Abstract
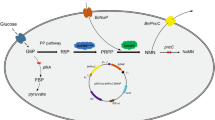
2-Deoxy-d-ribose 5-phosphate aldolase (DERA) accepts a wide variety of aldehydes and is used in de novo synthesis of 2-deoxysugars, which have important applications in drug manufacturing. However, DERA has low preference for non-phosphorylated substrates. In this study, DERA from Klebsiella pneumoniae (KDERA) was mutated to increase its enzyme activity and substrate tolerance towards non-phosphorylated polyhydroxy aldehyde. Mutant KDERAK12 (S238D/F200I/ΔY259) showed a 3.15-fold improvement in enzyme activity and a 1.54-fold increase in substrate tolerance towards d-glyceraldehyde compared with the wild type. Furthermore, a whole-cell transformation strategy using resting cells of the BL21(pKDERA12) strain, containing the expressed plasmid pKDERA12, resulted in increase in 2-deoxy-d-ribose yield from 0.41 mol/mol d-glyceraldehyde to 0.81 mol/mol d-glyceraldehyde and higher substrate tolerance from 0.5 to 3 M compared to in vitro assays. With further optimization of the transformation process, the BL21(pKDERA12) strain produced 2.14 M (287.06 g/L) 2-deoxy-d-robose (DR), with a yield of 0.71 mol/mol d-glyceraldehyde and average productivity of 0.13 mol/L·h (17.94 g/L·h). These results demonstrate the potential for large-scale production of 2-deoxy-d-ribose using the BL21(pKDERA12) strain. Furthermore, the BL21(pKDERA12) strain also exhibited the ability to efficiently produce 2-deoxy-d-altrose from d-erythrose, as well as 2-deoxy-l-xylose and 2-deoxy-l-ribose from l-glyceraldehyde.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäumchen C, Bringer-Meyer S (2007) Expression of glf Z.m increases D-mannitol formation in whole cell biotransformation with resting cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:545–552
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Giuliano S, Larbret F, Ponzio G, Gounon P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Cormont M, Bertolotto C, Deckert M, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Bost F (2010) Targeting cancer cell metabolism: the combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 70:2465–2475
Brovetto M, Gamenara D, Saenz Mendez P, Seoane GA (2011) C-C bond-forming lyases in organic synthesis. Chem Rev 111:4346–4403
Dean SM, Greenberg WA, Wong CH (2007) Recent advances in aldolase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis. Adv Synth Catal 349:1308–1320
DeSantis G, Liu J, Clark DP, Heine A, Wilson IA, Wong CH (2003) Structure-based mutagenesis approaches toward expanding the substrate specificity of D-2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase. Bioorg Med Chem 11:43–52
Fessner WD, Sinerius G, Schneider A, Dreyer M, Schulz GE, Badia J, Aguilar J (1991) Diastereoselective enzymatic aldol addition: L-rhamnulose and L-fuculose-1-phosphate aldolases from E. coli. Angew Chem Int Ed 30:555–558
Gijsen HJM, Wong CH (1994) Unprecedented asymmetric aldol reactions with three aldehyde substrates catalyzed by 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate aldolase. J Am Chem Soc 116:8422–8423
Gijsen HJM, Wong CH (1995) Sequential three and four-substrate aldol reactions catalyzed by aldolases. J Am Chem Soc 117:7585–7591
Helanto M, Kiviharju K, Granström T, Leisola M, Nyyssölä A (2009) Biotechnological production of L-ribose from L-arabinose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:77–83
Horinouchi N, Ogawa J, Sakai T, Kawano T, Matsumoto S, Sasaki M, Mikami Y, Shimizu S (2003) Construction of deoxyriboaldolase expressing Escherichia coli and its application to 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate synthesis from glucose and acetaldehyde for 2’-deoxyribonucleoside production. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3791–3797
Jennewein S, Schürmann M, Wolberg M, Hilker I, Luiten R, Wubbolts M, Mink D (2006) Directed evolution of an industrial biocatalyst: 2-deoxy-D-ribose 5-phosphate aldolase. Biotechnol J 1:537–548
Jung ME, Xu Y (1997) Efficient syntheses of L-ribose and 2-deoxy-L-ribose from D-ribose and L-arabinose. Tetrahedron Lett 38:4199–4202
Kang YB, Yang YH, Lee KW, Lee SG, Sohng JK, Lee HC, Liou K, Kim BG (2006) Preparative synthesis of dTDP-L-rhamnose through combined enzymatic pathways. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:21–27
Kirschning A, Bechthold AFW, Rohr J (1997) Chemical and biochemical aspects of deoxysugars and deoxysugar oligosaccharides. Top Curr Chem 188:1–84
Li Z, Cai L, Qi Q, Styslinge TJ, Zhao G, Wang PG (2011a) Synthesis of rare sugars with L-fuculose-1-phosphate aldolase (FucA) from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:5084–5087
Li Z, Cai L, Qi Q, Wang PG (2011b) Enzymatic synthesis of D-sorbose and D-psicose with aldolase RhaD: effect of acceptor configuration on enzyme stereoselectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:7081–7084
Nakajima Y, Gotanda T, Uchimiya H, Furukawa T, Haraguchi M, Ikeda R, Sumizawa T, Yoshida H, Akiyama S (2004) Inhibition of metastasis of tumor cells overexpressing thymidine phosphorylase by 2-deoxy-L-ribose. Cancer Res 64:1794–1801
Oh J, Kim BG, Sohng JK, Liou K, Lee HC (2003) One-pot enzymatic production of dTDP-4-keto-6-D- glucose from dTMP and glucose-1-phosphate. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:452–458
Olmo ML, Andreu C, Asensio G (2011) Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a whole cell system for aldol condensation in organic medium: study of the factors affecting the biotransformation. J Mol Catal B Enzym 72:90–94
Rodríguez L, Aguirrezabalaga I, Allende N, Braña AF, Méndez C, Salas JA (2002) Engineering deoxysugar biosynthetic pathways from antibiotic-producing microorganisms: a tool to produce novel glycosylated bioactive compounds. Chem Biol 9:721–729
Samland AK, Sprenger GA (2006) Microbial aldolases as C–C bonding enzymes—unknown treasures and new developments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:253–264
Trefzer A, Bechthold A, Salas JA (1999) Genes and enzymes involved in deoxysugar biosynthesis in bacteria. Nat Prod Rep 16:283–299
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA021403) and Science and Technology Projects of Tianjin (No. 13ZCZDSY05600).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jitao Li and Jiangang Yang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 945 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yang, J., Men, Y. et al. Biosynthesis of 2-deoxysugars using whole-cell catalyst expressing 2-deoxy-d-ribose 5-phosphate aldolase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 7963–7972 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6740-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6740-9