Abstract
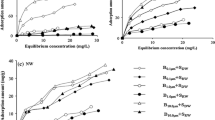
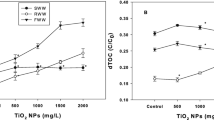
In this study, we examined the long-term effects of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) on the production and properties of EPS and the resulting variations in surface physicochemical characteristics of biofilms in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor. After exposure to 50 mg/L CuO NPs for 45 days, the protein (PRO) and polysaccharide (PS) contents in loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS) decreased as the production of LB-EPS decreased from 34.4 to 30 mg TOC/g EPS. However, the production of tightly bound EPS (TB-EPS) increased by 16.47 % as the PRO and PS contents increased. The content of humic-like substances (HS) increased significantly, becoming the predominant constituent in EPS with the presence of 50 mg/L CuO NPs. Furthermore, the results of three-dimensional excitation-emission fluorescence spectra confirmed the various changes in terms of the LB-EPS and TB-EPS contents after exposure to CuO NPs. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy showed that the –OH and –NH2 groups of proteins in EPS were involved in the reaction with CuO NPs. Moreover, the chronic exposure to CuO NPs induced a negative impact on the flocculating efficiency of EPS and on the hydrophobicity and aggregation ability of microbial cells. The PRO/PS ratios of different EPS fractions were consistent with their hydrophobicities (R 2 >0.98) and bioflocculating efficiencies (R 2 >0.95); however, there was no correlation with aggregation ability. Additionally, the presence of bovine serum albumin (BSA) prevented the physical contact between CuO NPs and EPS as a result of NP aggregation and electrostatic repulsion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applerot G, Lellouche J, Lipovsky A, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A, Banin E (2012) Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Small 8:3326–3337
Basuvaraj M, Fein J, Liss SN (2015) Protein and polysaccharide content of tightly and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances and the development of a granular activated sludge floc. Water Res 82:104–117
Chen Y, Su Y, Zheng X, Chen H, Yang H (2012) Alumina nanoparticles-induced effects on wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removal after short-term and long-term exposure. Water Res 46:4379–4386
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006) Relations between extraction protocols for activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and EPS complexation properties part I. Comparison of the efficiency of eight EPS extraction methods. Enzym Microb Technol 38:237–245
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Golden JH, Small R, Pagan L, Shang C, Raghavan S (2000) Evaluating and treating CMP wastewater. Semicond Int 23:85–98
Heinlaan M, Ivask A, Blinova I, Dubourguier HC, Kahru A (2008) Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 71:1308–1316
Hou J, Miao L, Wang C, Wang P, Ao Y, Lv B (2015a) Effect of CuO nanoparticles on the production and composition of extracellular polymeric substances and physicochemical stability of activated sludge flocs. Bioresour Technol 176:65–70
Hou J, Miao L, Wang C, Wang P, Ao Y, Qian J, Dai S (2014) Inhibitory effects of ZnO nanoparticles on aerobic wastewater biofilms from oxygen concentration profiles determined by microelectrodes. J Hazard Mater 276:164–170
Hou J, You G, Xu Y, Wang C, Wang P, Miao L, Ao Y, Li Y, Lv B (2015b) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on biological nitrogen removal in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor and mechanism of toxicity. Bioresour Technol 191:73–78
Janissen R, Murillo DM, Niza B, Sahoo PK, Nobrega MM, Cesar CL, Temperini MA, Carvalho HF, de Souza AA, Cotta MA (2015) Spatiotemporal distribution of different extracellular polymeric substances and filamentation mediate Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm formation. Sci Rep-UK 5:9856
Jing H, Mezgebe B, Hassan AA, Sahle-Demessie E, Sorial GA, Bennett-Stamper C (2014) Experimental and modeling studies of sorption of ceria nanoparticle on microbial biofilms. Bioresour Technol 161:109–117
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Gustafsson J, Möller L (2008) Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: a comparison between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1726–1732
Karri S, Sierra-Alvarez R, Field JA (2006) Toxicity of copper to acetoclastic and hydrogenotrophic activities of methanogens and sulfate reducers in anaerobic sludge. Chemosphere 62:121–127
Keller AA, Lazareva A (2013) Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: from global to regional to local. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:65–70
Keller AA, Wang H, Zhou D, Lenihan HS, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ, Miller R, Ji Z (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrixes. Environ Sci Technol 44:1962–1967
Laspidou CS, Rittmann BE (2002) A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res 36:2711–2720
Li XY, Yang SF (2007) Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res 41:1022–1030
Li LL, Tong ZH, Fang CY, Chu J, Yu HQ (2015) Response of anaerobic granular sludge to single-wall carbon nanotube exposure. Water Res 70:1–8
Lin L, Rosenberg M, Taylor KG, Doyle RJ (1995) Kinetic-analysis of ammonium sulfate dependent aggregation of bacteria. Colloid Surf B 5:127–134
Liu Y, Fang HH (2003) Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 33:237–273
Liu XM, Sheng GP, Luo HW, Zhang F, Yuan SJ, Xu J, Zeng RJ, Wu JG, Yu HQ (2010) Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the sludge aggregation. Environ Sci Technol 44:4355–4360
Majedi SM, Kelly BC, Lee HK (2014) Evaluation of a cloud point extraction approach for the preconcentration and quantification of trace CuO nanoparticles in environmental waters. Anal Chim Acta 814:39–48
Maquelin K, Kirschner C, Choo-Smith LP, van den Braak N, Endtz HP, Naumann D, Puppels GJ (2002) Identification of medically relevant microorganisms by vibrational spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 51:255–271
McSwain BS, Irvine RL, Hausner M, Wilderer PA (2005) Composition and distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic flocs and granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1051–1057
Otero-González L, Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2014) Inhibition of anaerobic wastewater treatment after long-term exposure to low levels of CuO nanoparticles. Water Res 58:160–168
Patel-Sorrentino N, Mounier S, Benaim JY (2002) Excitation-emission fluorescence matrix to study pH influence on organic matter fluorescence in the Amazon basin rivers. Water Res 36:2571–2581
Raszka A, Chorvatova M, Wanner J (2006) The role and significance of extracellular polymers in activated sludge. Part I: literature review. Acta hydrochim Hydrobio 34:411–426
Ren GG, Hu DW, Cheng EWC, Vargas-Reus MA, Reip P, Allaker RP (2009) Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:587–590
Sheng Z, Liu Y (2011) Effects of silver nanoparticles on wastewater biofilms. Water Res 45:6039–6050
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006a) Chemical-equilibrium-based model for describing the strength of sludge: taking hydrogen-producing sludge as an example. Environ Sci Technol 40:1280–1285
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006b) Relationship between the extracellular polymeric substances and surface characteristics of Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:126–131
Sheng GP, Xu J, Luo HW, Li WW, Li WH, Yu HQ, Xie Z, Wei SQ, Hu FC (2013) Thermodynamic analysis on the binding of heavy metals onto extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of activated sludge. Water Res 47:607–614
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894
Späth R, Flemming HC, Wuertz S (1998) Sorption properties of biofilms. Water Sci Technol 37:207–210
van der Mei HC, van de Belt-Gritter B, Busscher HJ (1995) Implications of microbial adhesion to hydrocarbons for evaluating cell surface hydrophobicity 2. Adhesion mechanisms. Colloid Surf B 5:117–126
von Moos N, Slaveykova VI (2014) Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae-state of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology 8:605–630
Wilén BM, Jin B, Lant P (2003) The influence of key chemical constituents in activated sludge on surface and flocculation properties. Water Res: 2127–2139
Wilén BM, Lumley D, Mattsson A, Mino T (2008) Relationship between floc composition and flocculation and settling properties studied at a full scale activated sludge plant. Water Res: 4404–4418
You G, Hou J, Xu Y, Wang C, Wang P, Miao L, Ao Y, Li Y, Lv B (2015) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on production and physicochemical characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 194:91–98
Zhang ZJ, Chen SH, Wang SM, Luo HY (2011) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from biofilm in the process of starting-up a partial nitrification process under salt stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1563–1571
Zhang P, Fang F, Chen YP, Shen Y, Zhang W, Yang JX, Li C, Guo JS, Liu SY, Huang Y, Li S, Gao X, Yan P (2014) Composition of EPS fractions from suspended sludge and biofilm and their roles in microbial cell aggregation. Chemosphere 117:59–65
Zhao J, Wang Z, Dai Y, Xing B (2013) Mitigation of CuO nanoparticle-induced bacterial membrane damage by dissolved organic matter. Water Res 47:4169–4178
Zhou XH, Huang BC, Zhou T, Liu YC, Shi HC (2015) Aggregation behavior of engineered nanoparticles and their impact on activated sludge in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 119:568–576
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the grants from the project supported by the National Science Funds for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51479047, 51479065, 51209069), the Outstanding Youth Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu, China (BK20160038), the Creative Research Groups of China (No. 51421006), the National Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 51225901), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT13061), the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41430751), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 2015B22014 and 2015B05714), and PAPD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 4.64 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., You, G., Xu, Y. et al. Long-term effects of CuO nanoparticles on the surface physicochemical properties of biofilms in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9629–9639 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7799-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7799-7