Abstract
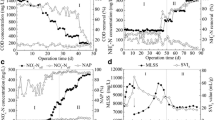
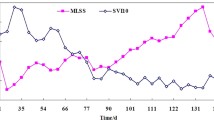
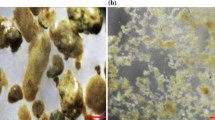
In this study, we demonstrated that anaerobic granular sludge could be successfully transformed into aerobic granular sludge in a continuous up-flow reactor in 45 days. An aerobic microbial community successfully developed in the granules and high organic matter and nitrogen removal performance was achieved. Under an ammonia nitrogen loading rate of 0.8 kg N/(m3 day), ammonia nitrogen and the total nitrogen removal efficiency of the reactor reached up to 100 and 93%, respectively. An obvious bacterial community shift in granular sludge was observed during the transformation process. By comparing with the bacterial community in aerobic granules cultivated from floccular activated sludge, some bacteria (affiliated with Comamonadaceae, Xanthomonadaceae, Rhodocyclaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Nitrosomonadaceae) playing significant roles in maintaining the structures and functions of aerobic granules were identified. After the transformation, the granules could be clearly separated into the inner core and outer shell. 16S rRNA gene sequencing results indicated many bacterial species present in both the inner core and outer shell; however, their abundance differed significantly. Overall, this study confirms the feasibility of transforming anaerobic granules into aerobic granules and provides novel approaches and insights to understand the microbial ecology in granular sludge.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2007) Degradation of phenol by Acinetobacter strain isolated from aerobic granules. Chemosphere 67(8):1566–1572
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Single-culture aerobic granules with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(3):551–557
Adav SS, Lee D-J, Lai J-Y (2010) Microbial community of acetate utilizing denitrifiers in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(3):753–762
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Show KY, Tay JH (2008) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26(5):411–423
Apah W (2005) AWWA. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Arrojo B, Mosquera-Corral A, Garrido JM, Méndez R (2004) Aerobic granulation with industrial wastewater in sequencing batch reactors. Water Res 38(14):3389–3399
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Meth 7(5):335–336
Carr EL, Kämpfer P, Patel BK, Gürtler V, Seviour RJ (2003) Seven novel species of Acinetobacter isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(4):953–963
Corsino S, Campo R, Di Bella G, Torregrossa M, Viviani G (2016) Study of aerobic granular sludge stability in a continuous-flow membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 200:1055–1059
De Kreuk M, Heijnen J, Van Loosdrecht M (2005) Simultaneous COD, nitrogen, and phosphate removal by aerobic granular sludge. Biotechnol Bioeng 90(6):761–769
de Kreuk MK, Kishida N, van Loosdrecht MCM (2007) Aerobic granular sludge—state of the art. Water Sci Technol 55(8–9):75–81
Figueroa M, Mosquera-Corral A, Campos J, Méndez R (2008) Treatment of saline wastewater in SBR aerobic granular reactors. Water Sci Technol 58(2):479–485
Franca RD, Vieira A, Mata AM, Carvalho GS, Pinheiro HM, Lourenço ND (2015) Effect of an azo dye on the performance of an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor treating a simulated textile wastewater. Water Res 85:327–336
Gao DW, Liu L, Liang H, Wu WM (2011) Aerobic granular sludge: characterization, mechanism of granulation and application to wastewater treatment. Crit Rev Biotechnol 31(2):137–152
Hu L, Wang J, Wen X, Qian Y (2005) The formation and characteristics of aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactor (SBR) by seeding anaerobic granules. Process Biochem 40(1):5–11
Jemaat Z, Suárez-Ojeda ME, Pérez J, Carrera J (2014) Partial nitritation and o-cresol removal with aerobic granular biomass in a continuous airlift reactor. Water Res 48:354–362
Juang YC, Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2010) Stable aerobic granules for continuous-flow reactors: precipitating calcium and iron salts in granular interiors. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8051–8057
Li D, Lv Y, Zeng H, Zhang J (2016a) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal using granules in continuous-flow reactor. Chem Eng J 298:107–116
Li D, Lv Y, Zeng H, Zhang J (2016b) Startup and long term operation of enhanced biological phosphorus removal in continuous-flow reactor with granules. Bioresour Technol 212:92–99
Liu WT, Chan OC, Fang HH (2002) Microbial community dynamics during start-up of acidogenic anaerobic reactors. Water Res 36(13):3203–3210
Liu Y, Tay JH (2002) The essential role of hydrodynamic shear force in the formation of biofilm and granular sludge. Water Res 36(7):1653–1665
Lv Y, Wan C, Lee D-J, Liu X, Tay J-H (2014) Microbial communities of aerobic granules: granulation mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 169:344–351
Nagendra H (2002) Opposite trends in response for the Shannon and Simpson indices of landscape diversity. Appl Geogr 22(2):175–186
Ni BJ, Xie WM, Liu SG, Yu HQ, Wang YZ, Wang G, Dai X-L (2009) Granulation of activated sludge in a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor for the treatment of low-strength municipal wastewater. Water Res 43(3):751–761
Oren A (2014) The family Rhodocyclaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, pp 975–998
Pronk M, de Kreuk M, de Bruin B, Kamminga P, Kleerebezem R, van Loosdrecht M (2015) Full scale performance of the aerobic granular sludge process for sewage treatment. Water Res 84:207–217
Satoh H, Miura Y, Tsushima I, Okabe S (2007) Layered structure of bacterial and archaeal communities and their in situ activities in anaerobic granules. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(22):7300–7307
Saunders AM, Albertsen M, Vollertsen J, Nielsen PH (2016) The activated sludge ecosystem contains a core community of abundant organisms. ISME J 10:11–20
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60
Song Y, Ishii S, Rathnayake L, Ito T, Satoh H, Okabe S (2013) Development and characterization of the partial nitrification aerobic granules in a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Bioresour Technol 139:285–291
Stein LY, Arp DJ, Berube PM, Chain PS, Hauser L, Jetten MS, Klotz MG, Larimer FW, Norton JM, Op den Camp HJ (2007) Whole-genome analysis of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, Nitrosomonas eutropha C91: implications for niche adaptation. Environ Microbiol 9(12):2993–3007
Teixeira LM, Merquior VLC (2014) The family Moraxellaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: Gammaproteobacteria. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, pp 443–476
Tsuneda S, Nagano T, Hoshino T, Ejiri Y, Noda N, Hirata A (2003) Characterization of nitrifying granules produced in an aerobic upflow fluidized bed reactor. Water Res 37(20):4965–4973
van der Roest H, de Bruin L, Gademan G, Coelho F (2011) Towards sustainable waste water treatment with Dutch Nereda® technology. Water Pract Technol 6(3):wpt2011059
Verawaty M, Pijuan M, Yuan Z, Bond P (2012) Determining the mechanisms for aerobic granulation from mixed seed of floccular and crushed granules in activated sludge wastewater treatment. Water Res 46(3):761–771
Wang Q, Du GC, Chen J (2004) Aerobic granular sludge cultivated under the selective pressure as a driving force. Process Biochem 39(5):557–563
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267
Willems A (2014) The family Comamonadaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 975–998
Winkler MH, Kleerebezem R, De Bruin L, Verheijen P, Abbas B, Habermacher J, Van Loosdrecht M (2013) Microbial diversity differences within aerobic granular sludge and activated sludge flocs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(16):7447–7458
Wu J-H, Liu W-T, Tseng I-C, Cheng S-S (2001) Characterization of microbial consortia in a terephthalate-degrading anaerobic granular sludge system. Microbiology 147(2):373–382
Xu G, Peng J, Feng C, Fang F, Chen S, Xu Y, Wang X (2015) Evaluation of simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrification processes and bacterial community structure analysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(15):6527–6536
Yan L, Zhang S, Hao G, Zhang X, Ren Y, Wen Y, Guo Y, Zhang Y (2016) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by EPSs in aerobic granular sludge enhanced nitrogen removal of ammonium-nitrogen-rich wastewater. Bioresour Technol 202:101–106
Ye L, Zhang T (2011) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria dominates over ammonia-oxidizing archaea in a saline nitrification reactor under low DO and high nitrogen loading. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(11):2544–2552
Ye L, Zhang T (2013) Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(6):2681–2690
Zhang B, Chen Z, Qiu Z, Jin M, Chen Z, Chen Z, Li J, Wang X, Wang J (2011) Dynamic and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria communities during sludge granulation in an anaerobic–aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 45(18):6207–6216
Zhang T, Shao MF, Ye L (2012) 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J 6(6):1137–1147
Zheng YM, Yu HQ, Liu SJ, Liu XZ (2006) Formation and instability of aerobic granules under high organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 63(10):1791–1800
Acknowledgements
We thank Kailong Huang for the assistance in the sequencing and data analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160657), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51608256, 51378252), Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province of China (SBK2015010297) and National Key Technology Support Program of China (2014BAC08B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 330 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Yu, P., Li, Q. et al. Transformation of anaerobic granules into aerobic granules and the succession of bacterial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7703–7713 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8491-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8491-2