Abstract
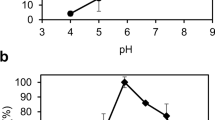
A putative diol synthase from the fungus Glomerella cingulate was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The putative diol synthase from G. cingulate was purified by His-Trap affinity chromatography with a specific activity of 0.87 U mg−1, an eightfold purification, and a yield of 28 %. One unit of activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol of 7,8-dihydroxy-9,12(Z,Z)-octadecadienoic acid (7,8-DiHODE) per min. The purified enzyme was estimated as a 127-kDa tetramer with a molecular mass of 510 kDa by gel filtration chromatography. The enzyme converted linoleic acid to a product, identified as 7S,8S-DiHODE by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The specific activity and catalytic efficiency (k cat/K m) of 7,8-diol synthase from G. cingulate for the conversion of fatty acid to dihydroxy fatty acid followed the order linoleic acid > α-linolenic acid > oleic acid > palmitoleic acid, indicating that the enzyme is a 7,8-linoleate diol synthase (7,8-LDS). The activity of the enzyme for the conversion of 7,8-DiHODE from linoleic acid was maximal at pH 6.5, 40 °C, and 2.5 % (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Under these conditions, 7,8-LDS from G. cingulate converted 1.0 mM linoleic acid to 0.62 mM 7,8-DiHODE for 30 min, with a conversion yield of 62 % (mol/mol), via 8-hydroperoxy-9,12(Z,Z)-octadecadienoic acid (8-HPODE) as an intermediate. The accumulation of 8-HPODE was due to a higher 8-dioxygenase activity in the N-terminal domain than hydroperoxide isomerase activity in the C-terminal domain.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreou A, Brodhun F, Feussner I (2009) Biosynthesis of oxylipins in non-mammals. Prog Lipid Res 48:148–170
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brodhun F, Gobel C, Hornung E, Feussner I (2009) Identification of PpoA from Aspergillus nidulans as a fusion protein of a fatty acid heme dioxygenase/peroxidase and a cytochrome P450. J Biol Chem 284:11792–11805
Brodowsky ID, Hamberg M, Oliw EH (1992) A linoleic acid (8R)-dioxygenase and hydroperoxide isomerase of the fungus Gaeumannomyces graminis. Biosynthesis of (8R)-hydroxylinoleic acid and (7S,8S)-dihydroxylinoleic acid from (8R)-hydroperoxylinoleic acid. J Biol Chem 267:14738–14745
Cary JW, Harris-Coward PY, Ehrlich KC, Moore GG, Wei Q, Bhatnagar D (2012) Functional and phylogenetic analysis of the Aspergillus ochraceoroseus aflQ (ordA) gene ortholog. Mycologia 104:857–864
Estupinan M, Diaz P, Manresa A (2014) Unveiling the genes responsible for the unique Pseudomonas aeruginosa oleate-diol synthase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1360–1371
Garscha U, Jernerén F, Chung D, Keller NP, Hamberg M, Oliw EH (2007) Identification of dioxygenases required for Aspergillus development. Studies of products, stereochemistry, and the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem 282:34707–34718
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA 3rd, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345
Hoffmann I, Oliw EH (2013) 7,8- and 5,8-Linoleate diol synthases support the heterolytic scission of oxygen-oxygen bonds by different amide residues. Arch Biochem Biophys 539:87–91
Hoffmann I, Jernerén F, Garscha U, Oliw EH (2011) Expression of 5,8-LDS of Aspergillus fumigatus and its dioxygenase domain. A comparison with 7,8-LDS, 10-dioxygenase, and cyclooxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 506:216–222
Hoffmann I, Jernerén F, Oliw EH (2013) Expression of fusion proteins of Aspergillus terreus reveals a novel allene oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 288:11459–11469
Jeong YJ, Seo MJ, Shin KC, Oh DK (2015) Production of 8-hydroxy-9,12(Z,Z)-octadecadienoic acid from linoleic acid by recombinant cells expressing H1004A–C1006S variant of Aspergillus nidulans diol synthase. J Mol Catal B Enzym 115:35–42
Jernerén F, Garscha U, Hoffmann I, Hamberg M, Oliw EH (2010a) Reaction mechanism of 5,8-linoleate diol synthase, 10R-dioxygenase, and 8,11-hydroperoxide isomerase of Aspergillus clavatus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:503–507
Jernerén F, Sesma A, Franceschetti M, Hamberg M, Oliw EH (2010b) Gene deletion of 7,8-linoleate diol synthase of the rice blast fungus: studies on pathogenicity, stereochemistry, and oxygenation mechanisms. J Biol Chem 285:5308–5316
Oliw EH, Su C, Skogstrom T, Benthin G (1998) Analysis of novel hydroperoxides and other metabolites of oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acids by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with ion trap MSn. Lipids 33:843–852
Sangeetha C, Rawal R (2008) Nutritional studies of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. and Sacc. the incitant of mango anthracnose. World J Agric Sci 4:717–720
Seo MJ, Shin KC, Oh DK (2014) Production of 5,8-dihydroxy-9,12(Z,Z)-octadecadienoic acid from linoleic acid by whole recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing diol synthase from Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7447–7456
Su C, Oliw EH (1996) Purification and characterization of linoleate 8-dioxygenase from the fungus Gaeumannomyces graminis as a novel hemoprotein. J Biol Chem 271:14112–14118
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tsitsigiannis DI, Kowieski TM, Zarnowski R, Keller NP (2004a) Endogenous lipogenic regulators of spore balance in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryotic Cell 3:1398–1411
Tsitsigiannis DI, Zarnowski R, Keller NP (2004b) The lipid body protein, PpoA, coordinates sexual and asexual sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 279:11344–11353
Wadman MW, de Vries RP, Kalkhove SI, Veldink GA, Vliegenthart JF (2009) Characterization of oxylipins and dioxygenase genes in the asexual fungus Aspergillus niger. BMC Microbiol 9:59
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Zhao B, Lei L, Kagawa N, Sundaramoorthy M, Banerjee S, Nagy LD, Guengerich FP, Waterman MR (2012) Three-dimensional structure of steroid 21-hydroxylase (cytochrome P450 21A2) with two substrates reveals locations of disease-associated variants. J Biol Chem 287:10613–10622
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by Konkuk University in 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Konkuk University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 798 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, MJ., Shin, KC., An, JU. et al. Characterization of a recombinant 7,8-linoleate diol synthase from Glomerella cingulate . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3087–3099 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7132-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7132-x