Abstract
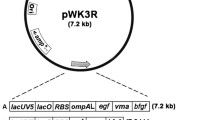
We have recently employed an intein, Saccharomyces cerevisiae vascular membrane ATPase (VMA), in conjunction with efficient expression and secretory functions formed between the ompA leader sequence and the human epidermal growth factor (EGF) gene (fused at the 5′ end of VMA), and the human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) gene (fused at the 3′ end of VMA), to engineer an efficient intein-based Escherichia coli system for high-level co-expression of EGF and bFGF as authentic mature products. Both products were found not only excreted to the culture medium but also located, surprisingly, in the cytoplasm (Kwong and Wong 2013). In this study, we employed two structurally varied inteins, VMA and Mycobacterium xenopi GyraseA (GyrA), and further demonstrated that despite acting alone, both VMA and GyrA were able to mediate successful co-expression of two widely different proteins, EGF and an endoglucanase (Eng) in E. coli. Although EGF and Eng were initially expressed as large precursors/intermediates, they were soluble and auto-cleavable to finally yield the desired products in both the cytoplasm and culture media. The results further substantiate our postulation that the aforementioned intein/E. coli approach might lead to the development of cost-effective and versatile host systems, wherein all culture fractions are involved in producing the target proteins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel F, Brent R, Kingston R, Moore D, Seidman J, Smith J, Strohl K (1993) Current protocols in molecular biology. 2:11.2.1–11.2.5
Coutinho JB, Gilkes NR, Warren R a J, Kilburn DG, Miller RC (1992) The binding of Cellulomonas fimi endoglucanase C (CenC) to cellulose and Sephadex is mediated by the N-terminal repeats. Mol Microbiol 6:1243–1252
Cui C, Zhao W, Chen J, Wang J, Li Q (2006) Elimination of in vivo cleavage between target protein and intein in the intein-mediated protein purification systems. Protein Expr Purif 50:74–81
Elleuche S, Pöggeler S (2010) Inteins, valuable genetic elements in molecular biology and biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:479–489
Esipov RS, Stepanenko VN, Chupova LA, Boyarskikh UA, Filipenko ML, Miroshnikov AI (2008) Production of recombinant human epidermal growth factor using Ssp dnaB mini-intein system. Protein Expr Purif 61:1–6
Fu ZB, Ng KL, Lam TL, Wong WKR (2005) Cell death caused by hyper-expression of a secretory exoglucanase in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 42:67–77
Huang R, Lam E, Chen Y, Hackett J, Lam T, Liu D, Ma M, Siu K, Sivakesava S, Xu Z, Wong RS, Wong WK (1999) Human epidermal growth factor excreted by recombinant Escherichia coli K-12 has the correct N-terminus and is fully bioactive. Process Biochem 35:1–5
Kurpiers T, Mootz HD (2008) Site‐Specific Chemical Modification of Proteins with a Prelabelled Cysteine Tag Using the Artificially Split Mxe GyrA Intein. ChemBioChem 9:2317–2325
Kwong KWY, Ng KL, Lam CC, Wang YY, Wong WKR (2013) Authentic human basic fibroblast growth factor produced by secretion in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6803–6811
Kwong KWY, Wong WKR (2013) A revolutionary approach facilitating co-expression of authentic human epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in both cytoplasm and culture medium of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9071–9080
Lam KH, Chow KC, Wong WK (1998) Construction of an efficient Bacillus subtilis system for extracellular production of heterologous proteins. J Biotechnol 63:167–77
Langsford ML, Gilkes NR, Singh B, Moser B, Miller RC, Warren RA, Kilburn DG (1987) Glycosylation of bacterial cellulases prevents proteolytic cleavage between functional domains. FEBS Lett 225:163–167
Li Y (2011) Self-cleaving fusion tags for recombinant protein production. Biotechnol Lett 33:869–881
Pietrokovski S (1994) Conserved sequence features of inteins (protein introns) and their use in identifying new inteins and related proteins. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc 3:2340–2350
Sivakesava S, Xu Z, Chen Y, Hackett J, Huang R, Lam E, Lam T, Siu K, Wong RS, Wong WK (1999) Production of excreted human epidermal growth factor (EGF) by an efficient recombinant Escherichia coli system. Process Biochem 34:893–900
Telenti A, Southworth M, Alcaide F, Daugelat S, Jacobs WR, Perler FB (1997) The Mycobacterium Xenopi GyrA Protein Splicing Element: Characterization of a Minimal Intein. J Bacteriol 179:6378–6382
Topilina NI, Mills KV (2014) Recent advances in in vivo applications of intein-mediated protein splicing. Mob DNA 5:5
Tsang MW, Chan CW, Chu CM, Lam EKH, Leung KC, Hung CS, Lai KM, Tang W, Cheung EYN, Kam G (2003) Human epidermal growth factor enhances healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 26:1856–61
Tsang MW, Tsang KY, Wong WKR (2004) The use of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (rEGF) in a gentleman with drug-induced Steven Johnson syndrome. Dermatol Online J 10:25
Urban A, Neukirchen S, Jaeger KE (1997) A rapid and efficient method for site-directed mutagenesis using one-step overlap extension PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2227–2228
Volkmann G, Mootz HD (2013) Recent progress in intein research: from mechanism to directed evolution and applications. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:1185–1206
Wang L, Kang JH, Kim KH, Lee EK (2010a) Expression of intein-tagged fusion protein and its applications in downstream processing. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:11–18
Wang YY, Ng KL, Lam CC, Chan AKN, Sze KF, Fu Z, Wong WKR (2010b) Efficient Bacillus subtilis promoters for graded expression of heterologous genes in Escherichia coli. Res J Biotechnol 5:5–14
Wong DKH, Lam KHE, Chan CKP, Wong YCV, Wong WKR, Hackett J (1998) Extracellular expression of human epidermal growth factor encoded by an Escherichia coli K-12 plasmid stabilized by the ytl2-incR system of Salmonella typhimurium. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 21:31–36
Wong WK, Gerhard B, Guo ZM, Kilburn DG, Warren AJ, Miller RC Jr (1986) Characterization and structure of an endoglucanase gene cenA of Cellulomonas fimi. Gene 44:315–324
Wong WKR, Fu Z, Wang YY, Ng KL, Chan AKN (2012) Engineering of efficient Escherichia coli excretion systems for the production of heterologous proteins for commercial applications. Recent Pat Chem Eng 5:44–55
Wong WKR, Lam KH, Tsang MW (2009) Method and composition for treating skin wounds with epidermal growth factor. US Patent:7517528
Ethical statement
This study was funded by RGC project: GRF16101515, and Research Contracts No. BWT001.04/05 and GVN002.06/07 managed by Research and Development of HKUST. The three authors, Keith W. Y. Kwong, Alan, K. L. Ng, and W.K.R. Wong, declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwong, K.W.Y., Ng, A.K.L. & Wong, W.K.R. Engineering versatile protein expression systems mediated by inteins in Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 255–262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6960-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6960-z