Abstract
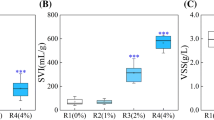
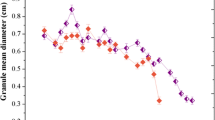
Methanosaeta strains are frequently involved in the granule formation during methanogenic wastewater treatment. To investigate the impact of Methanosaeta on granulation and performance of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors, three 1-L working volume reactors noted as R1, R2, and R3 were operated fed with a synthetic wastewater containing sodium acetate and glucose. R1 was inoculated with 1-L activated sludge, while R2 and R3 were inoculated with 200-mL concentrated pre-grown Methanosaeta harundinacea 6Ac culture and 800 mL of activated sludge. Additionally, R3 was daily dosed with 0.5 mL/L of acetyl ether extract of 6Ac spent culture containing its quorum sensing signal carboxyl acyl homoserine lactone (AHL). Compared to R1, R2 and R3 had a higher and more constant chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency and alkaline pH (8.2) during the granulation phase, particularly, R3 maintained approximately 90 % COD removal. Moreover, R3 formed the best granules, and microscopic images showed fluorescent Methanosaeta-like filaments dominating in the R3 granules, but rod cells dominating in the R2 granules. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene libraries showed increased diversity of methanogen species like Methanosarcina and Methanospirillum in R2 and R3, and increased bacteria diversity in R3 that included the syntrophic propionate degrader Syntrophobacter. Quantitative PCR determined that 6Ac made up more than 22 % of the total prokaryotes in R3, but only 3.6 % in R2. The carboxyl AHL was detected in R3. This work indicates that AHL-facilitated filaments of Methanosaeta contribute to the granulation and performance of UASB reactors, likely through immobilizing other functional microorganisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angenent LT, Sung S, Raskin L (2004) Formation of granules and Methanosaeta fibres in an anaerobic migrating blanket reactor (AMBR). Environ Microbiol 6:315–322
Baloch MI, Akunna JC, Kierans M, Collier PJ (2008) Structural analysis of anaerobic granules in a phase separated reactor by electron microscopy. Bioresour Technol 99:922–929
Batstone DJ, Landelli J, Saunders A, Webb RI, Blackall LL, Keller J (2002) The influence of calcium on granular sludge in a full-scale UASB treating paper mill wastewater. Water Sci Technol 10:187–193
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:4516–4522
Chao A (1987) Estimating the population size for capture-recapture data with unequal catchability. Biometrics 4:783–791
Chen J, Lun SY (1993) Study on mechanism of anaerobic sludge granulation in UASB reactors. Water Sci Technol 7:171–178
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, DC
Dong X, Plugge CM, Stams AJM (1994) Anaerobic degradation of propionate by a mesophilic acetogenic bacterium in coculture and tricultrue with different methanogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2834–2838
Donlon BA, Razo-Flores E, Field JA (1995) Toxicity of N-substituted aromatics to acetoclastic methanogenic activity in granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 11:3889–3893
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Feng H, Ding Y, Wang M, Zhou G, Zheng X, He H, Zhang X, Shen D, Shentu J (2014) Where are signal molecules likely to be located in anaerobic granular sludge? Water Res 50:1–9
Fredriksson NJ, Hermansson M, Wilén BM (2012) Diversity and dynamics of archaea in an activated sludge wastewater treatment plant. BMC Microbiol 12:140
Gonzalez-Gil G, Lens PNL, Van Aelst A, Van AH, Versprille AI, Lettinga G (2001) Cluster structure of anaerobic aggregates of an expanded granular sludge bed reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3683–3692
Hulshoff Pol LW (1989) The Phenomenon of Granulation of Anaerobic Sludge. Dissertation, Wageningen Agricultural University
Jetten M, Stams A, Zehnder A (1992) Methanogenesis from acetate: a comparison of the acetate metabolism in Methanothrix soehngenii and Methanosarcina spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 88:181–197
Kalogo Y, M'Bassiguié Séka A, Verstraete W (2001) Enhancing the start-up of a UASB reactor treating domestic wastewater by adding a water extract of Moringa oleifera seeds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 5:644–651
Khemkhao M, Nuntakumjorn B, Techkarnjanaruk S, Phalakornkul C (2011) Effect of chitosan on UASB treating POME during a transition from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions. Bio Res Technol 102:4674–4681
Lettinga G (1995) Anaerobic treatment of domestic sewage and wastewater. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1:3–28
Lettinga G, Hulshoff-Pol LW (1991) UASB process design for various types of waste waters. Water Sci Tech 24:88–107
Ma K, Liu X, Dong X (2006) Methanosaeta harundinacea, sp. nov., a novel acetate-scavenging methanogen isolated from a UASB reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:127–131
MacLeod FA, Guiot SR, Costerton JW (1990) Layered structure of bacterial aggregates produced in an upflow anaerobic sludge bed and filter reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1598–1607
Maidak BL, Olsen GL, Larsen N, Overbeek R, McCaughey ML, Woese CR (1997) The RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 25:109–110
Marañón E, Castrillón L, Vázquez I, Sastre H (2001) The influence of hydraulic residence time on the treatment of cattle manure in UASB reactors. Waste Manag Res 5:436–441
Miller MB, Bassler BL (2001) Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:165–199
Peng D, Zhang X, Jin Q, Xiang L, Zhang D (1994) Effects of the seed sludge on the performance of UASB reactors for treatment of toxic wastewater. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 2:171–176
Ren TT, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) The quorum-sensing effect of aerobic granules on bacterial adhesion, biofilm formation, and sludge granulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 3:789–797
Rodríguez JA, Peña MR, Manzi V (2001) Application of an innovative methodology to improve the starting-up of UASB reactors treating domestic sewage. Water Sci Technol 4:295–303
Schauer NL, Brown DP, Ferry JG (1982) Kinetics of formate metabolism in Methanobacterium formicicum and Methanospirillum hungatei. Appl Environ Microbiol 3:549–554
Schink B, Janssen PH, Frings J (1992) Microbial degradation of natural and of new synthetic polymers. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2–4:311–316
Sekiguchi Y, Kamagata Y, Nakamura K, Ohashi A, Harada H (1999) Fluorescence in situ hybridization using 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides reveals localization ofmethanogens and selected uncultured bacteria in mesophilic and thermophilic sludge granules. Appl Environ Microbiol 3:1280–1288
Siggins A, Enright AM, O'Flaherty V (2011) Methanogenic community development in anaerobic granular bioreactors treating trichloroethylene (TCE)-contaminated wastewater at 37 °C and 15 °C. Water Res 8:2452–2462
Sigler W, Turco R (2002) The impact of Chlorothalonil application on soil bacterial and fungal populations as assessed by DGGE. Appl Soil Ecol 2:107–118
Sun W, Sun X, Cupples AM (2012) Anaerobic methyl tert-butyl ether-degrading microorganisms identified in wastewater treatment plant samples by stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 8:2973–2980
Tan NCG, Prenafeta-Boldu FX, Opsteeg JL (1999) Biodegradation of azo dyes in cocultures of anaerobic granular sludge with aerobic aromatic amine degrading enrichment cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:865–871
Tiwari MK, Guha S, Harendranath CS, Tripathi S (2006) Influence of extrinsic factors on granulation in UASB reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2:145–154
Vlyssides A, Barampouti EM, Mai S (2008) Granulation mechanism of a UASB reactor supplemented with iron. Anaerobe 5:275–279
Wang MZ, Zheng X, He HZ, Shen DS, Feng HJ (2012) Ecological roles and release patterns of acylated homoserine lactones in Pseudomonas sp. HF-1 and their implications in bacterial bioaugmentation. Bio Res Technol 125:119–126
Yu Y, Lee C, Kim JH, Wang S (2005) Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol Bioeng 6:670–679
Zhang G, Zhang F, Ding G, Li J, Guo X, Zhu J, Zhou L, Cai S, Liu X, Luo Y, Zhang G, Shi W, Dong X (2012) Acyl homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing in a methanogenic archaeon. ISEM J 7:1336–1344
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under numbers 31100035 and 30621005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Lingyan Li and Mingyue Zheng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 162 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zheng, M., Ma, H. et al. Significant performance enhancement of a UASB reactor by using acyl homoserine lactones to facilitate the long filaments of Methanosaeta harundinacea 6Ac. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 6471–6480 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6478-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6478-4