Abstract
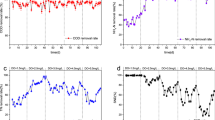
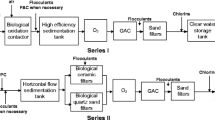
Linkages among bioreactor operation and performance and microbial community structure were investigated for a fixed-bed biofilm system designed to remove perchlorate from drinking water. Perchlorate removal was monitored to evaluate reactor performance during and after the frequency and intensity of the backwash procedure were changed, while the microbial community structure was studied using clone libraries and quantitative PCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene. When backwash frequency was increased from once per month to once per day, perchlorate removal initially deteriorated and then recovered, and the relative abundance of perchlorate-reducing bacteria (PRB) initially increased and then decreased. This apparent discrepancy suggested that bacterial populations other than PRB played an indirect role in perchlorate removal, likely by consuming dissolved oxygen, a competing electron acceptor. When backwash intensity was increased, the reactor gradually lost its ability to remove perchlorate, and concurrently the relative abundance of PRB decreased. The results indicated that changes in reactor operation had a profound impact on reactor performance through altering the microbial community structure. Backwashing is an important yet poorly characterized procedure when operating fixed-bed biofilm reactors. Compared to backwash intensity, changes in backwash frequency exerted less disturbance on the microbial community in the current study. If this finding can be confirmed in future work, backwash frequency may serve as the primary parameter when optimizing backwash procedures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad R, Amirtharajah A, Al-Shawwa A, Huck PM (1998) Effects of backwashing on biological filters. J Am Water Works Ass 90(12):62–73
Alm EW, Oerther DB, Larsen N, Stahl DA, Raskin L (1996) The oligonucleotide probe database. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(10):3557–3559
American Public Health Association (APHA) AWWAA, Water Environment Federation (WEF) (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ (2006) New screening software shows that most recent large 16S rRNA gene clone libraries contain chimeras. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(9):5734–5741
Bardiya N, Bae JH (2008) Isolation and characterization of Dechlorospirillum anomalous strain JB116 from a sewage treatment plant. Microbiol Res 163(2):182–191
Bouwer EJ, Crowe PB (1988) Biological processes in drinking water treatment. J Am Water Works Ass 80(9):82–93
Briones A, Raskin L (2003) Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in engineered environments and their implications for process stability. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(3):270–276
Brosius J, Dull TJ, Sleeter DD, Noller HF (1981) Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal-RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 148(2):107–127
Brown JC, Snoeyink VL, Raskin L, Lin R (2003) The sensitivity of fixed-bed biological perchlorate removal to changes in operating conditions and water quality characteristics. Water Res 37(1):206–214
CA-DHS (2005) Perchlorate drinking water action level and regulation. California Department of Health Services, http://www.dhs.ca.gov/ps/ddwem/chemicals/perchl/perchlindex.htm
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3497–3500
Choi YC, Li X, Raskin L, Morgenroth E (2007) Effect of backwashing on perchlorate removal in fixed bed biofilm reactors. Water Res 41(9):1949–1959
Choi YC, Li X, Raskin L, Morgenroth E (2008) Chemisorption of oxygen onto activated carbon can enhance the stability of biological perchlorate reduction in fixed bed biofilm reactors. Water Res 42(13):3425–3434
Coates JD, Achenbach LA (2004) Microbial perchlorate reduction: rocket-fuelled metabolism. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(7):569–580
Coates JD, Michaelidou U, Bruce RA, O'Connor SM, Crespi JN, Achenbach LA (1999) Ubiquity and diversity of dissimilatory (per)chlorate-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(12):5234–5241
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2007) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D169–D172
Corinaldesi C, Danovaro R, Dell'Anno A (2005) Simultaneous recovery of extracellular and intracellular DNA suitable for molecular studies from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(1):46–50
Curtis TP, Head IM, Graham DW (2003) Theoretical ecology for engineering biology. Environ Sci Technol 37(3):64a–70a
Ding L, Yokota A (2010) Curvibacter fontana sp. nov., a microaerobic bacteria isolated from well water. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:267–271
Ding LX, Yokota A (2004) Proposals of Curvibacter gracilis gen. nov., sp nov and Herbaspirillum putei sp nov for bacterial strains isolated from well water and reclassification of [Pseudomonas] huttiensis, [Pseudomonas] lanceolata, [Aquaspirillum] delicatum and [Aquaspirillum] autotrophicum as Herbaspirillum huttiense comb. nov., Curvibacter lanceolatus comb. nov., Curvibacter delicatus comb. nov and Herbaspirillum autotrophicum comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2223–2230
Dojka MA, Hugenholtz P, Haack SK, Pace NR (1998) Microbial diversity in a hydrocarbon- and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):3869–3877
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence-limits on phylogenies—an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791
Fields MW, Yan TF, Rhee SK, Carroll SL, Jardine PM, Watson DB, Criddle CS, Zhou JZ (2005) Impacts on microbial communities and cultivable isolates from groundwater contaminated with high levels of nitric acid-uranium waste. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53(3):417–428
Gentile G, Giuliano L, D'Auria G, Smedile F, Azzaro M, De Domenico M, Yakimov MM (2006) Study of bacterial communities in Antarctic coastal waters by a combination of 16S rRNA and 16S rDNA sequencing. Environ Microbiol 8(12):2150–2161
Greer MA, Goodman G, Pleus RC, Greer SE (2002) Health effects assessment for environmental perchlorate contamination: the dose response for inhibition of thyroidal radioiodine uptake in humans. Environ Health Perspect 110(9):927–937
Griffiths RI, Whiteley AS, O'Donnell AG, Bailey MJ (2000) Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA- and rRNA-based microbial community composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5488–5491
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hozalski RM, Bouwer EJ (1998) Deposition and retention of bacteria in backwashed filters. J Am Water Works Ass 90(1):71–85
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian Protein Metabolism. Academic, New York, pp 21–132
Lahav O, Artzi E, Tarre S, Green M (2001) Ammonium removal using a novel unsaturated flow biological filter with passive aeration. Water Res 35(2):397–404
Li X, Upadhyaya G, Yuen W, Brown J, Morgenroth E, Raskin L (2010) Changes in the structure and function of microbial communities in drinking water treatment bioreactors upon addition of phosphorus. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(22):7473–7481
Lin R, M.S. thesis, (2004) Bacterial community analysis and optimization of biologically active carbon filters used to remove perchlorate from groundwater. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
Logan B, Zhang H, Mulvaney P, Milner M, Head I, Unz R (2001) Kinetics of perchlorate- and chlorate-respiring bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(6):2499–2506
MA-DEP (2006) Drinking Water Status on Perchlorate by MA Department of Environmental Protection. http://www.mass.gov/dep/water/drinking/percinfo.htm#stds
Miller JP, Logan BE (2000) Sustained perchlorate degradation in an autotrophic, gas-phase, packed-bed bioreactor. Environ Sci Technol 34(14):3018–3022
Nerenberg R, Kawagoshi Y, Rittmann BE (2008) Microbial ecology of a perchlorate-reducing, hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor. Water Res 42(4–5):1151–1159
Nerenberg R, Rittmann BE (2004) Hydrogen-based, hollow-fiber membrane biofilm reactor for reduction of perchlorate and other oxidized contaminants. Water Sci Technol 49(11–12):223–230
Richardson RE, Bhupathiraju VK, Song DL, Goulet TA, Alvarez-Cohen L (2002) Phylogenetic characterization of microbial communities that reductively dechlorinate TCE based upon a combination of molecular techniques. Environ Sci Technol 36(12):2652–2662
Ritalahti KM, Amos BK, Sung Y, Wu QZ, Koenigsberg SS, Loffler FE (2006) Quantitative PCR targeting 16S rRNA and reductive dehalogenase genes simultaneously monitors multiple Dehalococcoides strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(4):2765–2774
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY
Rossellomora RA, Wagner M, Amann R, Schleifer KH (1995) The abundance of Zoogloea ramigera in sewage treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(2):702–707
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method—a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1501–1506
Schloss PD, Larget BR, Handelsman J (2004) Integration of microbial ecology and statistics: a test to compare gene libraries. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5485–5492
Servais P, Billen G, Ventresque C, Bablon GP (1991) Microbial activity in GAC filters at the Choisy-le-Roi treatment plant. J Am Water Works Ass 83(2):62–68
Steinberger RE, Allen AR, Hansma HG, Holden PA (2002) Elongation correlates with nutrient deprivation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-unsaturated biofilms. Microb Ecol 43(4):416–423
Steinberger RE, Holden PA (2005) Extracellular DNA in single- and multiple-species unsaturated biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):5404–5410
Suzuki MT, Taylor LT, DeLong EF (2000) Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 5′-nuclease assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(11):4605–4614
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599
Thomsen TR, Kong Y, Nielsen PH (2007) Ecophysiology of abundant denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60(3):370–382
Unz RF (1984) Genus IV. Zoogloea Itzigsohn 1868, 30AL. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 214–219
Upadhyaya G, Jackson J, Clancy TM, Hyun SP, Brown J, Hayes KF, Raskin L (2010) Simultaneous removal of nitrate and arsenic from drinking water sources utilizing a fixed-bed bioreactor system. Water Res 44(17):4958–4969
Urbansky ET (2002) Perchlorate as an environmental contaminant. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 9(3):187–192
US-EPA (2005) State Perchlorate Advisory Levels and Other Resources. http://www.epa.gov/fedfac/documents/perchlorate_links.htm
US-EPA (2008) Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 3 http://www.epa.gov/safewater/ccl/ccl3.html
Waller A, Cox E, Edwards E (2004) Perchlorate-reducing microorganisms isolated from contaminated sites. Environmental Microbiology 6(5):517–527
Xie CH, Yokota A (2006) Zoogloea oryzae sp nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from rice paddy soil, and reclassification of the strain ATCC 19623 as Crabtreella saccharophila gen. nov., sp nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:619–624
Xu J, Song Y, Min B, Steinberg L, Logan B (2003) Microbial degradation of perchlorate: principles and applications. Environmental engineering Science 20(5):405–422
Zhang H, Bruns M, Logan B (2002) Perchlorate reduction by a novel chemolithoautotrophic, hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium. Environ Microbiol 4(10):570–576
Zhang H, Logan BE, Regan JM, Achenbach LA, Bruns MA (2005) Molecular assessment of inoculated and indigenous bacteria in biofilms from a pilot-scale perchlorate-reducing bioreactor. Microb Ecol 49(3):388–398
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by the National Science Foundation (BES-0123342) and the Department of Defense (ESTCP: ER-0544). The authors would like to thank Young Chul Choi and Jess Brown for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yuen, W., Morgenroth, E. et al. Backwash intensity and frequency impact the microbial community structure and function in a fixed-bed biofilm reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 815–827 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3838-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3838-6