Abstract
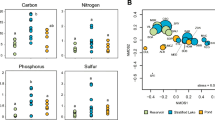
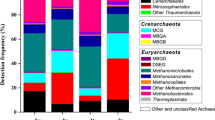
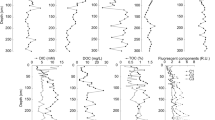
Archaea have multiple roles in global biogeochemical cycles. However, we still have limited knowledge about how environmental factors affect the diversity and function of different archaeal lineages. The goal of this study was to examine the change in the abundance and community structure of Archaea in the sediments collected from the lower Pearl River (mainly North River tributary), its estuary, and coastal South China Sea (SCS) in order to evaluate how archaeal ecological function might change along the salinity gradient. Pyrosequencing of the 16S rDNA gene of Archaea was performed on sediment samples from Feilaixia Dam on the North River tributary to Wanshan islands, which have a salinity range of 0.1 to 31.2 ‰. Consistent with the salt tolerance of cultivated representatives, methanogens in the genera Methanoregula, Methanosaeta, and Methanosarcina and Nitrososphaera within Thaumarchaeota of the ammonia-oxidizing Archaea (AOA) were abundant in freshwater sediments of the North River tributary, whereas the marine-associated genera Methanococcoides and Nitrosopumilus were the most abundant methanogens and AOA, respectively, in the estuary and coastal SCS. However, the percentages of total methanogens decreased and Thaumarchaeota increased with salinity, respectively. The phylum Crenarchaeota was largely represented by class-level lineages with no cultivated representatives, which collectively were more abundant in the estuary and coastal SCS in comparison to freshwater sites. This study indicates that salinity is the dominating factor affecting archaeal community structure and ecological function from the North River tributary of the Pearl River, its estuary, and coastal SCS, which is consistent with salinity control on microbial diversity in other regions of the world.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auguet JC, Casamayor EO (2008) A hotspot for cold crenarchaeota in the neuston of high mountain lakes. Environ Microbiol 10(4):1080–1086
Auguet JC, Barberan A, Casamayor EO (2010) Global ecological patterns in uncultured Archaea. ISME J 4(2):182–190
Bange HW, Bartell U, Rapsomanikis S, Andreae MO (1994) Methane in the Baltic and North Seas and a reassessment of the marine emissions of methane. Global Biogeochem Cycles 8(4):465–480
Bano N, Ruffin S, Ransom B, Hollibaugh JT (2004) Phylogenetic composition of Arctic Ocean archaeal assemblages and comparison with Antarctic assemblages. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(2):781–789
Bernhard AE, Colbert D, McManus J, Field KG (2005) Microbial community dynamics based on 16S rRNA gene profiles in a Pacific Northwest estuary and its tributaries. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52(1):115–128
Bernhard AE, Tucker J, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2007) Functionally distinct communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient. Environ Microbiol 9(6):1439–1447
Bernhard AE, Landry ZC, Blevins A, de la Torre JR, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2010) Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient in relation to potential nitrification rates. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(4):1285–1289
Biddle JF, Lipp JS, Lever MA, Lloyd KG, Sorensen KB, Anderson R, Fredricks HF, Elvert M, Kelly TJ, Schrag DP, Sogin ML, Brenchley JE, Teske A, House CH, Hinrichs KU (2006) Heterotrophic Archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(10):3846–3851
Blainey PC, Mosier AC, Potanina A, Francis CA, Quake SR (2011) Genome of a low-salinity ammonia-oxidizing archaeon determined by single-cell and metagenomic analysis. PLoS One 6(2):e16626
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu JD (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in sediments from the coastal Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100(4):545–556
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu JD (2012) Community shift of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an anthropogenic pollution gradient from the Pearl River Delta to the South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(1):247–259
Cao H, Auguet JC, Gu JD (2013) Global ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. PLoS One 8(2):e52853
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Chaban B, Ng SY, Jarrell KF (2006) Archaeal habitats—from the extreme to the ordinary. Can J Microbiol 52(2):73–116
Chen J, Wang F (2013) The community structure and diversity of methanogen-related organisms in Pearl River Estuary sediment. J Yunnan Univ 35(2):6
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Database issue):D141–D145
Crump BC, Baross JA (2000) Archaeaplankton in the Columbia River, its estuary and the adjacent coastal ocean, USA. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31(3):231–239
Crump BC, Baross JA, Simenstad CA (1998) Dominance of particle-attached bacteria in the Columbia River estuary, USA. Aquat Microb Ecol 14(1):7–18
Crump BC, Armbrust EV, Baross JA (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of particle-attached and free-living bacterial communities in the Columbia River, its estuary, and the adjacent coastal ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(7):3192–3204
Cunliffe M, Schafer H, Harrison E, Cleave S, Upstill-Goddard R, Murrell JC (2008) Phylogenetic and functional gene analysis of the bacterial and archaeal communities associated with the surface microlayer of an estuary. ISME J 2(7):776–789
de Wilde HP, de Bie MJ (2000) Nitrous oxide in the Schelde estuary: production by nitrification and emission to the atmosphere. Mar Chem 69(3):203–216
Dojka, M. A., P. Hugenholtz, S. K. Haack and N. R. Pace (1998) Microbial diversity in a hydrocarbon-and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10): 3869-3877
Dupont CL, Larsson J, Yooseph S, Ininbergs K, Goll J, Asplund-Samuelsson J, McCrow JP, Celepli N, Allen LZ, Ekman M, Lucas AJ, Hagstrom A, Thiagarajan M, Brindefalk B, Richter AR, Andersson AF, Tenney A, Lundin D, Tovchigrechko A, Nylander JA, Brami D, Badger JH, Allen AE, Rusch DB, Hoffman J, Norrby E, Friedman R, Pinhassi J, Venter JC, Bergman B (2014) Functional tradeoffs underpin salinity-driven divergence in microbial community composition. PLoS One 9(2):e89549
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Galand PE, Lovejoy C, Vincent WF (2006) Remarkably diverse and contrasting archaeal communities in a large arctic river and the coastal Arctic Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 44(2):115–126
Gantner S, Andersson AF, Alonso-Saez L, Bertilsson S (2011) Novel primers for 16S rRNA-based archaeal community analyses in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 84(1):12–18
Garnier J, Cébron A, Tallec G, Billen G, Sebilo M, Martinez A (2006) Nitrogen behaviour and nitrous oxide emission in the tidal Seine River estuary (France) as influenced by human activities in the upstream watershed. Biogeochemistry 77(3):305–326
Hao DM, Tashiro T, Kato M, Sohrin R, Ishibashi T, Katsuyama C, Nagaosa K, Kimura H, Thanh TD, Kato K (2010) Population dynamics of Crenarchaeota and Euryarchaeota in the mixing front of river and marine waters. Microbes Environ 25(2):126–132
Hu J, Peng P, Jia G, Mai B, Zhang G (2006) Distribution and sources of organic carbon, nitrogen and their isotopes in sediments of the subtropical Pearl River estuary and adjacent shelf, Southern China. Mar Chem 98(2):274–285
Hu J, Peng P, Chivas AR (2009) Molecular biomarker evidence of origins and transport of organic matter in sediments of the Pearl River estuary and adjacent South China Sea. Appl Geochem 24(9):1666–1676
Jiang L, Zheng Y, Chen J, Xiao X, Wang F (2011) Stratification of Archaeal communities in shallow sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 99(4):739–751
Jin T, Zhang T, Ye L, Lee OO, Wong YH, Qian PY (2011) Diversity and quantity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(3):1137–1145
Jurgens G, Glöckner FO, Amann R, Saano A, Montonen L, Likolammi M, Münster U (2000) Identification of novel Archaea in bacterioplankton of a boreal forest lake by phylogenetic analysis and fluorescent in situ hybridization1. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 34(1):45–56
Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437(7058):543–546
Lee CE, Bell MA (1999) Causes and consequences of recent freshwater invasions by saltwater animals. Trends Ecol Evol 14(7):284–288
Li Z, Jin W, Liang Z, Yue Y, Lv J (2013) Abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in response to various habitats in Pearl River Delta of China, a subtropical maritime zone. J Environ Sci 25(6):1195–1205
Llirós M, Casamayor EO, Borrego C (2008) High archaeal richness in the water column of a freshwater sulfurous karstic lake along an interannual study. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66(2):331–342
Lloyd KG, Schreiber L, Petersen DG, Kjeldsen KU, Lever MA, Steen AD, Stepanauskas R, Richter M, Kleindienst S, Lenk S, Schramm A, Jorgensen BB (2013) Predominant archaea in marine sediments degrade detrital proteins. Nature 496(7444):215–218
Logares R, Brate J, Bertilsson S, Clasen JL, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Rengefors K (2009) Infrequent marine-freshwater transitions in the microbial world. Trends Microbiol 17(9):414–422
Lozupone CA, Knight R (2007) Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(27):11436–11440
Luo H, Tolar BB, Swan BK, Zhang CL, Stepanauskas R, Ann Moran M, Hollibaugh JT (2013) Single-cell genomics shedding light on marine Thaumarchaeota diversification. ISME J 8(3):732–736
Magalhães CM, Joye SB, Moreira RM, Wiebe WJ, Bordalo AA (2005) Effect of salinity and inorganic nitrogen concentrations on nitrification and denitrification rates in intertidal sediments and rocky biofilms of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Water Res 39(9):1783–1794
Maindonald JH (2007) Data analysis and graphics using R: an example-based approach. Cambridge University Press, New York
Meng J, Wang F, Zheng Y, Peng X, Zhou H, Xiao X (2009) An uncultivated crenarchaeota contains functional bacteriochlorophyll a synthase. ISME J 3(1):106–116
Meng J, Xu J, Qin D, He Y, Xiao X, Wang F (2014) Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated MCG archaea assessed by metagenome and gene expression analyses. ISME J 8(3):650–659
Mosier AC, Francis CA (2008) Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(11):3002–3016
Mosier AC, Allen EE, Kim M, Ferriera S, Francis CA (2012) Genome sequence of “Candidatus Nitrosoarchaeum limnia” BG20, a low-salinity ammonia-oxidizing archaeon from the San Francisco Bay estuary. J Bacteriol 194(8):2119–2120
Mullins TD, Britschgi TB, Krest RL, Giovannoni SJ (1995) Genetic comparisons reveal the same unknown bacterial lineages in Atlantic and Pacific bacterioplankton communities. Limnol Oceanogr 40(1):148–158
Oline DK, Schmidt SK, Grant MC (2006) Biogeography and landscape-scale diversity of the dominant Crenarchaeota of soil. Microb Ecol 52(3):480–490
Pester M, Rattei T, Flechl S, Grongroft A, Richter A, Overmann J, Reinhold-Hurek B, Loy A, Wagner M (2012) amoA-based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ Microbiol 14(2):525–539
Ramette A, Tiedje JM (2007) Biogeography: an emerging cornerstone for understanding prokaryotic diversity, ecology, and evolution. Microb Ecol 53(2):197–207
Reed HE, Martiny JB (2013) Microbial composition affects the functioning of estuarine sediments. ISME J 7(4):868–879
Santoro AE, Francis CA, de Sieyes NR, Boehm AB (2008) Shifts in the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across physicochemical gradients in a subterranean estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(4):1068–1079
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Singh N, Kendall MM, Liu Y, Boone DR (2005) Isolation and characterization of methylotrophic methanogens from anoxic marine sediments in Skan Bay, Alaska: description of Methanococcoides alaskense sp. nov., and emended description of Methanosarcina baltica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(6):2531–2538
Sowers KR, Ferry JG (1983) Isolation and characterization of a methylotrophic marine methanogen, Methanococcoides methylutens gen. nov., sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 45(2):684–690
Stoeck, T. and S. Epstein (2003) Novel Eukaryotic Lineages Inferred from Small-Subunit rRNA Analyses of Oxygen-Depleted Marine Environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(5): 2657-2663
Takai K, Horikoshi K (1999) Genetic diversity of archaea in deep-sea hydrothermal vent environments. Genetics 152(4):1285–1297
Ter Braak C and Smilauer P (2002) Canoco for Windows version 4.5. Biometris-Plant Research International, Wageningen
Teske A, Sorensen KB (2008) Uncultured archaea in deep marine subsurface sediments: have we caught them all? ISME J 2(1):3–18
Teske A, Hinrichs K-U, Edgcomb V, de Vera Gomez A, Kysela D, Sylva SP, Sogin ML, Jannasch HW (2002) Microbial diversity of hydrothermal sediments in the Guaymas Basin: evidence for anaerobic methanotrophic communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1994–2007
Tian X (1994) The distribution characteristics of temperature in the Lingdingyang estuary of the Zhujiang River. Trop Oceanol 13:76–80
Tourna M, Stieglmeier M, Spang A, Konneke M, Schintlmeister A, Urich T, Engel M, Schloter M, Wagner M, Richter A, Schleper C (2011) Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(20):8420–8425
Urakawa H, Martens-Habbena W, Stahl DA (2010) High abundance of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in coastal waters, determined using a modified DNA extraction method. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(7):2129–2135
Vieira RP, Clementino MM, Cardoso AM, Oliveira DN, Albano RM, Gonzalez AM, Paranhos R, Martins OB (2007) Archaeal communities in a tropical estuarine ecosystem: Guanabara Bay, Brazil. Microb Ecol 54(3):460–468
Wai O, Wang C, Li Y, Li X (2004) The formation mechanisms of turbidity maximum in the Pearl River estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 48(5):441–448
Xu J, Wang Y, Wang Q and Yin J (2005) Nitrous oxide concentration and nitrification and denitrification in Zhujiang River Estuary, China. Acta Oceanol Sin 24(3): 122-130
Youssef NH, Ashlock-Savage KN, Elshahed MS (2012) Phylogenetic diversities and community structure of members of the extremely halophilic Archaea (order Halobacteriales) in multiple saline sediment habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(5):1332–1344
Zeng Y, Li H, Jiao N (2007) Phylogenetic diversity of planktonic archaea in the estuarine region of East China Sea. Microbiol Res 162(1):26–36
Zhang J, Yu Z, Wang J, Ren J, Chen H, Xiong H, Dong L, Xu W (1999) The subtropical Zhujiang (Pearl River) estuary: nutrient, trace species and their relationship to photosynthesis. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 49(3):385–400
Zhang CL, Wang J, Wei Y, Zhu C, Huang L, Dong H (2011) Production of branched tetraether lipids in the lower Pearl River and estuary: effects of extraction methods and impact on bGDGT proxies. Front Microbiol 2:274
Zhao H (1990) Evolution of the Pearl River estuary. China Ocean, Beijing, pp 116–147
Acknowledgments
We thank Wang J., Liu H., Dai L., Li F., and Courtney W. for helping with the sampling for this study. Captain Huang was greatly appreciated for helping with the field experiments during the cruise. We also thank J. Dodsworth for helpful comments during the preparation of the manuscript. This research was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China grants 2013CB955700 (C.Z.), the South China Sea-Deep program of the National Science Foundation of China (91028005), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation-funded project (92740), the National Science Foundation for Excellent Young Scholars of China (41306123), the National Science Foundation of China (41276125), and the “National Thousand Talents Program” at the State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology of Tongji University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Xie and Xuedan Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, W., Zhang, C., Zhou, X. et al. Salinity-dominated change in community structure and ecological function of Archaea from the lower Pearl River to coastal South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7971–7982 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5838-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5838-9