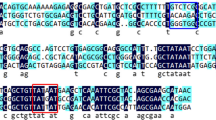
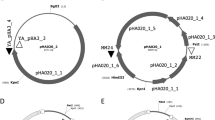
Abstract
Salinicoccus salsiraiae IM408 (=CGMCC13032) is a novel halophilic bacterium that we isolated from the saline soil of Da Gang Oilfield. It tolerates 60 g/l sodium chloride and up to 123 g/l (1.5 M) sodium acetate and has shown a potential application in bioremediation of wastewater with high salt and high chemical oxygen demand (COD). Two plasmids, pS408-1 and pS408-2, were identified in S. salsiraiae IM408, and the sequences and copy numbers of the plasmids were determined. Based on these plasmids, two shuttle vectors containing a replicon for Escherichia coli, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol resistance genes, as well as the replicon from pS408-1 or pS408-2, were constructed and named as pTCS101 and pTCS201, respectively. A suitable host strain, named S. salsiraiae PE01, was also developed from the wild-type by plasmid elimination. Using the plasmid pTCS101 as an expression vector, l-lactate dehydrogenase from Staphylococcus aureus was expressed successfully in S. salsiraiae PE01. This is the first gene expression system for the Salinicoccus genus. It has provided the potential for expression of desired proteins or for establishment of desired pathways in Salinicoccus strains, which would make these halophiles more advantageous in future biotechnological applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi S, Amoozegar MA, Khajeh K (2014) Enzyme(s) responsible for tellurite reducing activity in a moderately halophilic bacterium, Salinicoccus iranensis strain QW6. Extremophiles 18:953–961. doi:10.1007/s00792-014-0665-6
Amoozegar MA, Ashengroph M, Malekzadeh F, Razavi MR, Naddaf S, Kabiri M (2008a) Isolation and initial characterization of the tellurite reducing moderately halophilic bacterium, Salinicoccus sp. strain QW6. Microbiol Res 163:456–465. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2006.07.010
Amoozegar MA, Schumann P, Hajighasemi M, Ashengroph M, Razavi MR (2008b) Salinicoccus iranensis sp. nov., a novel moderate halophile. Int J Syst Evol Micr 58:178–183. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65221-0
Aslam Z, Lim JH, Im WT, Yasir M, Chung YR, Lee ST (2007) Salinicoccus jeotgali sp. nov., isolated from jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Micr 57:633–638. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64586-0
Breuert S, Allers T, Spohn G, Soppa J (2006) Regulated polyploidy in halophilic archaea. PLoS One 1:e92. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000092
Brückner R (1997) Gene replacement in Staphylococcus carnosus and Staphylococcus xylosus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 151:1–8
Byeon WH, Weisblum B (1984) Post-transcriptional regulation of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase. J Bacteriol 158:543–550
Chen YG, Cui XL, Li WJ, Xu LH, Wen ML, Peng Q, Jiang CL (2008) Salinicoccus salitudinis sp. nov., a new moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a saline soil sample. Extremophiles 12:197–203. doi:10.1007/s00792-007-0116-8
Chen YG, Cui XL, Pukall R, Li HM, Yang YL, Xu LH, Wen ML, Peng O, Jiang CL (2007) Salinicoccus kunmingensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt mine in Yunnan, south-west China. Int J Syst Evol Micr 57:2327–2332. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64783-0
Chen YG, Cui XL, Wang YX, Zhang YQ, Li QY, Liu ZX, Wen ML, Peng Q, Li WJ (2009) Salinicoccus albus sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium from a salt mine. Int J Syst Evol Micr 59:874–879. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.003251-0
Clewell DB (1972) Nature of ColE1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol 110:667–676
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. doi:10.2307/2408678
Franca L, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, da Costa MS (2006) Salinicoccus salsiraiae sp. nov.: a new moderately halophilic gram-positive bacterium isolated from salted skate. Extremophiles 10:531–536. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0532-1
Gao MA, Wang L, Chen SF, Zhou YG, Liu HC (2010) Salinicoccus kekensis sp. nov., a novel alkaliphile and moderate halophile isolated from Keke Salt Lake in Qinghai, China. Anton Leeuw Int J G 98:351–357. doi:10.1007/s10482-010-9449-x
Gros MF, Riele H, Ehrlich SD (1987) Rolling circle replication of single-stranded DNA plasmid pC194. EMBO J 6:3863–3869
Gruss AD, Ross HF, Novick RP (1987) Functional analysis of a palindromic sequence required for normal replication of several staphylococcal plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:2165–2169. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.8.2165
Guglielmetti S, Mora D, Parini C (2007) Small rolling circle plasmids in Bacillus subtilis and related species: organization, distribution, and their possible role in host physiology. Plasmid 57:245–264. doi:10.1016/j.plasmid.2006.09.002
Hyun DW, Whon TW, Cho YJ, Chun J, Kim MS, Jung MJ, Shin NR, Kim JY, Kim PS, Yun JH, Lee J, Oh SJ, Bae JW (2013) Genome sequence of the moderately halophilic bacterium Salinicoccus carnicancri type strain CrmT (= DSM 23852T). Stand Genomic Sci 8:255–263. doi:10.4056/sigs.3967649
Jiang K, Xue YF, Ma YH (2015a) Complete genome sequence of Salinicoccus halodurans H3B36, isolated from the Qaidam Basin in China. Stand Genomic Sci 10:116. doi:10.1186/S40793-015-0108-8
Jiang K, Xue YF, Ma YH (2015b) Identification of N α-acetyl-α-lysine as a probable thermolyte and its accumulation mechanism in Salinicoccus halodurans H3B36. Sci Rep-UK 5:18518. doi:10.1038/Srep18518
Jung MJ, Kim MS, Roh SW, Shin KS, Bae JW (2010) Salinicoccus carnicancri sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Micr 60:653–658. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.012047-0
Kämpfer P, Arun AB, Busse HJ, Young CC, Lai WA, Rekha PD, Chen WM (2011) Salinicoccus sesuvii sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of Sesuvium portulacastrum. Int J Syst Evol Micr 61:2348–2352. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.027524-0
Kumar RM, Kaur G, Kumar N, Kumar A, Singh NK, Bala M, Kaur N, Mayilraj S (2015) Taxonomic description and genome sequence of Salinicoccus sediminis sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Micr 65:3794–3799. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.000495
Marquez MC, Ventosa A, Ruiz-Berraquero F (1990) Marinococcus hispanicus, a new species of moderately halophilic gram-positive cocci. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:165–169
Marsin S, Forterre P (1998) A rolling circle replication initiator protein with a nucleotidyl-transferase activity encoded by the plasmid pGT5 from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus abyssi. Mol Microbiol 27:1183–1192. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00759.x
Morimoto T, Kadoya R, Endo K, Tohata M, Sawada K, Liu S, Ozawa T, Kodama T, Kakeshita H, Kageyama Y, Manabe K, Kanaya S, Ara K, Ozaki K, Ogasawara N (2008) Enhanced recombinant protein productivity by genome reduction in Bacillus subtilis. DNA Res 15:73–81. doi:10.1093/dnares/dsn002
Pakdeeto A, Tanasupawat S, Thawai C, Moonmangmee S, Kud T, Itoh T (2007) Salinicoccus siamensis sp. nov., isolated from fermented shrimp paste in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Micr 57:2004–2008. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64876-0
Posfai G, Plunkett G, Feher T, Frisch D, Keil GM, Umenhoffer K, Kolisnychenko V, Stahl B, Sharma SS, de Arruda M, Burland V, Harcum SW, Blattner FR (2006) Emergent properties of reduced-genome Escherichia coli. Science 312:1044–1046. doi:10.1126/science.1126439
Qu Z, Li Z, Zhang XM, Zhang XH (2012) Salinicoccus qingdaonensis sp. nov., isolated from coastal seawater during a bloom of green algae. Int J Syst Evol Micr 62:545–549. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.030551-0
Ramana CV, Srinivas A, Subhash Y, Tushar L, Mukherjee T, Kiran PU, Sasikala C (2013) Salinicoccus halitifaciens sp. nov., a novel bacterium participating in halite formation. Anton Leeuw Int J G 103:885–898. doi:10.1007/s10482-012-9870-4
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schenk S, Laddaga RA (1992) Improved method for electroporation of Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 94:133–138
Srinivas A, Divyasree B, Tushar L, Suresh G, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (2016) Salinicoccus amylolyticus sp. nov., isolated from a saltern. Int J Syst Evol Micr 66:3814–3820. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.001270
Sun CM, Zhou MX, Li Y, Xiang H (2006) Molecular characterization of the minimal replicon and the unidirectional θ replication of pSCM201 in extremely halophilic archaea. J Bacteriol 188:8136–8144. doi:10.1128/Jb.00988-06
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Ventosa A, Marquez MC, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Kocur M (1990) Salinicoccus roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new moderately halophilic gram-positive coccus. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:29–33
Ventosa A, Marquez MC, Weiss N, Tindall BJ (1992) Transfer of Marinococcus hispanicus to the genus Salinicoccus as Salinicoccus hispanicus comb. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:530–534
Wang HY, Wang LM, Yang H, Cai YM, Sun LF, Xue YF, Yu B, Ma YH (2015) Comparative proteomic insights into the lactate responses of halophilic Salinicoccus roseus W12. Sci Rep-UK 5:13776. doi:10.1038/Srep13776
Wang XW, Xue YF, Yuan SQ, Zhou C, Ma YH (2008) Salinicoccus halodurans sp. nov., a moderate halophile from saline soil in China. Int J Syst Evol Micr 58:1537–1541. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65467-0
Zhang WZ, Xue YF, Ma YH, Zhou PJ, Ventosa A, Grant WD (2002) Salinicoccus alkaliphilus sp. nov., a novel alkaliphile and moderate halophile from Baer Soda Lake in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Int J Syst Evol Micr 52:789–793. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.01912-0
Zhang YQ, Yu LY, Liu HY, Zhang YO, Xu LH, Li J (2007) Salinicoccus luteus sp. nov., isolated from a desert soil. Int J Syst Evol Micr 57:1901–1905. doi:10.1099/ijs.0-64967-0
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Dr. Rui Wang (Non-coding RNA and Drug Discovery Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu Medical College) and Dr. Guiming Liu (Technology Transfer Center, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for their help in sample collection and plasmid characterization during their study in our laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31330001) and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (to Hua Xiang).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Yang, H., Chen, J. et al. Development of the first gene expression system for Salinicoccus strains with potential application in bioremediation of hypersaline wastewaters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7249–7258 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8428-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8428-9