Abstract
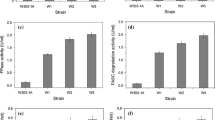
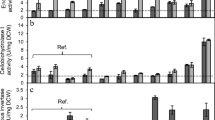
Two recombinant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y294 producing cellulase using different expression strategies were compared to a reference strain in aerobic culture to evaluate the potential metabolic burden that cellulase expression imposed on the yeast metabolism. In a chemically defined mineral medium with glucose as carbon source, S. cerevisiae strain Y294[CEL5] with plasmid-borne cellulase genes produced endoglucanase and β-glucosidase activities of 0.038 and 0.30 U mg dry cell weight−1, respectively. Chromosomal expression of these two cellulases in strain Y294[Y118p] resulted in no detectable activity, although low levels of episomally co-expressed cellobiohydrolase (CBH) activity were detected. Whereas the biomass concentration of strain Y294[CEL5] was slightly greater than that of a reference strain, CBH expression by Y294[Y118p] resulted in a 1.4-fold lower maximum specific growth rate than that of the reference. Supplementation of the growth medium with amino acids significantly improved culture growth and enzyme production, but only partially mitigated the physiological effects and metabolic burden of cellulase expression. Glycerol production was decreased significantly, up to threefold, in amino acid-supplemented cultures, apparently due to redox balancing. Disproportionately higher levels of glycerol production by Y294[CEL5] indicated a potential correlation between the redox balance of anabolism and the physiological stress of cellulase production. With the reliance on cellulase expression in yeast for the development of consolidated bioprocesses for bioethanol production, this work demonstrates the need for development of yeasts that are physiologically robust in response to burdens imposed by heterologous enzyme production.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers E, Larsson C, Lidén G, Niklasson C, Gustafsson L (1996) Influence of the nitrogen source on Saccharomyces cerevisiae anaerobic growth and product formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3187–3195
Bailey JE (1993) Host–vector interactions in Escherichia coli. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 48:29–52
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270
Bakker BM, Overkamp KM, van Maris AJA, Kötter P, Luttik MAH, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2001) Stoichiometry and compartmentation of NADH metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:15–37
Bentley WE, Mirjalili N, Andersen DC, Davis RH, Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the “metabolic burden” associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:668–681
Boer H, Teeri T, Koivula A (2000) Characterization of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel7A secreted from Pichia pastoris using two different promoters. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:486–494
Carlsen M, Jochumsen KV, Emborg C, Nielsen J (1997) Modeling the growth and proteinase A production in a continuous cultures of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 55:447–454
Chen CY, Oppermann H, Hitzeman RA (1984) Homologous versus heterologous gene expression in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucl Acid Res 12:8951–8970
Christen S, Sauer U (2011) Intracellular characterization of aerobic glucose metabolism in seven yeast species by 13C flux analysis and metabolomics. FEMS Yeast Res 11:263–272
Cudna RE, Dickson AJ (2003) Endoplasmatic reticulum signalling as a determinant of recombinant protein expression. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:56–65
Den Haan R, Rose SH, Lynd LR, van Zyl WH (2007a) Hydrolysis and fermentation of amorphous cellulose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metabol Eng 9:87–94
Den Haan R, Mcbride JE, La Grange JC, Lynd LR, van Zyl WH (2007b) Functional expression of cellobiohydrolases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae towards one-step conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enz Microb Technol 40:1291–1299
Dequin S, Barre P (1994) Mixed lactic acid-alcoholic fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the Lactobacillus casei L(+)-LDH. Bio/Technol 12:173–177
Díaz H, Andrews BA, Hayes A, Castrillo J, Oliver SG, Asenjo JA (2009) Global gene expression in recombinant and non-recombinant yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae in three different metabolic states. Biotechnol Adv 27:1092–1117
Donald KAG, Carle A, Gibbs MD, Bergquist PL (1994) Production of a bacterial thermophilic xylanase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:309–312
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv 13:247–261
Geertman J-M A (2006) Engineering of redox metabolism in yeast: new strategies for improved glycerol production. PhD Dissertation, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands
Goldemberg J (2007) Ethanol for a sustainable energy future. Science 315:808–810
Gonzalez R, Andrews BA, Molitor J, Asenjo JA (2003) Metabolic analysis of the synthesis of high levels of intracellular human SOD in Saccharomyces cerevisiae rhSOD 2060 411 SGA122. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:152–169
Gopal CV, Broad D, Lloyd D (1989) Bioenergetic consequences of protein overexpression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:160–165
Görgens JF, van Zyl WH, Knoetze JH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2001) The metabolic burden of the PGK1 and ADH2 promoter systems for heterologous xylanase production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in defined medium. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:238–245
Görgens JF, Planas J, van Zyl WH, Knoetze JH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2004) Comparison of three expression systems for heterologous xylanase production by S. cerevisiae in defined medium. Yeast 21:1205–1217
Görgens JF, van Zyl WH, Knoetze JH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2005a) Amino acid supplementation improves heterologous protein production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in defined medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:684–691
Görgens JF, Passoth V, van Zyl WH, Knoetze JH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2005b) Amino acid supplementation, controlled oxygen limitation and sequential double induction improves heterologous xylanase production by Pichia stipitis. FEMS Yeast Res 5:677–683
Goyal D, Sahni G, Sahoo DK (2009) Enhanced production of recombinant streptokinase in Escherichia coli using fed-batch culture. Biores Technol 100:4468–4474
Gu MB, Todd P, Kompala DS (1996) Metabolic burden in recombinant CHO cells: effect of dhfr gene amplification and lacZ expression. Cytotechnology 18:159–166
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Galbe M, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Lidén G, Zacchi G (2006) Bio-ethanol—the fuel of tomorrow from the residues of today. Trends Biotechnol 24:549–556
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhumaa K, Larsson CU, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Görgens JF, van Zyl WH (2005) Role of cultivation media in the development of yeast strains for large scale industrial use. Microb Cell Fact 4:31
Heyland J, Blank LM, Schmid A (2011) Quantification of metabolic limitations during recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 155:178–184
Higashide W, Li Y, Yang Y, Liao JC (2011) Metabolic engineering of Clostridium cellulolyticum for production of isobutanol from cellulose. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2727–2733
Hill J, Ian KA, Donald G, Griffiths DE (1991) DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucl Acid Res 19:5791
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2001) On-line estimation of the metabolic burden resulting from the synthesis of plasmid-encoded and heat-shock proteins by monitoring respiratory energy generation. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:333–340
Ibba M, Kuhla J, Smith A, Kuenzi M (1993) Stable continuous expression of a heterologous protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae without selection pressure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:526–531
Ilmén M, den Haan R, Brevnova E, McBride J, Wiswall E, FroehlichA KA, Voutilainen SP, Siika-aho M, la Grange DC, Thorngren N, Ahlgren S, Mellon M, Deleault K, Rajgarhia V, van Zyl WH, Penttilä M (2011) High level secretion of cellobiohydrolases by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:30–45
Janes M, Meyhack B, Zimmerman W, Hinnen A (1990) The influence of GAP promoter variants on hirudin production, average plasmid copy number and cell growth in S. cerevisiae. Curr Gen 18:97–103
Jin M, Balan V, Gunawan C, Dale BE (2011) Consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) performance of Clostridium phytofermentans on AFEX-treated corn stover for ethanol production. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:1290–1297
Jiranek V, Langridge P, Henschke PA (1995) Amino acid and ammonium utilization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeasts from a chemically defined medium. Am J Enol Vit 46:75–83
Kaufman RJ (2002) Orchestrating the unfolded protein in health and disease. J Clin Invest 110:1389–1398
La Grange DC, Pretorius IS, Claeyssens M, van Zyl WH (2001) Degradation of xylan to D-xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae coexpressing the Aspergillus niger β-xylosidase (xlnD) and the Trichoderma reesei xylanase II (xyn2) genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5512–5519
La Grange DC, Pretorius IS, van Zyl WH (1996) Expression of a Trichoderma reesei B-xylanase gene (XYN2) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1036–1044
Lang C, Looman AC (1995) Efficient expression and secretion of Aspergillus niger RH5344 polygalacturonase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:147–156
Lee SK, Chou H, Ham TS, Lee TS, Keasling JD (2008) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for biofuels production: from bugs to synthetic biology to fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:556–563
Lopes TS, Wijs IJ, Steenhauer SI, Verbakel J, Planta RJ (1996) Factors affecting the mitotic stability of high-copy-number integration into ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 12:467–477
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, van Zyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:577–583
Machida M, Ohtsuki I, Fukui S, Yamashita I (1988) Nucleotide sequences of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera genes for extracellular r-glucosidases as expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:3147–3155
Martinez A, York SW, Yomano LP, Pineda VL, Davis FC, Shelton JC, Ingram LO (1999) Biosynthetic burden and plasmid burden limit expression of chromosomally integrated heterologous genes (pdc, adhB) in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 15:891–897
McBride JEE, Deleault KM, Lynd LR, Pronk JT (2008) Recombinant yeast strains expressing tethered cellulase enzymes. Patent PCT/US2007/085390
Mattanovich D, Gasser B, Hohenblum H, Sauer M (2004) Stress in recombinant protein producing yeasts. J Biotechnol 113:121–135
Meinander B, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1997) Fed-batch xylitol production with two recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing XYL 1 at different levels, using glucose as co-substrate: a comparison of production parameters and strain stability. Biotechnol Bioeng 54:391–399
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Nordström K (1966) Yeast growth and glycerol formation. Acta Chem Scand 20:6–15
Nissen TL, Hamann CW, Kielland-Brandt MC, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (2000) Anaerobic and aerobic batch cultivations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants impaired in glycerol synthesis. Yeast 16:463–474
Nuyens F, van Zyl WH, Iserentant D, Verachtert H, Michiels C (2001) Heterologous expression of the Bacillus pumilus endo-β-xylanase (xynA) gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:431–434
Peretti SW, Bailey JE (1987) Simulations of host-plasmid interactions in Escherichia coli: copy number, promoter strength and ribosome binding site strength effects on metabolic activity and plasmid gene expression. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:316–328
Pérez-González JA, De Graaff LH, Visser J, Ramón D (1996) Molecular cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of two Aspergillus nidulans xylanase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2179–2182
Pronk JT (2002) Auxotrophic yeast strains in fundamental and applied research. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2095–2100
Radler F, Schütz H (1982) Glycerol production of various strains of Saccharomyces. Am J Enol Vit 33:36–40
Ramérez DM, Bentley WE (2004) Enhancement of recombinant protein synthesis and stability via coordinated amino acid addition. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:557–565
Romanos MA, Scorer CA, Clare JJ (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast: a review. Yeast 8:423–488
Sardonini CA, DiBiasio D (1987) A model for growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing a recombinant plasmid in selective media. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:469–475
Schmidt FR (2004) Recombinant expression systems in the pharmaceutical industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:363–372
Schröder M (2006) The unfolded protein response. Mol Biotechnol 34:279–290
Snoep JL, Yomano LP, Westerhoff HV, Ingram LO (1995) Protein burden in Zymomonas mobilis: negative flux and growth control due to overproduction of glycolytic enzymes. Microbiol 141:2329–2337
Stephanopoulos G (2007) Challenges in engineering microbes for biofuels production. Science 315:801–804
Stouthamer AH, Van Verseveld HW (1987) Microbial energetics should be considered in manipulating metabolism for biotechnological purposes. Trends Biotechnol 5:149–155
Taherzadeh MJ, Adler L, Lidén G (2002) Strategies for enhancing fermentative production of glycerol—a review. Enz Microb Technol 31:53–66
Travers KJ, Patil CK, Wodicka L, Lockhart DJ, Weissman JS, Walter P (2000) Functional and genomic analyses reveal an essential coordination between the unfolded protein response and ER-associated degradation. Cell 101:249–258
Valadi Å, Granath K, Gustafsson L, Adler L (2004) Distinct intracellular localization of Gpd1p and Gpd2p, the two yeast isoforms of NAD+-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, explains their different contributions to redox-driven glycerol production. J Biol Chem 279:39677–39658
Van Arsdell JN, Kwok S, Schweickart VL, Ladner MB, Gelfand DH, Innis MA (1987) Cloning, characterisation and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of endoglucanase I from Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol 5:60–64
Van der Aar PC, van den Heuvel JJ, Röling WFM, Raué HA, Stouthamer SH, van Verseveld HW (1992) Effects of phosphoglycerate kinase overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the physiology and plasmid stability. Yeast 8:47–55
Van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1986) Redox balances in the metabolism of sugars by yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:199–225
Van Hoek P, Flikweert MT, van der Aardt QJ, de Steensma HY, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (1998) Effects of pyruvate decarboxylase overproduction on flux distribution at the pyruvate branch point in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2133–2140
Van Rooyen R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, La Grange DC, van Zyl WH (2005) Construction of cellobiose-growing and fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. J Biotechnol 120:284–295
van Zyl WH, Lynd LR, Den Haan R, McBride JE (2007) Consolidated bioprocessing for bioethanol production using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:205–235
Verduyn C, Postma E, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1992) Effect of benzoic acid metabolism on metabolic fluxes in yeast: a continuous culture study on the regulation of respiration and alcoholic fermentation. Yeast 8:501–507
Wang ZX, Zhuge J, Fang H, Prior BA (2001) Glycerol production by microbial fermentation: a review. Biotechnol Adv 19:201–223
Xu Q, Singh A, Himmel ME (2009) Perspectives and new directions for the production of bioethanol using consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulose. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:364–371
Yamada R, Taniguchi N, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2010) Cocktail delta-integration: a novel method to construct cellulolytic enzyme expression ratio-optimized yeast strains. Microb Cell Fact 9:32
Yang B, Wyman CE (2008) Pretreatment: the key to unlocking low-cost cellulosic ethanol. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 2:26–40
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. M Stander and Ms. MJ Adonis of the Central Analytical Facility at Stellenbosch University for assistance with amino acid analyses and the National Research Foundation and the Senior Chair in Energy Research: Biofuels at Stellenbosch University for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Rensburg, E., den Haan, R., Smith, J. et al. The metabolic burden of cellulase expression by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y294 in aerobic batch culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 197–209 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4037-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4037-9