Abstract
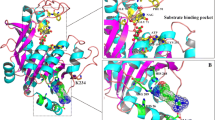
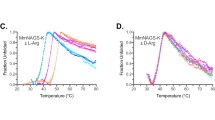
N-acetyl glutamate kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the synthesis of L-arginine, and L-arginine-sensitive NAGK typically has hexameric architecture. Defining the relationship between this architecture and L-arginine inhibition can provide a foundation to identify the key amino acids involved in the allosteric regulation network of L-arginine. In the present study, the key amino acids in the N-terminal helix (N-helix) of Corynebacterium glutamicum (Cg) NAGK required for hexamer formation were determined using structural homology modeling and site-directed mutagenesis. It was also verified that hexameric architecture is required for the positive cooperativity of inhibition by L-arginine and for efficient catalysis, but that it is not the determinant of inhibition by L-arginine. Monomeric mutants retained a similar sensitivity to L-arginine as the hexameric form, indicating that monomers contain an independent, sensitive signal transduction network of L-arginine to mediate allosteric regulation. Mutation studies of CgNAGKs also revealed that amino acid residues 18–23 of the N-helix are required for inhibition by L-arginine, and that E19 may be an essential amino acid influencing the apparent affinity of L-arginine. Collectively, these studies may illuminate the basic mechanism of metabolic homeostasis of C. glutamicum.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V (1986) Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 50(3):314
Fernández-Murga ML, Rubio V (2008) Basis of arginine sensitivity of microbial N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinases: mutagenesis and protein engineering study with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli enzymes. J Bacteriol 190(8):3018–3025. doi:10.1128/JB.01831-07
Fernández-Murga ML, Gil-Ortiz F, Llácer JL, Rubio V (2004) Arginine biosynthesis in Thermotoga maritima: characterization of the arginine-sensitive N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase. J Bacteriol 186(18):6142–6149. doi:10.1128/JB.186.18.6142-6149.2004
Gil-Ortiz F, Ramón-Maiques S, Fernández-Murga ML, Fita I, Rubio V (2010) Two crystal structures of Escherichia coli N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase demonstrate the cycling between open and closed conformations. J Mol Biol 399(3):476–490. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.025
Haas D, Leisinger T (1975) N-acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Catalytic and regulatory properties. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 52(2):377–393. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04005.x
Huang Y, Zhang H, Tian H, Li C, Han S, Lin Y, Zheng S (2015) Mutational analysis to identify the residues essential for the inhibition of N-acetyl glutamate kinase of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1–11 doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6469-5
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown N, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26(2):283–291. doi:10.1107/S0021889892009944
Liithy R, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (1992) Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 356(6364):83–85. doi:10.1038/356083a0
Marco-Marín C, Ramón-Maiques S, Tavárez S, Rubio V (2003) Site-directed mutagenesis of Escherichia coli acetylglutamate kinase and aspartokinase III probes the catalytic and substrate-binding mechanisms of these amino acid kinase family enzymes and allows three-dimensional modelling of aspartokinase. J Mol Biol 334(3):459–476. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.09.038
Marvin J, Corcoran E, Hattangadi N, Zhang J, Gere S, Hellinga H (1997) The rational design of allosteric interactions in a monomeric protein and its applications to the construction of biosensors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(9):4366–4371
Mizuno Y, Moorhead GB, Ng KK-S (2007) Structural basis for the regulation of N-acetylglutamate kinase by PII in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 282(49):35733–35740. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707127200
Ramón-Maiques S, Marina A, Gil-Ortiz F, Fita I, Rubio V (2002) Structure of acetylglutamate kinase, a key enzyme for arginine biosynthesis and a prototype for the amino acid kinase enzyme family, during catalysis. Structure 10(3):329–342. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(02)00721-9
Ramón-Maiques S, Fernández-Murga ML, Gil-Ortiz F, Vagin A, Fita I, Rubio V (2006) Structural Bases of Feed-back Control of Arginine Biosynthesis, Revealed by the Structures of Two Hexameric N-Acetylglutamate Kinases, from Thermotoga maritima and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Mol Biol 356(3):695–713. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.079
Sakanyan V, Petrosyan P, Lecocq M, Boyen A, Legrain C, Demarez M, Hallet J-N, Glansdorff N (1996) Genes and enzymes of the acetyl cycle of arginine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum: enzyme evolution in the early steps of the arginine pathway. Microbiology 142(1):99–108. doi:10.1099/13500872-142-1-99
Sundaresan R, Ragunathan P, Kuramitsu S, Yokoyama S, Kumarevel T, Ponnuraj K (2012) The structure of putative N-acetyl glutamate kinase from Thermus thermophilus reveals an intermediate active site conformation of the enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420(3):692–697. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.072
Xu M, Rao Z, Dou W, Jin J, Xu Z (2012) Site-directed mutagenesis studies on the L-arginine-binding sites of feedback inhibition in N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase (NAGK) from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Curr Microbiol 64(2):164–172. doi:10.1007/s00284-011-0042-y
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171633) to S Zheng and the National Key Technology Support Program to Y Lin (No. 2013BAD10B01) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities to Y Lin. This work was also partially supported by startup funds from the School of Bioscience and Biotechnology, South China University of Technology and the Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. y507k81001) to X Yang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 245 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Li, C., Zhang, H. et al. Monomeric Corynebacterium glutamicum N-acetyl glutamate kinase maintains sensitivity to L-arginine but has a lower intrinsic catalytic activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1789–1798 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7065-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7065-4