Abstract
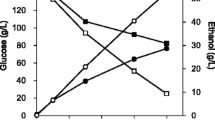
Two genes from Zymomonas mobilis that are responsible for ethanol production, pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase II (adhII), were heterologously expressed in the Gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces lividans TK24. An examination of carbon distribution revealed that a significant portion of carbon metabolism was switched from biomass and organic acid biosynthesis to ethanol production upon the expression of pdc and adhII. The recombinant S. lividans TK24 produced ethanol from glucose with a yield of 23.7 % based on the carbohydrate consumed. The recombinant was able to produce ethanol from xylose, l-arabinose, mannose, l-rhamnose, galactose, ribose, and cellobiose with yields of 16.0, 25.6, 21.5, 33.6, 30.6, 14.6, and 33.3 %, respectively. Polymeric substances such as starch and xylan were directly converted to ethanol by the recombinant with ethanol yields of 18.9 and 8.8 %, respectively. The recombinant S. lividans TK24/Tpet developed in this study is potentially a useful microbial resource for ethanol production from various sources of biomasses, especially microalgae.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee N, Bhatnagar R, Viswanathan L (1981) Development of resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae against inhibitory effects of browning reaction products. Enzyme Microb Technol 3:24–28
Borowitzka MA (1995) Microalgae as sources of pharmaceuticals and other biologically active compounds. J Appl Phycol 7:3–15
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microorganism quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown MR (1991) The amino-acid and sugar composition of 16 species of microalgae used in mariculture. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 145:79–99
Carlsson AS, van Beilen JB, Möller R, Clayton D (2007) Micro-and macro-algae: utility for industrial applications. In: Bowles D (ed) Outputs from the EPOBIO project. CPL Press, Berks, pp 9–11
Chen J, Zhang W, Tan L, Wang Y, He G (2009) Optimization of metabolic pathways for bioconversion of lignocellulose to ethanol through genetic engineering. Biotechnol Adv 27:593–598
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Clark TA, Mackie KL (1984) Fermentation inhibitors in wood hydrolysates derived from the softwood Pinus radiata. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 34:101–110
Cochrane VW, Conn JE (1947) The growth and pigmentation of Actinomyces coelicolor as affected by cultural conditions. J Bacteriol 54:213–218
Cripps RE, Eley K, Leak DJ, Rudd B, Taylor M, Todd M, Boakes S, Martin S, Atkinson T (2009) Metabolic engineering of Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius for high yield ethanol production. Metab Eng 11:398–408
Eksteen JM, van Rensburg P, Otero RRC, Pretorius IS (2003) Starch fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing the α-amylase and glucoamylase genes from Lipomyces kononenkoae and Saccharomycopsis fibuligera. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:639–646
Gancedo JM (1998) Yeast carbon catabolite repression. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:334–361
Gold RS, Meagher MM, Tong S, Hutkins RW, Conway T (1996) Cloning and expression of the Zymomonas mobilis “production of ethanol” genes in Lactobacillus casei. Curr Microbiol 33:256–260
Ha SJ, Galazka JM, Kim SR, Choi JH, Yang X, Seo JH, Glass NL, Cate JHD, Jin YS (2011) Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of simultaneous cellobiose and xylose fermentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:504–509
Hoppner TC, Doelle HW (1983) Purification and kinetic characteristics of pyruvate decarboxylase and ethanol dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis in relation to ethanol production. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 17:152–157
Ingram LO, Conway T (1988) Expression of different levels of ethanologenic enzymes from Zymomonas mobilis in recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:397–404
Ingram LO, Conway T, Clark DP, Sewell GW, Preston JF (1987) Genetic engineering of ethanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2420–2425
Jaurin B, Granstrom M (1989) Beta-glucosidase genes of naturally occurring and cellulolytic Streptomyces species: characterization of two such genes in Streptomyces lividans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:502–508
John RP, Anisha GS, Nampoothiri KM, Pandey A (2011) Micro and macroalgal biomass: a renewable source for bioethanol. Bioresour Technol 102:186–193
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Sterptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim NJ, Li H, Jung K, Chang HN, Lee PC (2011) Ethanol production from marine algal hydrolysates using Escherichia coli KO11. Bioresour Technol 102:7466–7469
Kluepfel D, Shareck F, Mondou F, Morosoli R (1986) Characterization of cellulase and xylanase activities of Streptomyces lividans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 24:230–234
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Liu S, Dien BS, Nichols NN, Bischoff KM, Hughes SR, Cotta MA (2007) Coexpression of pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase genes in Lactobacillus brevis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 274:291–297
Liu S, Nichols NN, Dien BS, Cotta MA (2006) Metabolic engineering of a Lactobacillus plantarum double ldh knockout strain for enhanced ethanol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:1–7
Liu S, Qureshi N (2009) How microbes tolerate ethanol and butanol. New Biotechnol 26:117–121
Mackay SJ (1977) Improved enumeration of Streptomyces spp. on a starch casein salt medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:227–230
Michel G, Nyval-Collen P, Barbeyron T, Czjzek M, Helbert W (2006) Bioconversion of red seaweed galactans: a focus on bacterial agarases and carrageenases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:23–33
Mihoc A, Kluepfel D (1990) Purification and characterization of a β-glucosidase from Streptomyces lividans 66. Can J Microbiol 36:53–56
Mills TY, Sandoval NR, Gill RT (2009) Cellulosic hydrolysate toxicity and tolerance mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Biofuels 2:26
Morosoli R, Bertrand JL, Mondou F, Shareck F, Kluepfel D (1986) Purification and properties of a xylanase from Streptomyces lividans. Biochem J 239:587–592
Navarro AR (1994) Effects of furfural on ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mathematical models. Curr Microbiol 29:87–90
Rxomero S, Merino E, Bolı-var F, Gosset G, Martinez A (2007) Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis for ethanol production:lactate dehydrogenase plays a key role in fermentative metabolism. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5190–5198
Shaw AJ, Podkaminer KK, Desai SG, Bardsley JS, Rogers SR, Thorne PG, Hogsett DA, Lynd LR (2008) Metabolic engineering of a thermophilic bacterium to produce ethanol at high yield. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:13769–13774
Stülke J, Hillen W (1999) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:195–201
Takaya T, Sugimoto Y, Fuwa H, Wako K (1979) Degradation of starch granules by alpha-amylase of Streptomyces precox NA-273. Starch/Stärke 31:205–208
Zaldivar J, Martinez A, Ingram LO (1999) Effect of selected aldehydes on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:24–33
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (no. 2011-0027563).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 484 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.S., Chi, WJ., Hong, SK. et al. Bioethanol production by heterologous expression of Pdc and AdhII in Streptomyces lividans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6089–6097 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4951-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4951-5