Abstract
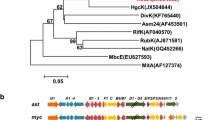
The cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) receptor protein/fumarate and nitrate reductase regulatory protein (Crp/Fnr) family of transcriptional regulators are pleiotropic transcriptional regulators that control a broad range of cellular functions. Leinamycin (LNM) is a potent antitumor antibiotic produced by Streptomyces atroolivaceus S-140. We previously cloned and characterized the lnm biosynthetic gene cluster from S. atroolivaceus S-140. We here report inactivation of lnmO in S. atroolivaceus S-140 and overexpression of lnmO in the S. atroolivaceus S-140 wild-type and ∆lnmE mutant SB3033 to investigate its role in LNM biosynthesis. Bioinformatics analysis revealed LnmO as the only regulator within the lnm gene cluster, exhibiting high sequence similarity to known Crp/Fnr family regulators. The inactivation of lnmO in S. atroolivaceus S-140 completely abolished LNM production but caused no apparent morphological changes, supporting that LnmO is indispensable and specific to LNM biosynthesis. Overexpression of lnmO in S. atroolivaceus S-140 and SB3033 resulted in three- and fourfold increase in LNM and LNM E1 production, respectively, supporting that LnmO acts as a positive regulator. While all of the Crp/Fnr family regulators studied to date appeared to be pleiotropic, our results support LnmO as the first Crp/Fnr family regulator that is pathway-specific. LnmO joins the growing list of regulators that could be exploited to improve secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces. Engineered strains overproducing LNM and LNM E1 will facilitate further mechanistic studies and clinical evaluation of LNM and LNM E1 as novel anticancer drugs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asai A, Hara M, Kakita S, Kanda Y, Yoshida M, Saito H, Saitoh Y (1996) Thiol-mediated DNA alkylation by the novel antitumor antibiotic leinamycin. J Am Chem Soc 118:6802–6803
Ashizawa T, Kawashima K, Kanda Y, Gomi K, Okabe M, Ueda K, Tamaoki T (1999) Antitumor activity of KF22678, a novel thioester derivative of leinamycin. Anti-cancer Drugs 10:829–836
Bibb MJ (2005) Regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:208–215
Bierman M, Logan R, O'Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Busby S, Ebright RH (1999) Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP). J Mol Biol 293:199–213
Chen YH, Smanski MJ, Shen B (2010) Improvement of secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces by manipulating pathway regulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:19–25
Cheng YQ, Tang GL, Shen B (2002) Identification and localization of the gene cluster encoding biosynthesis of the antitumor macrolactam leinamycin in Streptomyces atroolivaceus S-140. J Bacteriol 184:7013–7024
Cheng YQ, Tang GL, Shen B (2003) Type I polyketide synthase requiring a discrete acyltransferase for polyketide biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:3149–3154
Derouaux A, Halici S, Nothaft H, Neutelings T, Moutzourelis G, Dusart J, Titgemeyer F, Rigali S (2004a) Deletion of a cyclic AMP receptor protein homologue diminishes germination and affects morphological development of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 186:1893–1897
Derouaux A, Dehareng D, Lecocq E, Halici S, Nothaft H, Giannotta F, Moutzourelis G, Dusart J, Devreese B, Titgemeyer F, Van Beeumen J, Rigali S (2004b) Crp of Streptomyces coelicolor is the third transcription factor of the large CRP-FNR superfamily able to bind cAMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:983–990
Fekry MI, Szekely J, Dutta S, Breydo L, Zang H, Gates KS (2011) Noncovalent DNA binding drives DNA alkylation by leinamycin: evidence that the Z,E-5-(thiazol-4-yl)-penta-2,4-dienone moiety of the natural product serves as an atypical DNA intercalator. J Am Chem Soc 133:17641–17651
Gao C, Hindra, Mulder D, Yin C, Elliot MA (2012) Crp is a global regulator of antibiotic production in Streptomyces. MBio 3:e00407–e00412
Gates KS (2000) Mechanisms of DNA damage by leinamycin. Chem Res Toxicol 13:953–956
Görke B, Stülke J (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nature Rev Microbiol 6:613–624
Green J, Scott C, Guest JR (2001) Functional versatility in the CRP-FNR superfamily of transcription factors: FNR and FLP. Adv Microbiol Physiol 44:1–34
Hara M, Asano K, Kawamoto I, Takiguchi T, Katsumata S, Takahashi K, Nakano H (1989) Leinamycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from Streptomyces: producing organism, fermentation and isolation. J Antibiot 42:1768–1774
Hara M, Saitoh Y, Nakano H (1990) DNA strand scission by the novel antitumor antibiotic leinamycin. Biochemistry 29:5676–5681
Huang SX, Yun BS, Ma M, Basu HS, Church DR, Ingenhorst G, Huang Y, Yang D, Lohman JR, Tang GL, Ju J, Liu T, Wilding G, Shen B (2015) Leinamycin E1 acting as an anticancer prodrug activated by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:8278–8283
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Körner H, Sofia HJ, Zumft WG (2003) Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp-Fnr transcription regulators: exploiting the metabolic spectrum by controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:559–592
Lawson CL, Swigon D, Murakami KS, Darst SA, Berman HM, Ebright RH (2004) Catabolite activator protein: DNA binding and transcription activation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14:10–20
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:112–143
Liu Y, Ryu H, Ge B, Pan G, Sun L, Park K, Zhang K (2014) Improvement of Wuyiencin biosynthesis in Streptomyces wuyiensis CK-15 by identification of a key regulator, WysR. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1644–1653
Liu T, Ma M, Ge HM, Yang C, Cleveland J, Shen B (2015) Synthesis and evaluation of 8,4′-dideshydroxy-leinamycin revealing new insights into the structure–activity relationship of the anticancer natural product leinamycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25:4899–4902
Ma M, Lohman JR, Liu T, Shen B (2015) C-S bond cleavage by a polyketide synthase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:10359–10364
Matsui M, Tomita M, Kanai A (2013) Comprehensive computational analysis of bacterial CRP/FNR superfamily and its target motifs reveals stepwise evolution of transcriptional networks. Genome Biol Evol 5:267–282
McKay DB, Steitz TA (1981) Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 Å resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature 290:744–749
McWilliam H, Li W, Uludag M, Squizzato S, Park YM, Buso N, Cowley AP, Lopez R (2013) Analysis tool web services from the EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res 41:W597–W600
Piette A, Derouaux A, Gerkens P, Noens EEE, Mazzucchelli G, Vion S, Koerten HK, Titgemeyer F, De Pauw E, Leprince P, van Wezel GP, Galleni M, Rigali S (2005) From dormant to germinating spores of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): new perspectives from the crp null mutant. J Proteome Res 4:1699–1708
Prado L, Lombo F, Brana AF, Mendez C, Rohr J, Salas JA (1999) Analysis of two chromosomal regions adjacent to genes for a type II polyketide synthase involved in the biosynthesis of the antitumor polyketide mithramycin in Streptomyces argillaceus. Mol Gen Genet 261:216–225
Rickman L, Scott C, Hunt DM, Hutchinson T, Menéndez MC, Whalan R, Hinds J, Colston MJ, Green J, Buxton RS (2005) A member of the cAMP receptor protein family of transcription regulators in Mycobacterium tuberculosis is required for virulence in mice and controls transcription of the rpfA gene coding for a resuscitation promoting factor. Mol Microbiol 56:1274–1286
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W320–W324
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schultz SC, Shields GC, Steitz TA (1991) Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90°. Science 253:1001–1007
Shen B, Hutchinson CR (1996) Deciphering the mechanism for the assembly of aromatic polyketides by a bacterial polyketide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6600–6604
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tang GL, Cheng YQ, Shen B (2004) Leinamycin biosynthesis revealing unprecedented architectural complexity for a hybrid polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Chem Biol 11:33–45
Tang GL, Cheng YQ, Shen B (2006) Polyketide chain skipping mechanism in the biosynthesis of the hybrid nonribosomal peptide-polyketide antitumor antibiotic leinamycin in Streptomyces atroolivaceus S-140. J Nat Prod 69:387–393
Tao M, Wang L, Wendt-Pienkowski E, George NP, Galm U, Zhang G, Coughlin JM, Shen B (2007) The tallysomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insights into the biosynthesis of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics. Mol BioSyst 3:60–74
Zhang B, Yang D, Yan Y, Pan G, Xiang W, Shen B (2016) Overproduction of lactimidomycin by cross-overexpression of genes encoding Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2267–2277
Acknowledgments
We thank Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) for the wild-type S. atroolivaceus S-140 strain. This work was supported in part by NIH Grant CA106150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Animal and human subjects
This article does not contain any studies with human participation or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Yong Huang and Dong Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yang, D., Pan, G. et al. Characterization of LnmO as a pathway-specific Crp/Fnr-type positive regulator for leinamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces atroolivaceus and its application for titer improvement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 10555–10562 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7864-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7864-2