Abstract
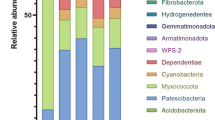
Pyrosequencing-based analysis was used to characterize and compare bacterial communities in manure samples of piglets (GSPM) and adult pigs (GBPM) bred with green feeds without additives, and piglets (ASPM) and adult pigs (ABPM) bred with synthetic feeds containing additives. For each sample, 5,010 effective sequences were selected and utilized to do the bacterial composition analysis, respectively. In total, 1,489, 1,327, 941, and 883 operational taxonomic units were obtained at 5 % distance cutoff in GBPM, GSPM, ABPM, and ASPM, respectively. Bacterial phylotype richness in GBPM was higher than the other samples, and ASPM had the least richness. The most dominant class in the four samples is Bacteroidia. Approximately 41 % sequences in GBPM were affiliated with the Clostridiales order. Campylobacter, Clostridium and Streptococcus genera containing pathogenic bacteria were detected in the four samples. Bacterial diversity and abundance in swine manures varied with piglets, adult pigs, and feeds. In the four samples, higher bacterial diversity but less potentially pathogenic bacterial genera in manures of adult pigs bred with green feeds were found, which indicated that those manures were more suitable for resource utilization. This study also provides evidence for the reasonableness of pig farming with green feeds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Ansorge WJ (2009) Next-generation DNA sequencing techniques. New Biotechnol 25(4):195–203
Auguet JC, Barberan A, Casamayor EO (2010) Global ecological patterns in uncultured Archaea. ISME J 4:182–190
Biddle JF, Fitz-Gibbon S, Schuster SC, Brenchley JE, House CH (2008) Metagenomic signatures of the Peru Margin subseafloor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(30):10583–10588
Claesson M, óSullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi J, Smidt H, De Vos W, Ross R, O'Toole P (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4(8): e6669
Cotta MA, Whitehead TR, Zeltwanger RL (2003) Isolation, characterization and comparison of bacteria from swine faeces and manure storage pits. Environ Microbiol 5(9):737–745
Dae-Young L, Susan CW, Hung L, Jack TT (2010) Quantitative identification of fecal water pollution sources by TaqMan real-time PCR assays using Bacteroidales 16S rRNA genetic markers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(6):1373–1383
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5069–5072
Dohrmann AB, Baumert S, Klingebiel L, Weiland P, Tebbe CC (2011) Bacterial community structure in experimental methanogenic bioreactors and search for pathogenic Clostridia as community members. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(6):1991–2004
Drury B, Rosi-Marshall E, Kelly JJ (2013) Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(6):1897–1905
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E (2011) Chimeric 16 S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21(3):494–504
Han I, Congeevaram S, Ki DW, Oh BT, Park J (2011) Bacterial community analysis of swine manure treated with autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(3):835–842
Hugenholtz P, Hooper SD, Kyrpides NC (2009) Focus: Synergistetes. Environ Microbiol 11(6):1327–1329
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12(7):1889–1898
Huson D, Auch A, Qi J, Schuster S (2007) MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res 17(3):377–386
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(15):5111–5120
McLellan S, Huse S, Mueller Spitz S, Andreishcheva E, Sogin M (2010) Diversity and population structure of sewage derived microorganisms in wastewater treatment plant influent. Environ Microbiol 12(2):378–392
Mieszkin S, Yala JF, Joubrel R, Gourmelon M (2010) Phylogenetic analysis of Bacteroidales 16S rRNA gene sequences from human and animal effluents and assessment of ruminant faecal pollution by real-time PCR. J Appl Microbiol 108(3):974–984
Peu P, Brugère H, Pourcher AM, Kérourédan M, Godon JJ, Delgenès JP, Dabert P (2006) Dynamics of a pig slurry microbial community during anaerobic storage and management. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(5):3578–3585
Ronaghi M, Uhlén M, Nyrén P (1998) A sequencing method based on real-time pyrophosphate. Science 281(5375):363–365
Rothberg JM, Leamon JH (2008) The development and impact of 454 sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 26(10):1117–1124
Snell-Castro R, Godon JJ, Delgenès JP, Dabert P (2005) Characterisation of the microbial diversity in a pig manure storage pit using small subunit rDNA sequence analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52(2):229–242
Sogin ML, Morrison HG, Huber JA, Welch DM, Huse SM, Neal PR, Arrieta JM, Herndl GJ (2006) Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored "rare biosphere". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(32):12115–12120
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, Egholm M, Henrissat B, Heath AC, Knight R, Gordon JI (2008) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457(7228):480–484
Urich T, Lanzén A, Qi J, Huson D, Schleper C, Schuster S (2008) Simultaneous assessment of soil microbial community structure and function through analysis of the meta-transcriptome. PLoS One 3(6):e2527
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naǐve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267
Wang XH, Hu M, Xia Y, Wen XH, Ding K (2012) Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in 14 wastewater treatment systems in China. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(19):7042–7047
Whitehead TR, Cotta MA (2001) Characterisation and comparison of microbial populations in swine faeces and manure storage pits by 16S rDNA gene sequence analyses. Anaerobe 7(4):181–187
Ye L, Zhang T (2011) Pathogenic bacteria in sewage treatment plants as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. Environ Sci Technol 45(17):7173–7179
Ye L, Zhang T (2013) Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(6):2681–2690
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Wenzhou City (No. C2012005-03) and the Foundation of Zhejiang Educational Committee (No. Y201224611).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
4
(PDF 172 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, XM., Lu, PZ. & Zhang, H. Bacterial communities in manures of piglets and adult pigs bred with different feeds revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 2657–2665 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5211-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5211-4