Announc 4(1):e01510–e01515
Maruyama K, Akita K, Naitou C, Yoshida M, Kitamura T (2005) Purification and characterization of an esterase hydrolyzing monoalkyl phthalates from Micrococcus sp. YGJ1. J Biochem 137(1): 27-32.
Mathieu-Denoncourt J, de Solla SR, Langlois VS (2015) Chronic exposures to monomethyl phthalate in western clawed frogs. Gen Comp Endocr 219:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.01.019
Mathieu-Denoncourt J, Wallace SJ, de Solla SR, Langlois VS (2016) Influence of lipophilicity on the toxicity of bisphenol A and phthalates to aquatic organisms. B Environ Contam Tox 97(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1812-9
Mu D, Gao F, Fan Z, Shen H, Peng H, Hu J (2015) Levels of phthalate metabolites in urine of pregnant women and risk of clinical pregnancy loss. Environ Sci Technol 49(17):10651–10657. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02617
Nahurira R, Ren L, Song J, Jia Y, Wang J, Fan S, Wang H, Yan Y (2017) Degradation of di(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate by a novel Gordonia alkanivorans strain YC-RL2. Curr Microbiol 74(3):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1159-9
Navacharoen A, Vangnai AS (2011) Biodegradation of diethyl phthalate by an organic-solvent-tolerant Bacillus subtilis strain 3C3 and effect of phthalate ester coexistence. Int Biodeter Biodegr 65(6):818–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.05.005
Net S, Sempéré R, Delmont A, Paluselli A, Ouddane B (2015) Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ Sci Technol 49(7):4019–4035. https://doi.org/10.1021/es505233b
Nishioka T, Iwata M, Imaoka T, Mutoh M, Egashira Y, Nishiyama T, Shin T, Fujii T (2006) A mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate hydrolase from a Gordonia sp. that is able to dissimilate di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate. Appl Environ Microb 72(4):2394–2399. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.4.2394-2399.2006
Nomura Y, Nakagawa M, Ogawa N, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1992) Genes in pht plasmid encoding the initial degradation pathway of phthalate in Pseudomonas putida. J Ferm Bioeng 74(6):333–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(92)90028-S
Patil NK, Kundapur R, Shouche YS, Karegoudar TB (2006) Degradation of plasticizer di-n-butylphthalate by Delftia sp. TBKNP-05. Curr Microb 52(5):369–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-5258-2
Rahman M, Brazel C (2004) The plasticizer market: an assessment of traditional plasticizers and research trends to meet new challenges. Prog Polym Sci 29(12):1223–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.10.001
Ren L, Jia Y, Ruth N, Qiao C, Wang J, Zhao B, Yan Y (2016) Biodegradation of phthalic acid esters by a newly isolated Mycobacterium sp. YC-RL4 and the bioprocess with environmental samples. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(16):16609–16619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6829-4
Ren L, Shuanghu F, Junhuan W, Nahurira R, Cheng Q, Yang J, Yanchun Y (2017) Complete genome sequence of a phthalic acid esters degrading Mycobacterium sp. YC-RL4. Braz J Microbiol 48(4):607–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.09.022
Robinson L, Miller R (2015) The impact of bisphenol A and phthalates on allergy, asthma, and immune function: a review of latest findings. Curr Environ Health R 2(4):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-015-0066-8
Romao MJ, Turk D, Gomis-Ruth FX, Huber R, Schumacher G, Mollering H, Russmann L (1992) Crystal structure analysis, refinement and enzymatic reaction mechanism of N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase from Arthrobacter sp. at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol 226(4):1111–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(92)91056-U
Rosato (1976) Plastics technology handbook, Fourth edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Sarkar J, Chowdhury PP, Dutta TK (2013) Complete degradation of di-n-octyl phthalate by Gordonia sp. strain Dop5. Chemosphere 90(10):2571–2577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.101
Sayyad G, Price GW, Sharifi M, Khosravi K (2017) Fate and transport modeling of phthalate esters from biosolid amended soil under corn cultivation. J Hazard Mater 323(Pt A):264–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.032
Schiedek T (1995) Impact of plasticizers (phthalic acid esters) on soil and groundwater quality. Groundwater Quality Remediation & Protection 225:149–156
Stojanoska MM, Milosevic N, Milic N, Abenavoli L (2017) The influence of phthalates and bisphenol A on the obesity development and glucose metabolism disorders. Endocrine 55(3):666–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1158-4
Sun J, Wu X, Gan J (2015) Uptake and metabolism of phthalate esters by edible plants. Environ Sci Technol 49(14):8471–8478. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01233
Tang WJ, Zhou Y, Ye BC (2015) Draft genome sequence of a phthalate ester-degrading bacterium, Rhizobium sp. LMB-1, isolated from cultured soil. Genome Announc 3(3):e00392–e00315
USEPA, 1992 and update. Code of federal regulations. 40 CFR, Part 136
Union E (1993) Council Regulation (EEC), No 793/93 of 23 March 1993 on the evaluation and control of the risks of existing substances (OJ L84, 5 April 1993). European Union, Brussels
Vaillancourt FH, Bolin JT, Eltis LD (2006) The ins and outs of ring-cleaving dioxygenases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol 41(4):241–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409230600817422
Vieira MGA, Da Silva MA, Dos Santos LO, Beppu MM (2011) Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: a review. Eur Polym J 47(3):254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.12.011
Wang J, Luo Y, Teng Y, Ma W, Christie P, Li Z (2013) Soil contamination by phthalate esters in Chinese intensive vegetable production systems with different modes of use of plastic film. Environ Pollut 180:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.05.036
Wang J, Zhang M, Chen T, Zhu Y, Teng Y, Luo Y, Christie P (2015) Isolation and identification of a di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-degrading bacterium and its role in the bioremediation of a contaminated soil. Pedosphere 25(2):202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60005-4
Wang Y, Miao B, Hou D, Wu X, Peng B (2012) Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate and expression of the 3,4-phthalate dioxygenase gene in Arthrobacter sp. ZH2 strain. Process Biochem 47(6):936–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.02.027
Whangsuk W, Sungkeeree P, Nakasiri M, Thiengmag S, Mongkolsuk S, Loprasert S (2015) Two endocrine disrupting dibutyl phthalate degrading esterases and their compensatory gene expression in Sphingobium sp. SM42. Int Biodeter Biodegr 99:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.12.006
Wu D, Mahmood Q, Zheng P, Hassan MJ (2007) Isolation and physiology of a dimethyl phthalate degrading bacterial strain YZ2. Environ Prog 26(4):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10237
Wu J, Liao X, Yu F, Wei Z, Yang L (2013) Cloning of a dibutyl phthalate hydrolase gene from Acinetobacter sp. strain M673 and functional analysis of its expression product in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biot 97(6):2483–2491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4232-8
Wu X, Liang R, Dai Q, Jin D, Wang Y, Chao W (2010) Complete degradation of di-n-octyl phthalate by biochemical cooperation between Gordonia sp. strain JDC-2 and Arthrobacter sp. strain JDC-32 isolated from activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 176(1-3):262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.022
Xia X, Yang L, Bu Q, Liu R (2011) Levels, distribution, and health risk of phthalate esters in urban soils of Beijing, China. J Environ Qual 40(5):1643–1651. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0032
Xu X, Li H, Gu J (2005) Biodegradation of an endocrine-disrupting chemical di-n-butyl phthalate ester by Pseudomonas fluorescens B-1. Int Biodeter Biodegr 55(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2004.05.005
Zajc A, Romao MJ, Turk B, Huber R (1996) Crystallographic and fluorescence studies of ligand binding to N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase from Arthrobacter sp. J Mol Biol 263(2):269–283. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0574
Zeng F, Cui K, Li X, Fu J, Sheng G (2004) Biodegradation kinetics of phthalate esters by Pseudomonas fluoresences FS1. Process Biochem 39(9):1125–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00226-7
Zeng P, Moy BY, Song Y, Tay J (2008) Biodegradation of dimethyl phthalate by Sphingomonas sp. isolated from phthalic-acid-degrading aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biot 80(5):899–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1632-x
Zhang XY, Fan X, Qiu XJ, Li CY, Xing S, Zheng YT, Xu JH (2014) Newly identified thermostable esterase from Sulfobacillus acidophilus: properties and performance in phthalate ester degradation. Appl Environ Micro 80(22): 6870-6878.
Zhang Y, Tao Y, Zhang H, Wang L, Sun G, Sun X, Erinle KO, Feng C, Song Q, Li M (2015) Effect of di-n-butyl phthalate on root physiology and rhizosphere microbial community of cucumber seedlings. J Hazard Mater 289:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.071
Zhao H, Du H, Feng N, Xiang L, Li Y, Li H, Cai Q, Mo C (2016a) Biodegradation of di-n-butylphthalate and phthalic acid by a novel Providencia sp. 2D and its stimulation in a compost-amended soil. Biol Fert Soils 52:65–76
Zhao H, Du H, Lin J, Chen X, Li Y, Li H, Cai Q, Mo C, Qin H, Wong M (2016b) Complete degradation of the endocrine disruptor di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a novel Agromyces sp. MT-O strain and its application to bioremediation of contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 562:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.171
Acknowledgements
We thank Nahurira Ruth (Graduate School, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) for the revision of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Nos. 31700097 and 41301252), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (No. 2016A030310330), and Guangdong Scientific and Technological Research Program (2013B020309010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1538 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Lin, Z., Liu, H. et al. Bacteria-mediated phthalic acid esters degradation and related molecular mechanisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 1085–1096 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8687-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8687-5