Abstract
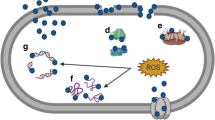
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a leading opportunistic pathogen and its expanding drug resistance is a growing menace to public health. Its ubiquitous nature and multiple resistance mechanisms make it a difficult target for antimicrobial chemotherapy and require a fresh approach for developing new antimicrobial agents against it. The broad-spectrum antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles (SNPs) make them an excellent candidate for use in the medical field. However, attempts made to check their potency against extensively drug-resistant (XDR) microbes are meager. This study describes the biosynthesis and biostabilization of SNPs by Helicteres isora aqueous fruit extract and their characterization by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Majority of SNPs synthesized were of 8-–20-nm size. SNPs exhibited dose-dependent antibacterial activities against four XDR P. aeruginosa (XDR-PA) clinical isolates as revealed by growth curves, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 300 μg/ml. The SNPs exhibited antimicrobial activity against all strains, with maximum zone of inhibition (16.4 mm) in XRD-PA-2 at 1000 μg/ml. Amongst four strains, their susceptibilities to SNPs were in the following order: XDR-PA-2 > XDR-PA-4 > XDR-PA-3 > XDR-PA-1. The exposure of bacterial cells to 300 μg/ml SNPs resulted into a substantial leakage of reducing sugars and proteins, inactivation of respiratory chain dehydrogenases, and eventual cell death. SNPs also induced lipid peroxidation, a possible underlying factor to membrane porosity. The effects were more pronounced in XDR-PA-2 which may be correlated with its higher susceptibility to SNPs. These results are indicative of SNP-induced turbulence of membranous permeability as an important causal factor in XDR-PA growth inhibition and death.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud Y, Saffaj T, Chagraoui A, El Bouari A, Tanane O, Ihssane B (2014) Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CONPs) produced using brown alga extract (Bifurcaria bifurcata). Appl Nanosci 4:571–576. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0233-x
Allaker RP, Memarzadeh K (2014) Nanoparticles and the control of oral infections. Int J Antimicrob Ag 43:95–104. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.11.002
Amirulhusni AN, Palanisamy NK, Zaini M-Z, Ping LJ, Durairaj R (2012) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on multi drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 6:208–211
Atti MCD, Bernaschi P, Carletti M, Luzzi I, García-Fernandez A, Bertaina A, Sisto A, Locatelli F, Raponi M (2014) An outbreak of extremely drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a tertiary care pediatric hospital in Italy. BMC Infect Dis 14:494. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-494
Bhati-Kushwaha H, Malik CP (2014) Assessment of antibacterial and antifungal activities of silver nanoparticles obtained from the callus extracts (stem and leaf) of Tridax procumbens L. Indian J Biotechnol 13:114–120
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2014) Green synthesis of protein capped silver nanoparticles from phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid with antimicrobial properties against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:365. doi:10.1186/1556-276x-9-365
CLSI (2014) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty fourth informational supplement Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) document M100-S24. Wayne, PA, USA
Dar MA, Ingle A, Rai M (2013) Enhanced antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cryphonectria sp. evaluated singly and in combination with antibiotics. Nanomedicine: NBM 9:105–110. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2012.04.007
Dutta RK, Nenavathu BP, Gangishetty MK, Reddy AVR (2012) Studies on antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles by ROS induced lipid peroxidation. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 94:143–150. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.01.046
Falagas ME, Karageorgopoulos DE (2008) Pandrug resistance (PDR), extensive drug resistance (XDR), and multidrug resistance (MDR) among gram-negative bacilli: need for international harmonization in terminology. Clin Infect Dis 46:1121–1122. doi:10.1086/528867
Gurunathan S (2014) Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial effects against Escherichia fergusonii and Streptococcus mutans. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.11.014
Jeeva K, Thiyagarajan M, Elangovan V, Geetha N, Venkatachalam P (2014) Caesalpinia coriaria leaf extracts mediated biosynthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Ind Crop Prod 52:714–720. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.037
Kerr KG, Snelling AM (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a formidable and ever-present adversary. J Hosp Infect 73:338–344. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2009.04.020
Krychowiak M, Grinholc M, Banasiuk R, Krauze-Baranowska M, Głod D, Kawiak A, Krolicka A (2014) Combination of silver nanoparticles and Drosera binata extract as a possible alternative for antibiotic treatment of burn wound infections caused by resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One 9(12):e115727. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115727
Kumar V, Sharma M, Lemos M, Shriram V (2013) Efficacy of Helicteres isora L. against free radicals, lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation and DNA damage. J Pharm Res 6:620–625. doi:10.1016/j.jopr.2013.05.017
Kumar V, Yadav SK (2009) Plant mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:151–157. doi:10.1002/jctb.2023
Lanini S, D’Arezzo S, Puro V, Martini L, Imperi F, Piselli P, Montanaro M, Paoletti S, Visca P, Ippolito G (2011) Molecular epidemiology of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa hospital outbreak driven by a contaminated disinfectant-soap dispenser. PLoS One 6(2):e17064. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017064
Li WR, Xie XB, Shi QS, Zeng HY, YS OU-Y, Chen YB (2010) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1115–1122. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2159-5
Lim TP, Lee W, Tan TY, Sasikala S, Teo J, Hsu LY, Tan TT, Syahidah N, Kwa AL (2011) Effective antibiotics in combination against extreme drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with decreased susceptibility to polymyxin B. PLoS One 6(12):e28177. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028177
Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, Harbarth S, Hindler JF, Kahlmeter G, Olsson-Liljequist B, Paterson DL, Rice LB, Stelling J, Struelens MJ, Vatopoulos A, Weber JT, Monnet DL (2011) Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18:268–281. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x
Martinez-Castanon GA, Nino-Martinez N, Martinez-Gutierrez F, Martinez-Mendoza JR, Facundo R (2008) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J Nanoparticle Res 10:1343–1348. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9428-6
Meletis G, Bagkeri M (2013). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: multi-drug-resistance development and treatment options, infection control. In: Basak S (ed) Infection control, InTech, pp 33–56. doi: 10.5772/55616.
Miller G (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–429
Moore NM, Flaws ML (2011) Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Lab Sci 24:47–51
Ong DS, Jongerden IP, Buiting AG (2011) Antibiotic exposure and resistance development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter species in intensive care units. Crit Care Med 39:2458–2463. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318225756d
Paterson DL, Doi Y (2007) A step closer to extreme drug resistance (XDR) in gram-negative bacilli. Clin Infect Dis 45:1179–1181. doi:10.1086/522287
Pena C, Gomez-Zorrilla S, Suarez C, Dorninguez MA, Tabau F, Arch Q, Oliver A, Pujol M, Ariza J (2012) Extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: risk of bloodstream infections in hospitalized patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:2791–2797. doi:10.1007/s10096-012-1629-3
Perez C, Pauli M, Bezevque P (1990) An antibiotic assay by agar well diffusion method. Acta Biol Med Exp 15:113–115
Porras-Gomez M, Vega-Baudrit J, Nunez-Corrales S (2012) Overview of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and novel therapeutic approaches. J Biomat Nanobiotechnol 3:519–527. doi:10.4236/jbnb.2012.324053
Prabhu S, Poulose E (2012) Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett 2:32. doi:10.1186/2228-5326-2-32
Rai M, Yadav A (2013) Plants as potential synthesizer of precious metal nanoparticles: progress and prospects. IET Nanobiotechnol 7:117–124. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2012.0031
Rai MK, Deshmukh SD, Ingle AP, Gade AK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: the powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 112:841–852. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05253.x
Raju D, Paneliya N, Mehta UJ (2013) Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using living peanut seedling. Appl Nanosci 4:875–879. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0269-y
Seil JT, Webster TJ (2012) Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: methods and literature. Int J Nanomedicine 7:2767–2781. doi:10.2147/IJN.S24805
Shanmugam N, Rajkamal P, Cholan S, Kannadasan N, Sathishkumar K, Viruthagiri G, Sundaramanickam A (2014) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from the marine seaweed Sargassum wightii and their antibacterial activity against some human pathogens. Appl Nanosci 4:881–888. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0271-4
Shriram V, Jahagirdar S, Latha C, Kumar V, Dhakephalkar P, Rojatkar S, Shitole MG (2010a) Antibacterial and antiplasmid activities of Helicteres isora L. Indian J Med Res 132:94–99
Shriram V, Kumar V, Kishor PBK, Suryawanshi SB, Upadhyay AK, Bhat MK (2010b) Cytotoxic activity of 9,10-dihydro-2,5-dimethoxyphenanthrene-1,7-diol from Eulophia nuda against human cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol 128:251–253. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2009.12.031
Singh D, Rathod V, Ninganagouda S, Hiremath J, Singh AK, Mathew J (2014b) Optimization and characterization of silver nanoparticle by endophytic fungi Penicillium sp. isolated from Curcuma longa (turmeric) and application studies against MDR E. coli and S. aureus. Bioinorg Chem Appl:1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/408021
Singh HL, Singh J, Mukherjee A (2013) Synthesis, spectral, and in vitro antibacterial studies of organosilicon (iv) complexes with schiff bases derived from amino acids. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2013:1–8. doi:10.1155/2013/425832
Singh K, Panghal M, Kadyan S, Chaudhary U, Yadav JP (2014b) Green silver nanoparticles of Phyllanthus amarus: as an antibacterial agent against multi drug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nanobiotechnol 12:40. doi:10.1186/s12951-014-0040-x
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:177–182. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012
Su HL, Chou CC, Hung DJ, Lin SH, Pao IC, Lin JH, Huang FL, Dong RX, Lin JJ (2009) The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials 30:5979–5987. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.030
Thombre R, Chitnis A, Kadam V, Bhagwat Y, Colaco R, Kale A (2014) A facile method for synthesis of biostabilized silver nanoparticles using Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms (water hyacinth). Indian J Biotechnol 13:337–341
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the use of facilities created under the DST-FIST program implemented at Modern College, Ganeshkhind, Pune. The authors sincerely thank the Dean, B.J. Govt. Medical College, and the Principal, Modern College, for permitting to work and utilize the necessary facilities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nikunj Mapara and Mansi Sharma contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 131 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mapara, N., Sharma, M., Shriram, V. et al. Antimicrobial potentials of Helicteres isora silver nanoparticles against extensively drug-resistant (XDR) clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 10655–10667 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6938-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6938-x