Abstract
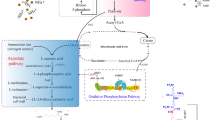
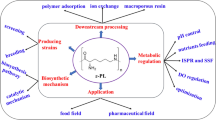
Poly(ɛ-l-lysine) (ɛ-PL) is an unusual biopolymer composed of l-lysine connected between α-carboxyl and ɛ-amino groups. It has been used as a preservative in food and cosmetics industries, drug carrier in medicines, and gene carrier in gene therapy. Modern biotechnology has significantly improved the synthetic efficiency of this novel homopoly(amino acid) on an industrial scale and has expanded its industrial applications. In the latest years, studies have focused on the biotechnological production and understanding the biosynthetic mechanism of microbial ɛ-PL. Herein, this review focuses on the current trends and future perspectives of microbial ɛ-PL. Information on the screening of ɛ-PL-producing strains, fermentative production of ɛ-PL, breeding of high-ɛ-PL-producing strains, genomic data of ɛ-PL-producing strains, biosynthetic mechanism of microbial ɛ-PL, and the control of molecular weight of microbial ɛ-PL is included. This review will contribute to the development of this novel homopoly(amino acid) and serve as a basis of studies on other biopolymers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badle SS, Jayaraman G, Ramachandran KB (2014) Ratio of intracellular precursors concentration and their flux influences hyaluronic acid molecular weight in Streptococcus zooepidemicus and recombinant Lactococcus lactis. Bioresour Technol 163:222–227
Bajaj I, Singhal R (2011) Poly (glutamic acid)—an emerging biopolymer of commercial interest. Bioresour Technol 102:5551–5561
Bankar SB, Singhal RS (2010) Optimization of poly-ε-lysine production by Streptomyces noursei NRRL 5126. Bioresour Technol 101:8370–8375
Bankar SB, Singhal RS (2011) Improved poly-ε-lysine biosynthesis using Streptomyces noursei NRRL 5126 by controlling dissolved oxygen during fermentation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:652–658
Bankar SB, Singhal RS (2013) Panorama of poly-ε-lysine. RSC Adv 3:8586–8603
Chen X, Li S, Liao L, Ren X, Li F, Tang L, Zhang J, Mao Z (2011a) Production of ε-poly-l-lysine using a novel two-stage pH control strategy by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 from glycerol. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:561–567
Chen X, Tang L, Li S, Liao L, Zhang J, Mao Z (2011b) Optimization of medium for enhancement of ε-poly-l-lysine production by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 with glycerol as carbon source. Bioresour Technol 102:1727–1732
Chen X, Ren X, Dong N, Li S, Li F, Zhao F, Tang L, Zhang J, Mao Z (2012) Culture medium containing glucose and glycerol as a mixed carbon source improves ε-poly-l-lysine production by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:469–475
Chheda AH, Vernekar MR (2014) Improved production of natural food preservative ε-poly-l-lysine using a novel producer Bacillus cereus. Food Biosci 7:56–63
Chheda AH, Vernekar MR (2015a) Enhancement of ε-poly-l-lysine (ε-PL) production by a novel producer Bacillus cereus using metabolic precursors and glucose feeding. 3 Biotech 5:839–846
Chheda AH, Vernekar MR (2015b) A natural preservative ε-poly-l-lysine: fermentative production and applications in food industry. Int Food Res J 22:23–30
Condurso H, Bruner D (2012) Structure and noncanonical chemistry of nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic machinery. Nat Prod Rep 29:1099–1110
Dodd A, Swanevelder D, Featherston J, Rumbold K (2013) Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces albulus strain CCRC 11814, an ε-poly-l-lysine-producing actinomycete. Genome Announc 1(5):e00696-13
El-Sersy NA, Abdelwahab AE, Abouelkhiir SS, Abou-Zeid DM, Sabry SA (2012) Antibacterial and anticancer activity of ε-poly-l-lysine (ε-PL) produced by a marine Bacillus subtilis sp. J Basic Microbiol 52:513–522
Geng W, Yang C, Gu Y, Liu R, Guo W, Wang X, Song C, Wang S (2014) Cloning of ε-poly-l-lysine (ε-PL) synthetase gene from a newly isolated ε-PL producing Streptomyces albulus NK660 and its heterologous expression in Streptomyces lividans. Microb Biotechnol 7:155–164
Gu Y, Yang C, Wang X, Geng W, Sun Y, Feng J, Wang Y, Quan Y, Che Y, Zhang C, Gong T, Zhang W, Gao W, Zuo Z, Song C, Wang S (2014) Genome sequence of the ε-poly-l-lysine-producing strain Streptomyces albulus NK660, isolated from soil in Gutian, Fujian Province, China. Genome Announc 2(3):e00532-14
Hamano Y, Yoshida T, Kito M, Nakamori S, Nagasawa T, Takagi H (2006) Biological function of the pld gene product that degrades ε-poly-l-lysine in Streptomyces albulus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:173–181
Hamano Y, Nicchu I, Shimizu T, Onji Y, Hiraki J, Takagi H (2007) ɛ-poly-l-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus, has feedback-inhibition resistant aspartokinase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:873–882
Hamano Y, Arai T, Ashiuchi M, Kino K (2013) NRPSs and amide ligases producing homopoly(amino acid)s and homooligo(amino acid)s. Nat Prod Rep 30:1087–1097
Hamano Y, Kito N, Kita A, Imokawa Y, Yamanaka K, Maruyama C, Katano H (2014) ε-poly-l-lysine peptide chain length regulated by the linkers connecting the transmembrane domains of ε-poly-l-lysine synthetase. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:4993–5000
Harrison J, Studholme DJ (2014) Recently published Streptomyces genome sequences. Microb Biotechnol 7:373–380
Hiraki J, Hatakeyama M, Morita H, Izumi Y (1998) Improved epsilon-poly-l-lysine production of an S-(2-aminoethyl)-l-cysteine resistant mutant of Streptomyces albulus. Seibutsu-Kogaku Kaishi 76:487–493
Hiraki J, Ichikawa T, Ninomiya S, Seki H, Uohama K, Seki H, Kimura S, Yanagimoto Y, Barnett JW (2003) Use of ADME studies to confirm the safety of ε-polylysine as a preservative in food. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 37:328–340
Hirohara H, Takehara M, Saimura M, Masayuki A, Miyamoto M (2006) Biosynthesis of poly(ɛ-l-lysine)s in two newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:321–331
Hirohara H, Saimura M, Takehara M, Miyamoto M, Ikezaki A (2007) Substantially monodispersed poly(ɛ-l-lysine)s frequently occurred in newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1009–1016
Ivanovics G, Bruckner V (1937) Chemische und immunologische Studien uber den Mechanismus der Milzbrandinfektion und Immunitat die chemische Struktur der Kapel-substanz des Milzbrand-bacillus und der serolisch identischen spezifichen Substanz des Bacillus mesentericus. Z Immun Exp Ther 90:304–310
Jia Y, Zhu J, Chen X, Tang D, Su D, Yao W, Gao X (2013) Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis for the efficient biosynthesis of uniform hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights. Bioresour Technol 132:427–431
Kahar P, Iwata T, Hiraki J, Park EY, Okabe M (2001) Enhancement of ε-polylysine production by Streptomyces albulus strain 410 using pH control. J Biosci Bioeng 91:190–194
Kahar P, Kobayashi K, Iwata T, Hiraki J, Kojima M, Okabe M (2002) Production of ε-polylysine in an airlift bioreactor (ABR). J Biosci Bioeng 93:274–280
Kawai T, Kubota T, Hiraki J, Izumi Y (2003) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine in a cell-free system of Streptomyces albulus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:635–640
Kito M, Takimoto R, Yoshida T, Nagasawa T (2002) Purification and characterization of an ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme from an ε-poly-l-lysine-producing strain of Streptomyces albulus. Arch Microbiol 178:325–330
Kito N, Maruyama C, Yamanaka K, Imokawa Y, Utagawa T, Hamano Y (2013) Mutational analysis of the three tandem domains of ε-poly-l-lysine synthetase catalyzing the l-lysine polymerization reaction. J Biosci Bioeng 115:523–526
Kushwaha DRS, Mathur KB, Balasubramanian D (1980) Poly(ε-l-lysine): synthesis and conformation. Biopolymers 19:219–229
Li S, Tang L, Chen X, Liao L, Li F, Mao Z (2011) Isolation and characterization of a novel ε-poly-l-lysine producing strain: Streptomyces griseofuscus. J Ind Microbiol 38:557–563
Li S, Li F, Chen X, Wang L, Xu J, Tang L, Mao Z (2012) Genome shuffling enhanced ε-poly-l-lysine production by improving glucose tolerance of Streptomyces graminearus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:414–423
Li S, Chen X, Dong C, Zhao F, Tang L, Mao Z (2013) Combining genome shuffling and interspecific hybridization among Streptomyces improved ε-poly-l-lysine production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:338–350
Li J, Jaitzig J, Hillig F, Süssmuth R, Neubauer P (2014) Enhanced production of the nonribosomal peptide antibiotic valinomycin in Escherichia coli through small-scale high cell density fed-batch cultivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:591–601
Liu S, Wu Q, Zhang J, Mo S (2011) Production of ε-poly-l-lysine by Streptomyces sp. using resin-based, in situ product removal. Biotechnol Lett 33:1581–1585
Nishikawa M (2009) Molecular mass control using polyanionic cyclodextrin derivatives for the epsilon-poly-l-lysine biosynthesis by Streptomyces. Enzym Microb Technol 45:295–298
Nishikawa M, Ogawa KI (2002) Distribution of microbes producing antimicrobial ε-poly-l-lysine polymers in soil microflora determined by a novel method. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3575–3581
Nishikawa M, Ogawa K (2006) Inhibition of epsilon-poly-l-lysine biosynthesis in Streptomycetaceae bacteria by short-chain polyols. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2306–2312
Ouyang J, Xu H, Li S, Zhu H, Chen W, Zhou J, Wu Q, Xu L, Ouyang P (2006) Production of ε-poly-l-lysine by newly isolated Kitasatospora sp. PL6-3. Biotechnol J 1:1459–1463
Pandey AK, Kumar A (2014) Improved microbial biosynthesis strategies and multifarious applications of the natural biopolymer epsilon-poly-l-lysine. Process Biochem 49:496–505
Posada JA, Rincón LE, Cardona CA (2012) Design and analysis of biorefineries based on raw glycerol: addressing the glycerol problem. Bioresour Technol 111:282–293
Ren X, Chen X, Tang L, Sun Q, Zeng X, Mao Z (2015a) Efficient production of ε-poly-l-lysine from agro-industrial by-products by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18. Ann Microbiol 65:733–743
Ren X, Chen X, Zeng X, Wang L, Tang L, Mao Z (2015b) Acidic pH shock induced overproduction of ε-poly-l-lysine in fed-batch fermentation by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 from agro-industrial by-products. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:1113–1125
Ren X, Xu Y, Zeng X, Chen X, Tang L, Mao Z (2015c) Microparticle-enhanced production of ε-poly-l-lysine in fed-batch fermentation. RSC Adv 5:82138–82143
Shih IL, Shen MH (2006a) Application of response surface methodology to optimize production of poly-ɛ-lysine by Streptomyces albulus IFO 14147. Enzym Microb Technol 39:15–21
Shih IL, Shen MH (2006b) Optimization of cell growth and poly(ε-lysine) production in batch and fed-batch cultures by Streptomyces albulus IFO 14147. Process Biochem 41:1644–1649
Shih IL, Van YT (2001) The production of poly-(γ-glutamic acid) from microorganisms and its various applications. Bioresour Technol 79:207–225
Shih IL, Shen MH, Van YT (2006) Microbial synthesis of poly(ε-lysine) and its various applications. Bioresour Technol 97:1148–1159
Shih I, Wang T, Chou S, Lee G (2011) Sequential production of two biopolymers-levan and poly-ε-lysine by microbial fermentation. Bioresour Technol 102:3966–3969
Shima S, Sakai H (1977) Polylysine produced by Streptomyces. Agric Biol Chem 41:1807–1809
Shima S, Sakai H (1981) Poly-l-lysine produced by Streptomyces. Part II. Taxonomy and fermentation studies. Agric Biol Chem 45:2497–2502
Shima S, Oshima S, Sakai H (1983) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine by washed mycelium of Streptomyces albulus no. 346. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 57:221–226
Shima S, Matsuoka H, Iwamoto T, Sakai H (1984) Antimicrobial action of ɛ-poly-l-lysine. J Antibiot 37:1449–1455
Shiru J, Guoliang W, Yanfang S, Zhilei T (2009) Improvement of epsilon-poly-l-lysine production by Streptomyces albulus TUST2 employing a feeding strategy. In: 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, (ICBBE 2009), Beijing, China, pp. 1–4
Shukla SC, Singh A, Pandey AK, Mishra A (2012) Review on production and medical applications of ɛ-polylysine. Biochem Eng J 65:70–81
Stern R, Asari AA, Sugahara KN (2006) Hyaluronan fragments: an information rich system. Eur J Cell Biol 85:699–715
Strieker M, Tanović A, Marahiel M (2010) Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: structures and dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 20:234–240
Sun Q, Chen X, Ren X, Mao Z (2015) Improvement of ε-poly-l-lysine production through seed stage development based on in situ pH monitoring. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:802–812
Takehara M, Saimura M, Inaba H, Hirohara H (2008) Poly(γ-l-diaminobutanoic acid), a novel poly(amino acid), coproduced with poly(ε-l-lysine) by two strains of Streptomyces celluloflavus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 286:110–117
Tao Y, Chen X, Jia F, Wang S, Xiao C, Cui F, Li Y, Bian Z, Chen X, Wang X (2015) New chemosynthetic route to linear ε-poly-lysine. Chem Sci 6:6385–6391
Wang L, Gao C, Tang N, Hu S, Wu Q (2015) Identification of genetic variations associated with epsilon-poly-lysine biosynthesis in Streptomyces albulus ZPM by genome sequencing. Sci Rep 5:9201
Xia J, Xu H, Feng X, Xu Z, Chi B (2013) Poly(l-diaminopropionic acid), a novel non-proteinic amino acid oligomer co-produced with poly(ε-l-lysine) by Streptomyces albulus PD-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7597–7605
Xia J, Xu Z, Xu H, Liang J, Li S, Feng X (2014) Economical production of poly(ε-l-lysine) and poly(l-diaminopropionic acid) using cane molasses and hydrolysate of Streptomyces cells by Streptomyces albulus PD-1. Bioresour Technol 164:241–247
Xu Z, Xia J, Feng X, Li S, Xu H, Bo F, Sun Z (2014) Genome sequence of Streptomyces albulus PD-1, a productive strain for epsilon-poly-l-lysine and poly-l-diaminopropionic acid. Genome Announc 2(2):e00297-14
Xu Z, Bo F, Xia J, Sun Z, Li S, Feng X, Xu H (2015a) Effects of oxygen-vectors on the synthesis of epsilon-poly-lysine and the metabolic characterization of Streptomyces albulus PD-1. Biochem Eng J 94:58–64
Xu Z, Cao C, Sun Z, Li S, Xu Z, Feng X, Xu H (2015b) Construction of a genetic system for Streptomyces albulus PD-1 and improving poly(ε-l-lysine) production through expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1819–1826
Xu Z, Feng X, Sun Z, Cao C, Li S, Xu Z, Xu Z, Bo F, Xu H (2015c) Economic process to co-produce poly(ε-l-lysine) and poly(l-diaminopropionic acid) by a pH and dissolved oxygen control strategy. Bioresour Technol 187:70–76
Xu Z, Sun Z, Li S, Xu Z, Cao C, Xu Z, Feng X, Xu H (2015d) Systematic unravelling of the biosynthesis of poly (l-diaminopropionic acid) in Streptomyces albulus PD-1. Sci Rep 5:17400
Yamanaka K, Maruyama C, Takagi H, Hamano Y (2008) ε-poly-l-lysine dispersity is controlled by a highly unusual nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Nat Chem Biol 4:766–772
Yamanaka K, Kito N, Imokawa Y, Maruyama C, Utagawa T, Hamano Y (2010) Mechanism of ε-poly-l-lysine production and accumulation revealed by identification and analysis of an ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5669–5675
Yamanaka K, Kito N, Kita A, Imokawa Y, Maruyama C, Utagawa T, Hamano Y (2011) Development of a recombinant ε-poly-l-lysine synthetase expression system to perform mutational analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 111:646–649
Yoshimura T, Shibata N, Hamano Y, Yamanaka K (2015) Heterologous production of hyaluronic acid in an ε-poly-l-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3631–3640
Zeng X, Chen X, Ren X, Liu Q, Wang L, Sun Q, Tang L, Mao Z (2014) Insights into the role of glucose and glycerol as a mixed carbon source in the improvement of ε-poly-l-lysine productivity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:2211–2224
Zhang Y, Feng X, Xu H, Yao Z, Ouyang P (2010) ε-poly-l-lysine production by immobilized cells of Kitasatospora sp. MY 5-36 in repeated fed-batch cultures. Bioresour Technol 101:5523–5527
Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Feng X, Li S, Xia J, Xu H (2012) A novel agar diffusion assay for qualitative and quantitative estimation of ε-polylysine in fermentation broths and foods. Food Res Int 48:49–56
Zhou Z, Gu J, Li YQ, Wang Y (2012) Genome plasticity and systems evolution in Streptomyces. BMC Bioinforma 13:S8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 21476112), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140933), the State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering (ZK201403), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20113221130001), the Key Project of Science and Technology Project of Fujian Province (No. 2014Y0015), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863) (No. 2015AA020951).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Zhaoxian Xu and Zheng Xu had equal contributions to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Xu, Z., Feng, X. et al. Recent advances in the biotechnological production of microbial poly(ɛ-l-lysine) and understanding of its biosynthetic mechanism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 6619–6630 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7677-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7677-3